|
|||||
|
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | Stemness, Senescence, Metaplasia and NeoTCR signature analysis |
Tissue: Cervix |
Tissue samples summary |
| Epithelia | Immune | Stromal |
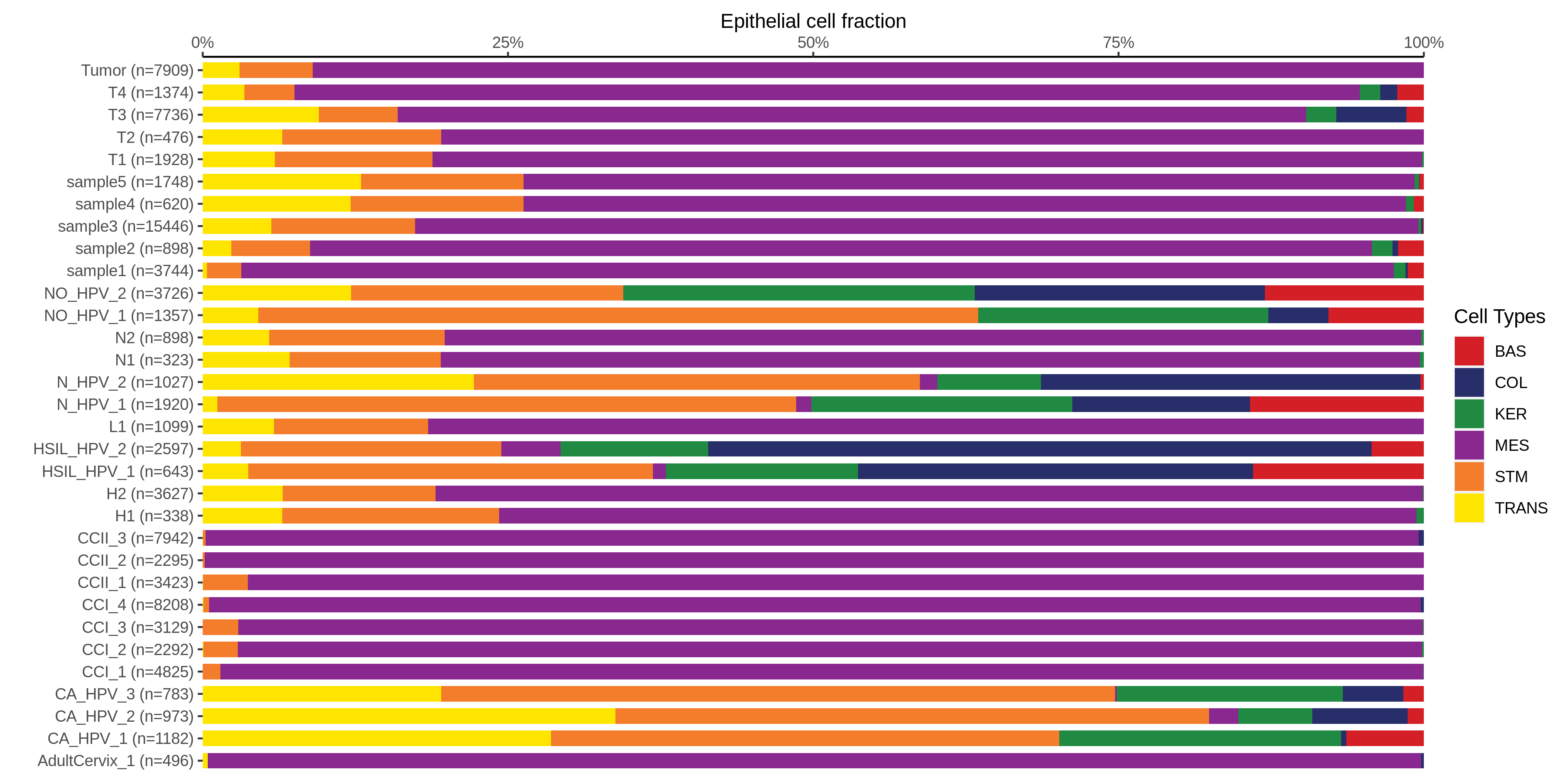 | 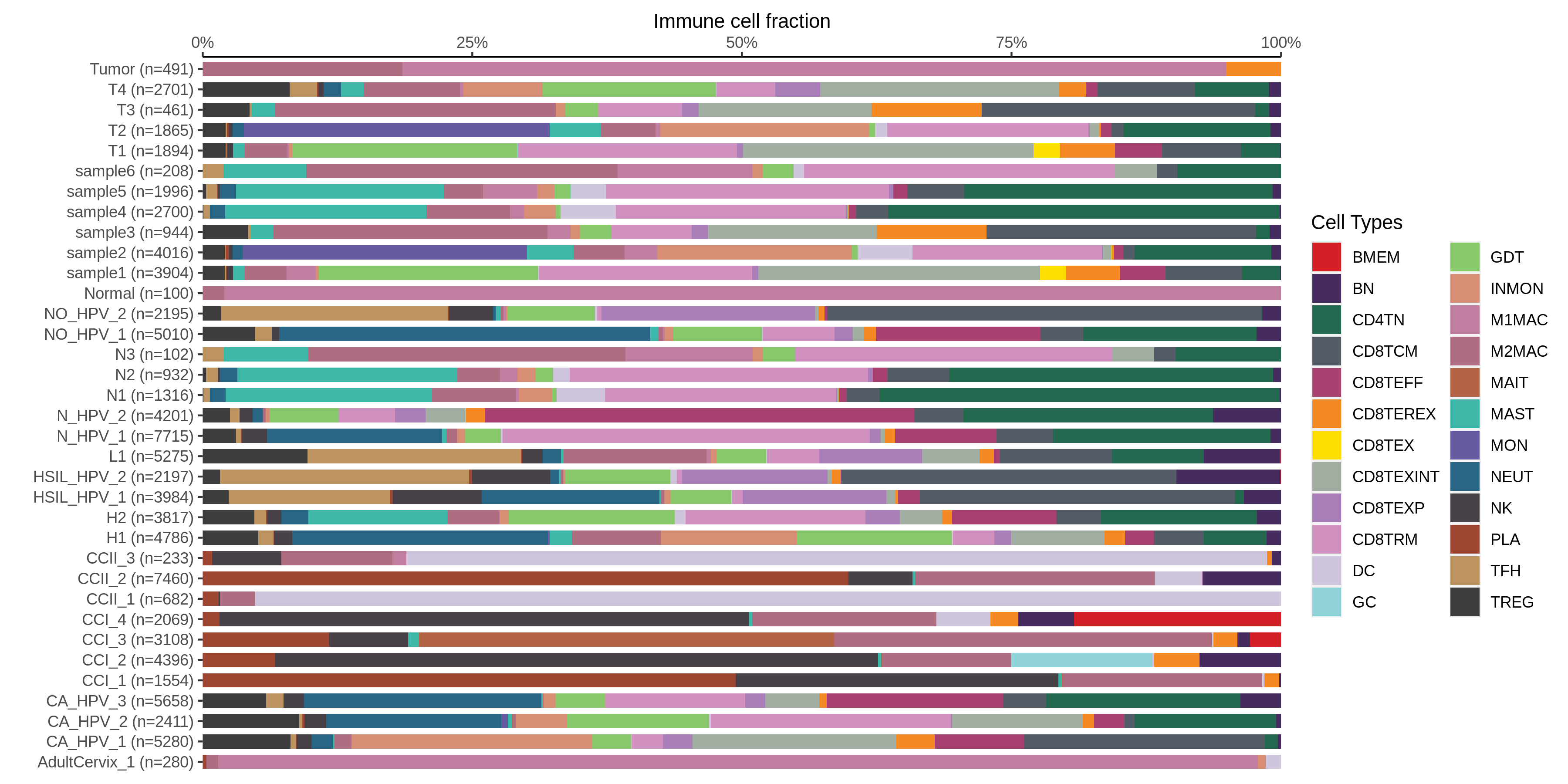 | 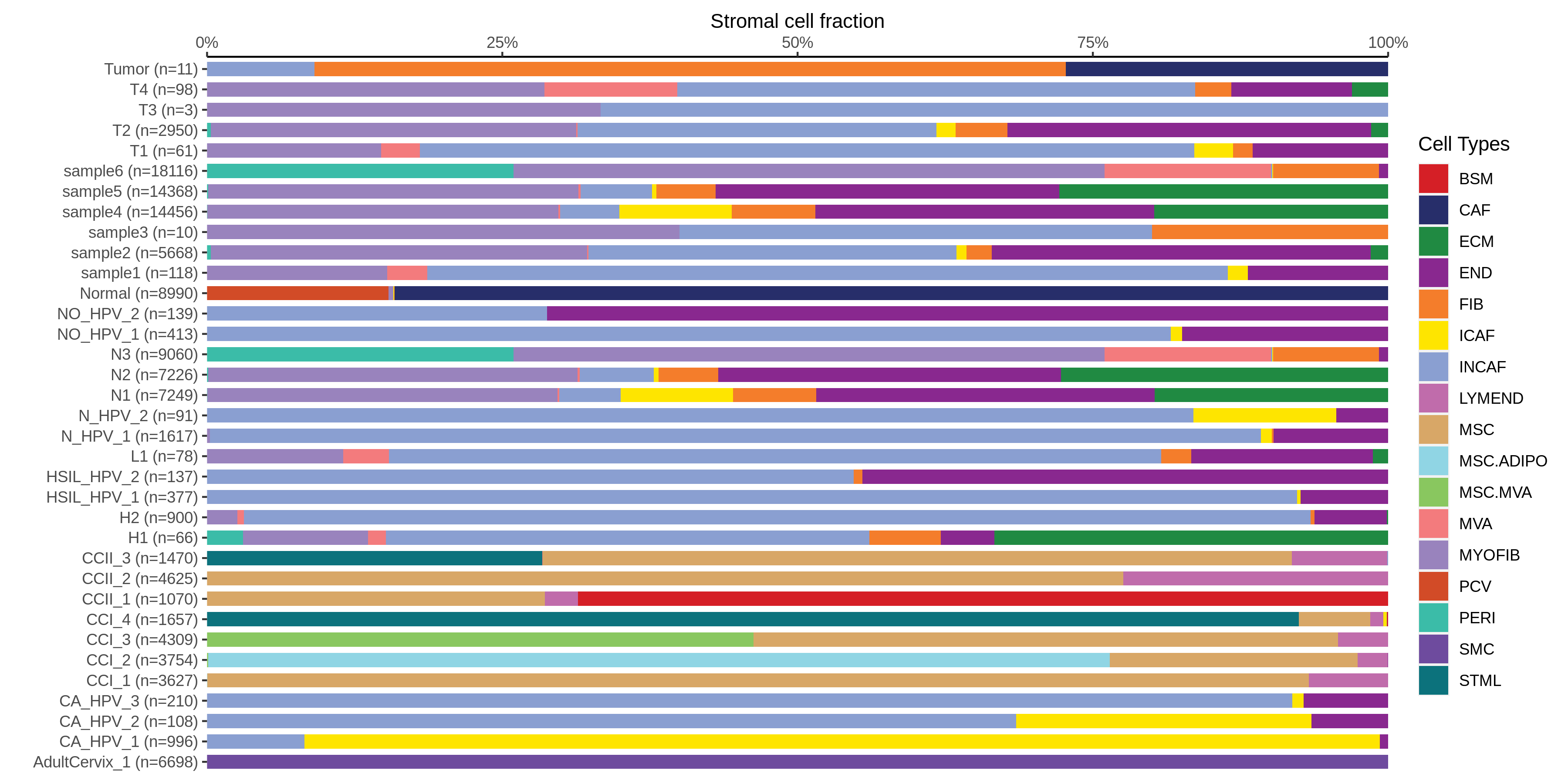 |
| ∗Bar plot representation of the fraction of all Epithelial, Immune and Stromal cells in each sample composed of each cell type for the integrated scRNA-seq datasets of Cervix tissue. Each row represents a single sample, with each color representing a different cell type present in the sample. |
| Tissue | Disease State | Replicates | Epithelia UMAP | PMID | Source | Platform |
| Cervix | CC | CA_HPV_1 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CA_HPV_2 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CA_HPV_3 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | HSIL_HPV | HSIL_HPV_1 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | HSIL_HPV | HSIL_HPV_2 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | N_HPV | N_HPV_1 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | N_HPV | N_HPV_2 | Projection | 36967539 | GSE208653 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCI_1 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCI_2 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCI_3 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCI_4 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCII_1 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCII_2 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | CCII_3 | Projection | NA | SCP1950 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | Tumor | Projection | 33996252 | GSE168652 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | sample1 | Projection | 36357663 | E-MTAB-11948 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | sample2 | Projection | 36357663 | E-MTAB-11948 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | CC | sample3 | Projection | 36357663 | E-MTAB-11948 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | ADJ | sample4 | Projection | 36357663 | E-MTAB-11948 | 10X Genomics |
| Cervix | ADJ | sample5 | Projection | 36357663 | E-MTAB-11948 | 10X Genomics |
| ∗Projection of epithelial scRNA-seq cells from Cervix diseased tissue samples into the manifold of normal tissue epithelial cells. Projected cells are colored by nearest normal cells in the projection and normal epithelial cells are colored gray. |
| Page: 1 2 3 |
Top |
Annotation details for different cell compartments |
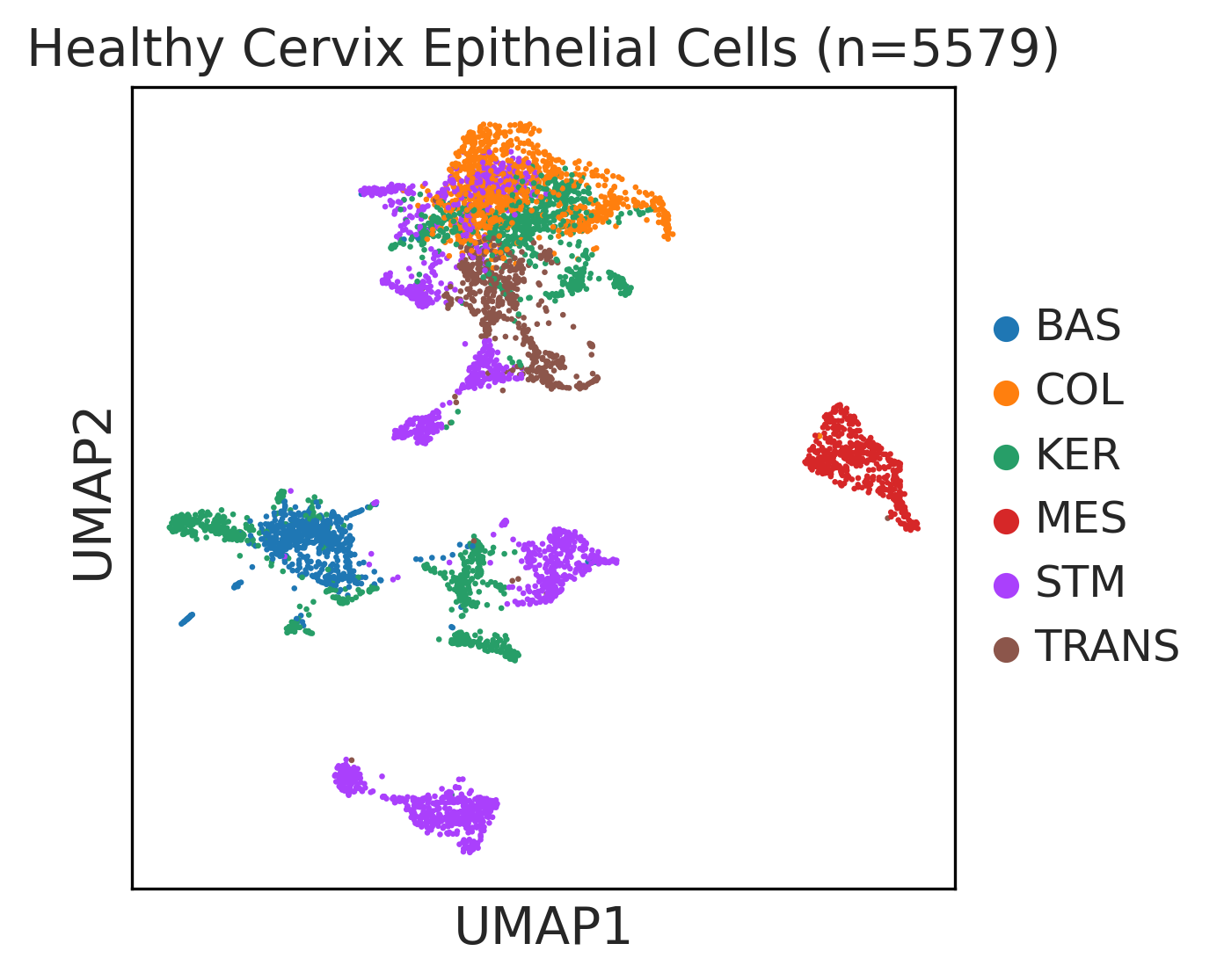 | 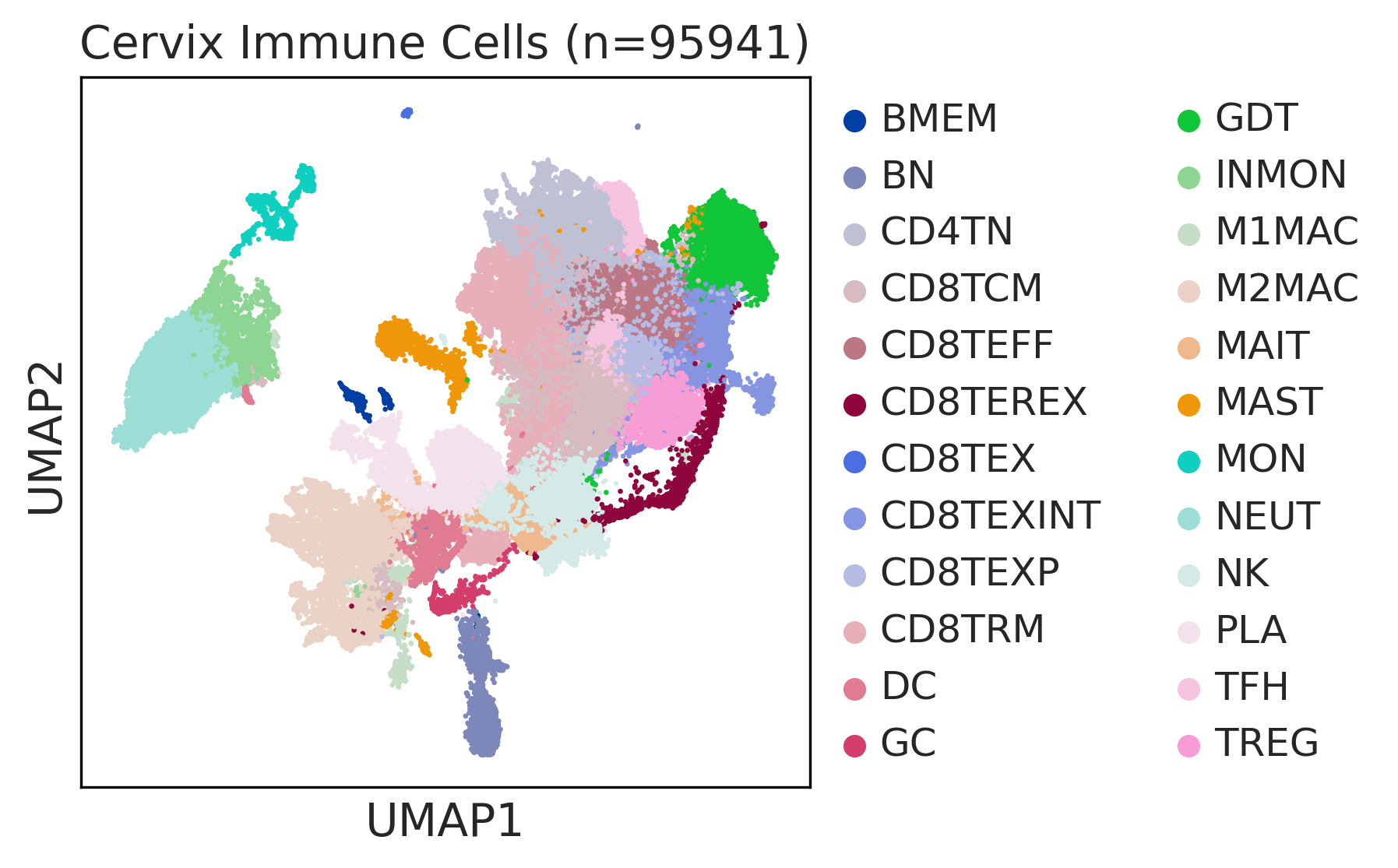 | 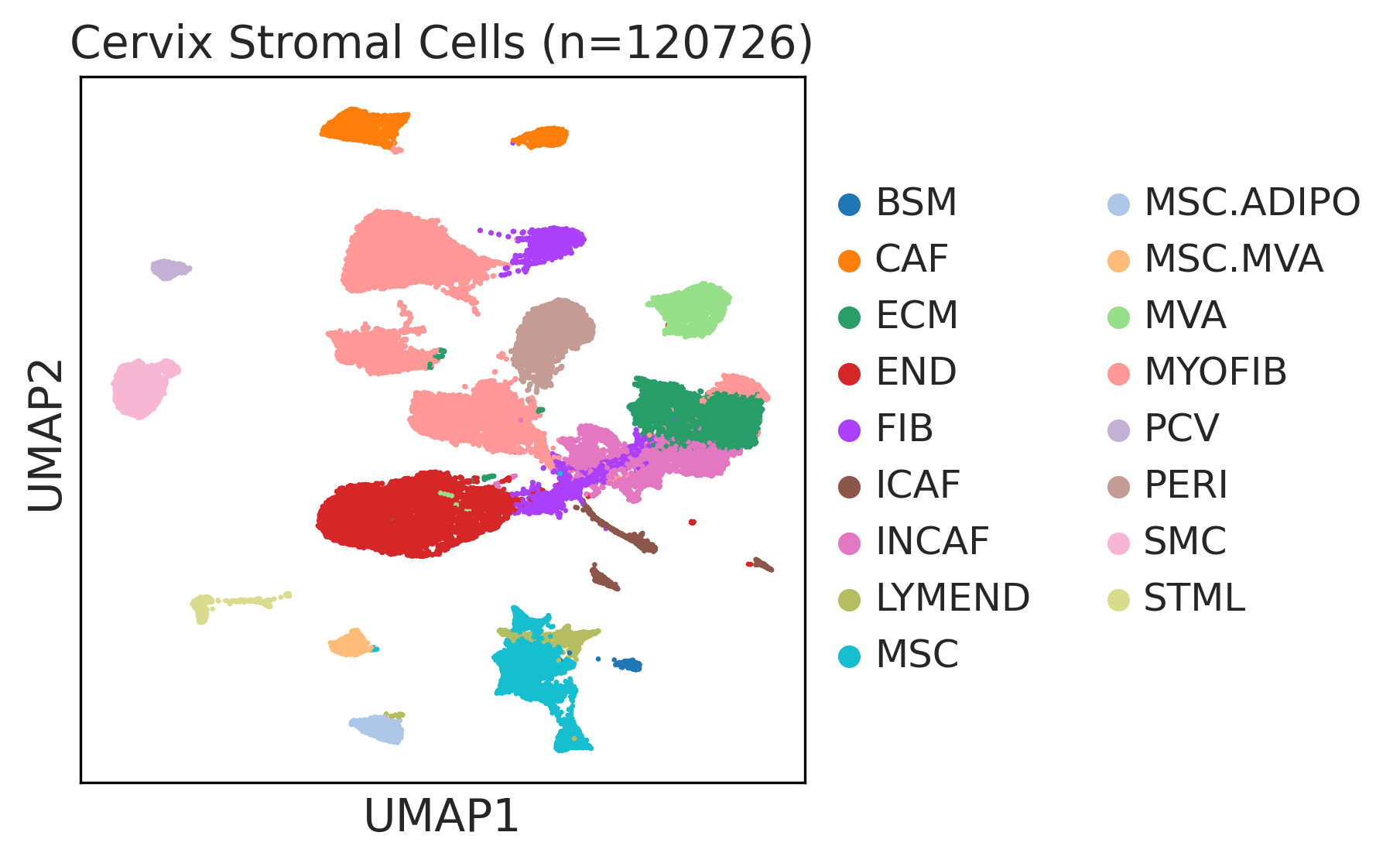 |
| ∗UMAP representations and annotations of Epithelial, Immune, Stromal cells in the integrated scRNA-seq data of Cervix tissue. Colors represent cell types of each compartment. |
| Tissue | Major Cell Type | Minor Cell Type | Full Name | Markers |
| Cervix | Epi | STM | Stem-like cells | ALDH3A1,ALDH1A1,BMI1,SFRP1,ITGB1,LGR5,SOX2,POU5F1,NANOG,CD44,TP63,ABCG2,PROM1,ALCAM |
| Cervix | Epi | BAS | Basal cells | KRT5,KRT14,KRT6A,KRT15,TP63,ITGA6,ITGB4 |
| Cervix | Epi | MES | Cervical Mesothelial cells | WT1,CALB1,VIM,CDH1,MSLN,BAP1 |
| Cervix | Epi | COL | Columnar epithelial cells | SOX17,CLDN15,MUC17,MUC16,MUC5B,MUC6,PAX8 |
| Cervix | Epi | KER | Keratinocytes | KRT5,KRT13,KRT14,KRT4,KRT18,KRT17,IVL,LOR,SPRR3 |
| Cervix | Epi | TRANS | Transit-amplifying cells | UPK1A,DSP,SERPINB3 |
| Cervix | Imm | NEUT | Neutriphils | CEACAM3,FCGR3B,CXCR2 |
| Cervix | Imm | MAST | Mast cells | TPSAB1,CPA3,HDC,CTSG,TPSB2,CMA1,MS4A2 |
| Cervix | Imm | DC | Dendritic cells | HLA-DQA1,HLA-DQB1,CLEC10A,CLEC9A,FCER1A,CST3,CD1C |
| Cervix | Imm | NK | Natural killer cells | KLRF1,SH2D1B,NCAM1,FCGR3A,GNLY,NKG7,GZMH,FGFBP2,CX3CR1,NCR1,NCR3,B3GAT1 |
| Cervix | Imm | MON | Monocytes | CD14,CLEC9A,FCGR1A,LILRB2,CD209,CD1E,FCN1,VCAN |
| Cervix | Imm | M1MAC | M1 macrophages | FOLR2,FABP3,PLA2G2D,ITGAM,ITGAX,CSF1R,CD68,CD163,THBD |
| Cervix | Imm | INMON | Inflamotory monocytes | CD14,CLEC9A,FCGR1A,LILRB2,CD209,CD1E,FCN1,VCAN,S100A8,S100A9 |
| Cervix | Imm | M2MAC | M2 macrophages | CSF1R,CSF3R,MRC1,IL10,CCL18,VSIG4,CHI3L1 |
| Cervix | Imm | BN | Naive B cells | CD19,IGHD,IGLL1,CD27,CD38 |
| Cervix | Imm | BMEM | Memory B cells | PAX5,MS4A1,CD19,IGLL5,VPREB3,CD79A,CD79B,IGKC,CD74,HLA-DRA,CD37,CD22 |
| Cervix | Imm | GC | Germinal center B cells | SERPINA9,HRK,HTR3A,BCL6,CD180,FCRLA |
| Cervix | Imm | PLA | Plasma cells | SSR4,IGLL5,IGLL1,AMPD1,IGHA1,IGHA2,JCHAIN,CD38,TNFRSF17,SDC1,IGHG1,MZB1 |
| Cervix | Imm | GDT | Gamma-delta T cells | TRDC,TRGC1,TRGC2,NKG7,TIGIT |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TEX | Exhausted CD8+ T cells | PDCD1,LAG3,CD101,CD38,CXCR6,TIGIT |
| Cervix | Imm | CD4TN | Naive CD4+ T cells | IL7R,SELL,CCR7,S100A4,TCF7 |
| Cervix | Imm | TFH | T follicular helper | CXCR5,BCL6,ICA1,TOX,TOX2,IL6ST,MAGEH1,BTLA,ICOS,PDCD1,CD200 |
| Cervix | Imm | TREG | Regulatory T cells | BATF,TNFRSF4,FOXP3,CTLA4,LAIR2,IL2RA |
| Cervix | Imm | MAIT | Mucosal-associated invariant T cells | SLC4A10,DPP4,KLRB1,ZBTB16,NCR3,RORC,RORA |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TEXP | Progenitor exhausted CD8+ T cells | PDCD1,IL7R,GPR183,NR4A3,REL,TCF7 |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TEXINT | Intermediate exhausted CD8+ T cells | PDCD1,LAG3,CD101,CD38,CXCR6,TIGIT |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TEREX | Terminally exhausted CD8+ T cells | TOX,GZMB,ENTPD1,ITGAE,HAVCR2,CXCL13,PDCD1,LAYN,TOX,IFNG,GZMB,MIR155HG,TNFRSF9,ITGAE |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TCM | Central memory CD8+ T cells | CCR7,SELL,IL7R,CD27,CD28,PRF1,GZMA,CCL5,GPR183,S1PR1 |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TRM | CD8+ tissue resident memory T cells | CD6,XCL1,XCL2,MYADM,CAPG,RORA,NR4A1,NR4A2,NR4A3,CD69,ITGAE |
| Cervix | Imm | CD8TEFF | Effector CD8+ T cells | CX3CR1,FCGR3A,FGFBP2,PRF1,GZMH,TBX21,EOMES,S1PR1 |
| Cervix | Str | END | Endothelial cells | PECAM1,PLVAP,VWF,CLDN5,FLT1,RAMP2,FAM110D,INHBB,NPR1,NOVA2,GPIHBP1,SOX17 |
| Cervix | Str | LYMEND | Lymphatic endothelial cells | PROX1,LYVE1,PDPN,PROCR,FLT4 |
| Cervix | Str | FIB | Fibroblasts | BMP7,MAP3K2,COL6A1,CD36,CD44,CBLN2,SPOCK1,ACSS3,FN1,COL3A1,BGN,DCN,POSTN,C1R,MMP2,FGF7,MME,CD47 |
| Cervix | Str | SMC | Smooth muscle cells | ACTA2,CNN1,MYH11,TAGLN,CALD1,TAGLN2 |
| Cervix | Str | MYOFIB | Myofibroblasts | SYT10,SOSTDC1,DES,TAGLN,MYH11,TPM4 |
| Cervix | Str | PERI | Pericytes | PDGFRA,CSPG4,RGS5,MCAM,COX4I2,KCNJ8,HIGD1B,NOTCH3,HEYL,FAM162B |
| Cervix | Str | STML | Stem-like cells | WNT5B,WNT2B,RSPO3,LGR5,FGF10,DLL1 |
| Cervix | Str | ADIPO | Adipocytes | PPARG,FABP4,ADIPOQ,LEP,CD36,PLIN1 |
| Cervix | Str | PVA | Post capillary venules | SELP,ZNF385D,FAM155A,GALNT15,MADCAM1,CORT |
| Cervix | Str | MVA | Microvascular cells | PLVAP,CD36,DYSF,NRP1,SH3BP5,EXOC3L2,FABP5,VWA1,BAALC,PRSS23,RAPGEF4,APLN,HTRA1 |
| Cervix | Str | ECM | Extracellular matrix | FBLN1,PCOLCE2,MFAP5 |
| Cervix | Str | BSM | Basement membrane | COL4A5,COL4A6 |
| Cervix | Str | INCAF | Intermediate cancer-associated fibroblasts | PDGFRA,POSTN,ID1,ID3 |
| Cervix | Str | ICAF | Inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts | TWIST1,WNT2,FAP,CXCL1,CXCL2,CYR61,IL1B,IL6,HGF |
| Cervix | Str | CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblasts | TWIST1,WNT2,FAP,CXCL1,CXCL2,CYR61 |
Top |
Cell type statistics by disease state |
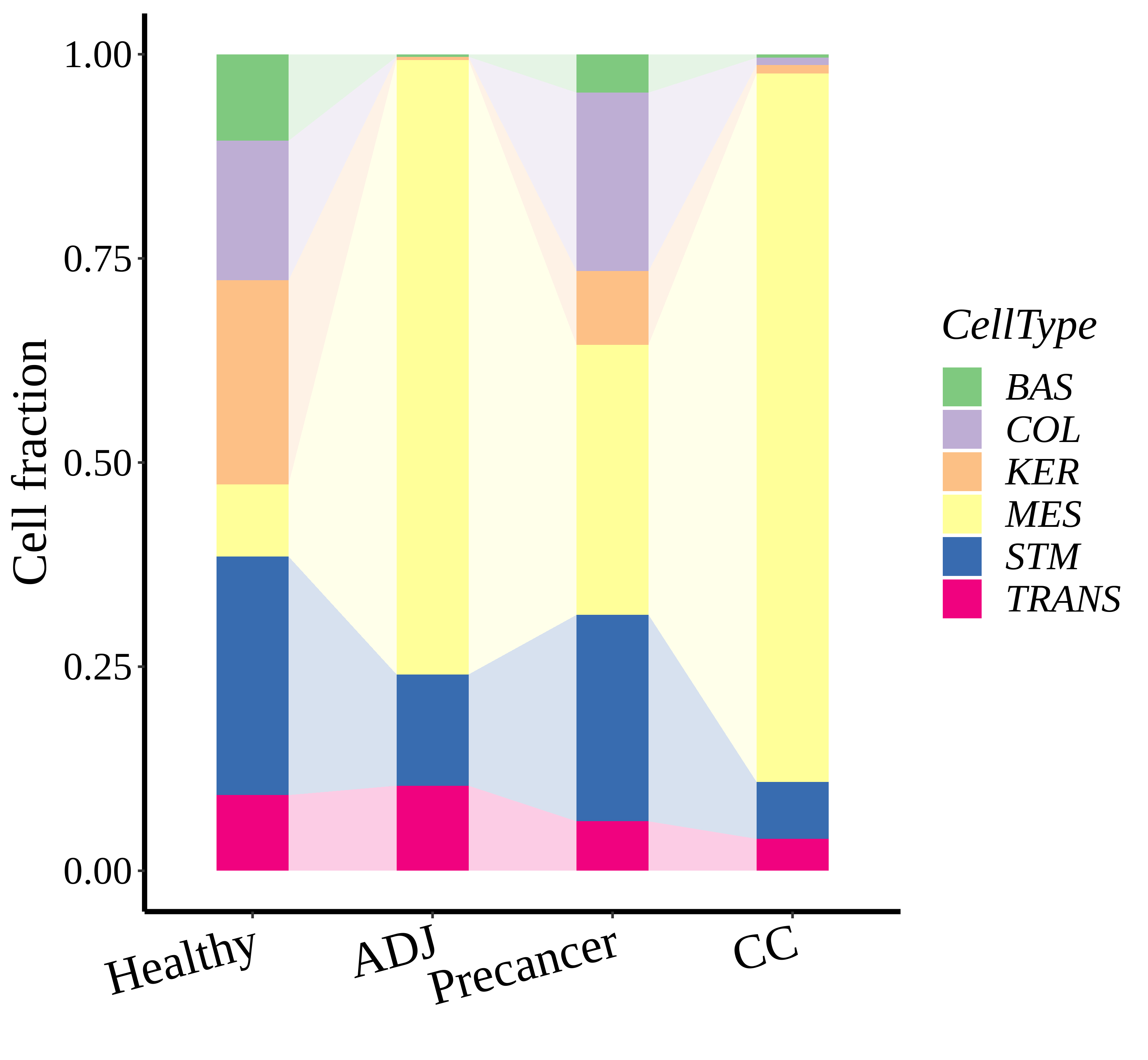 | 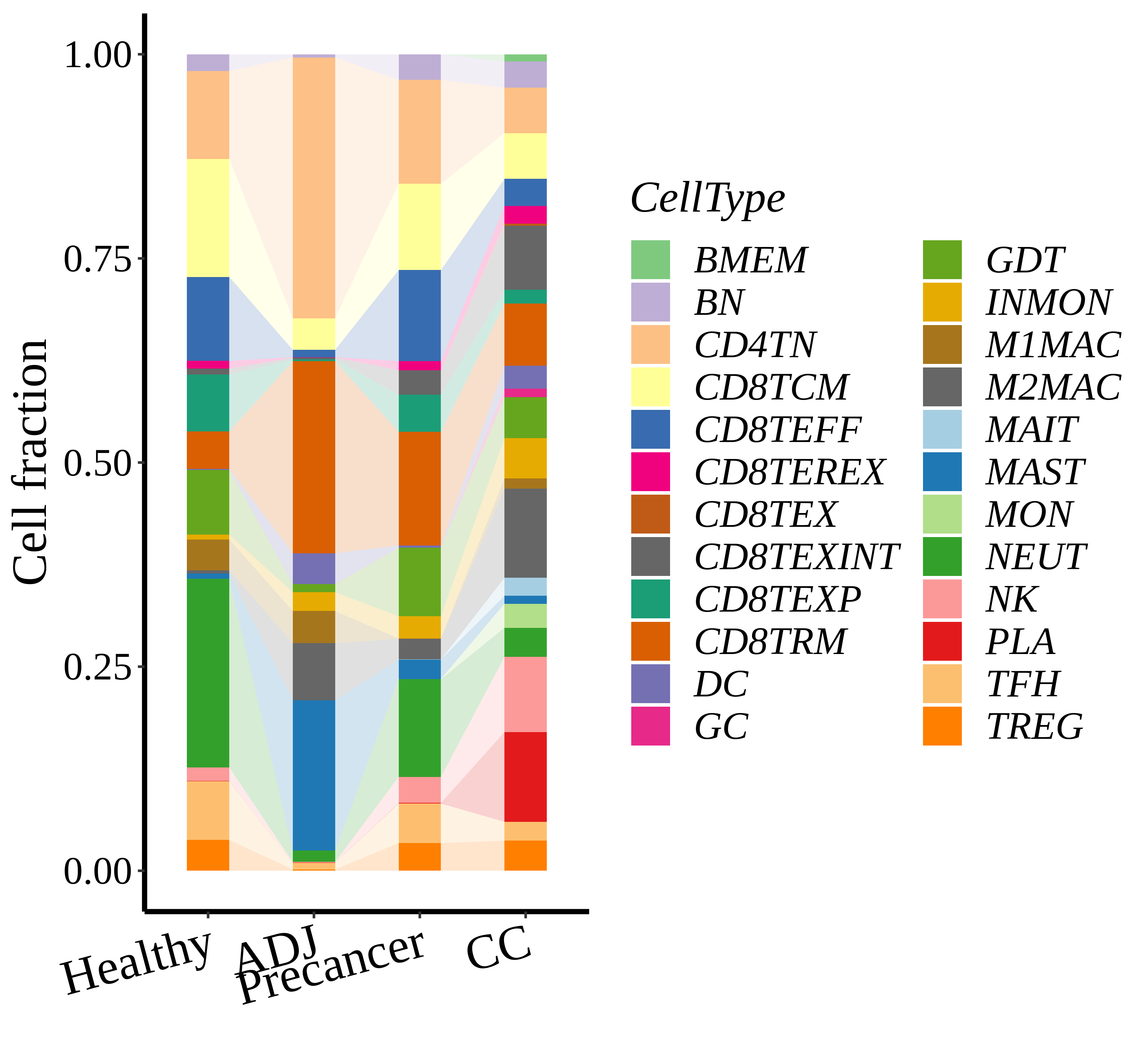 | 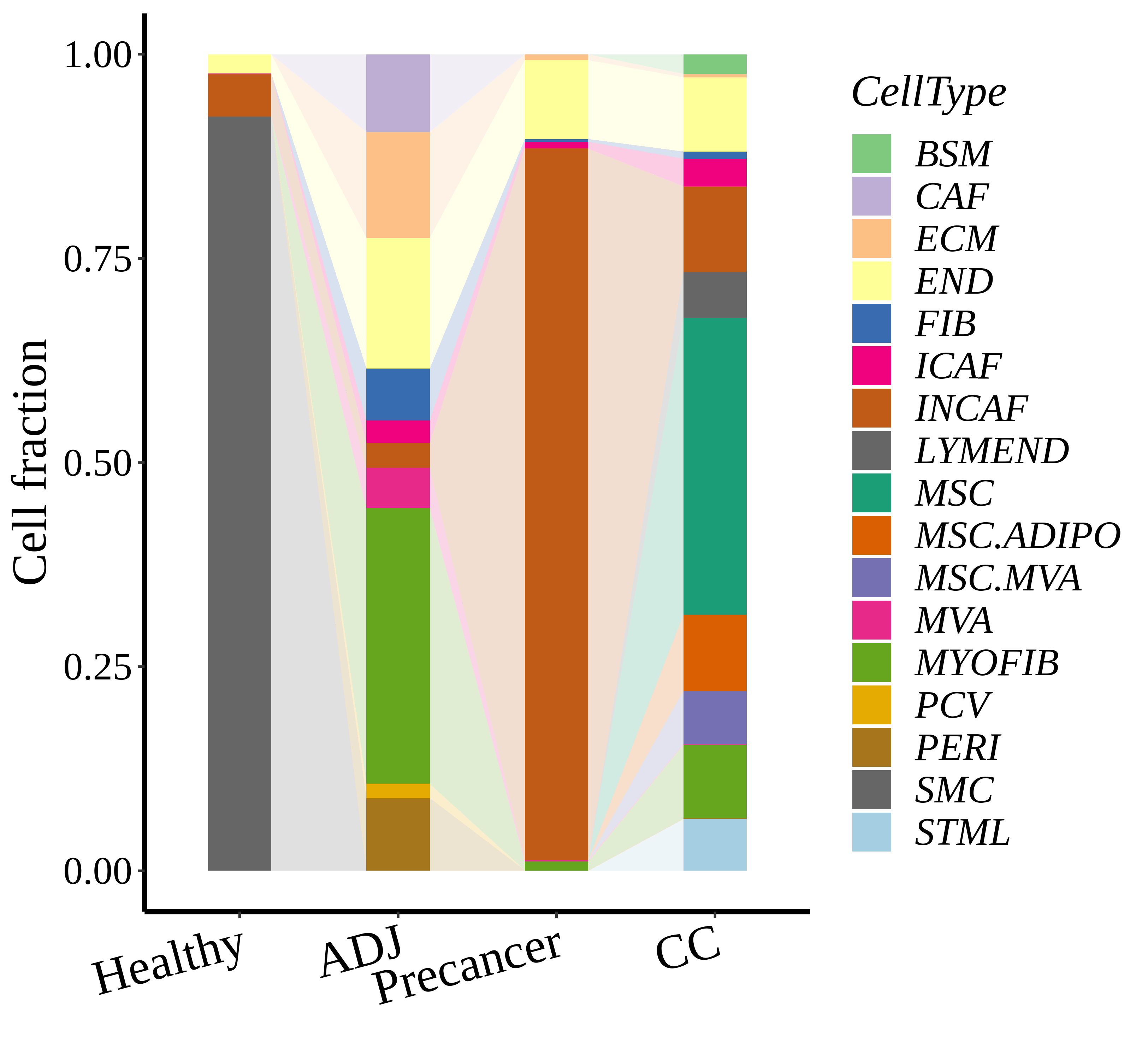 |
| ∗Stacked bar graph representation of the fraction of each epithelial cell type derived from samples with different Disease States in the integrated dataset of Cervix tissue. Cells from each Disease State sample have a different color. |
Top |
Cell type dynamics in malignant transformation |
 |  | 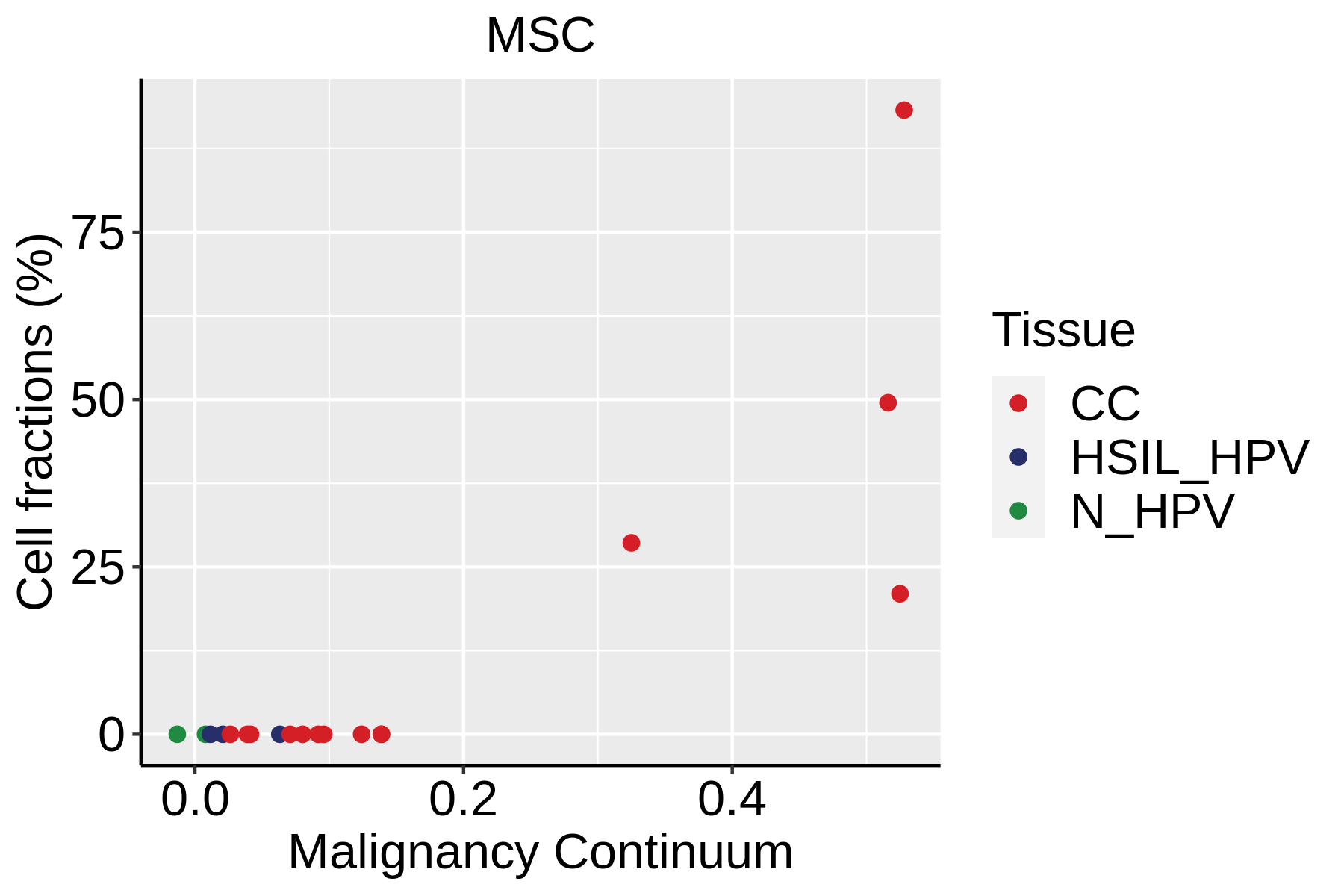 |
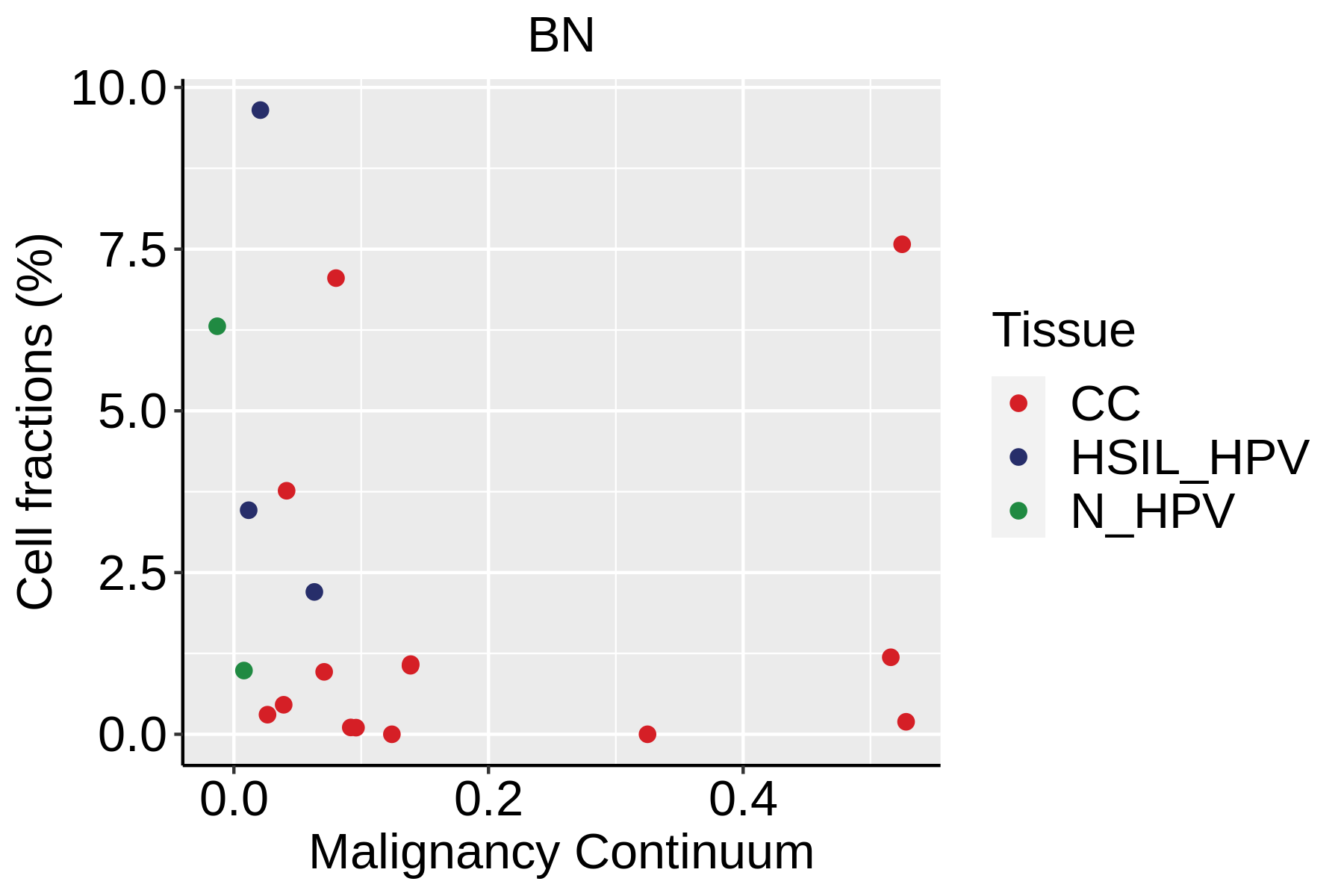 | 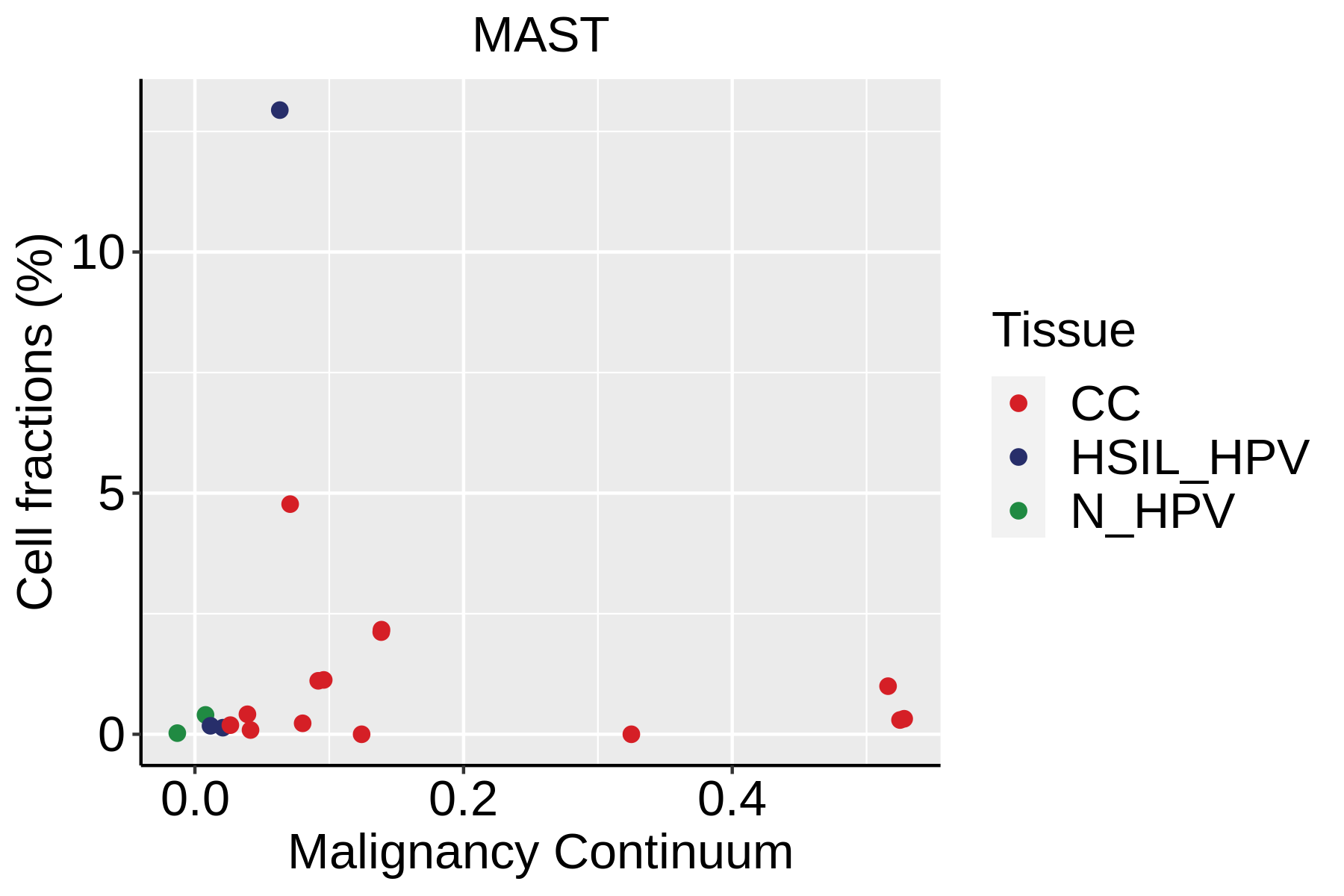 | 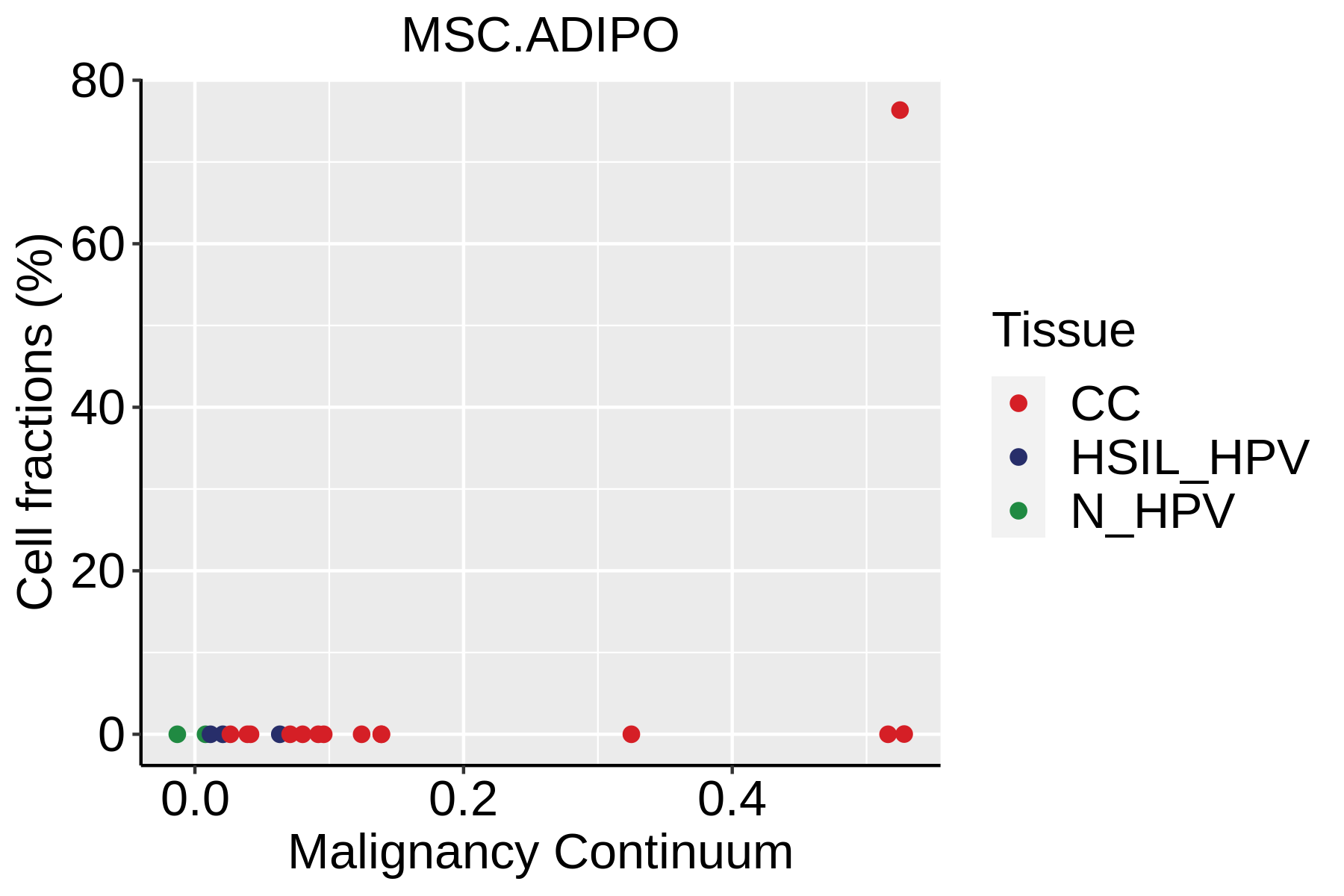 |
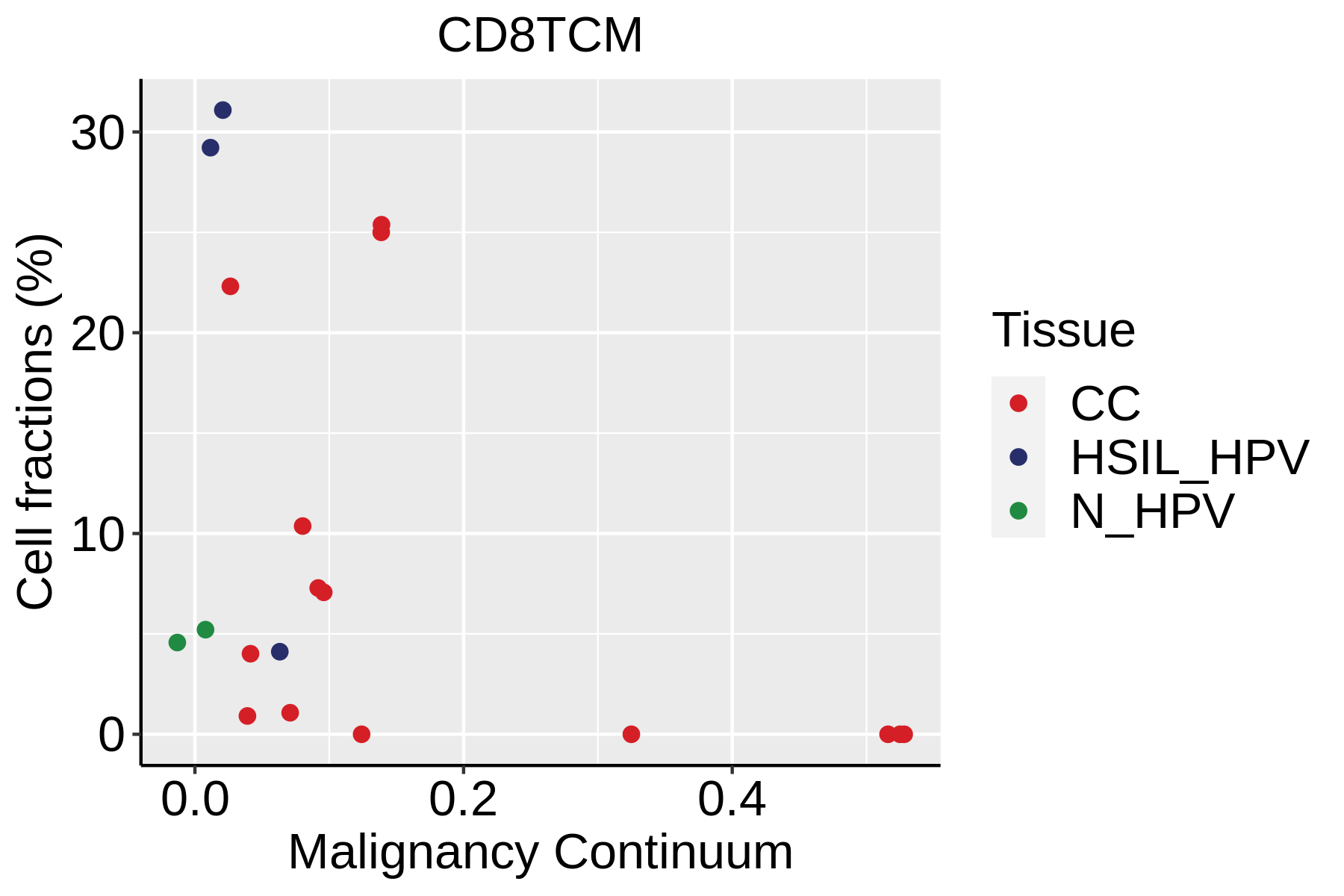
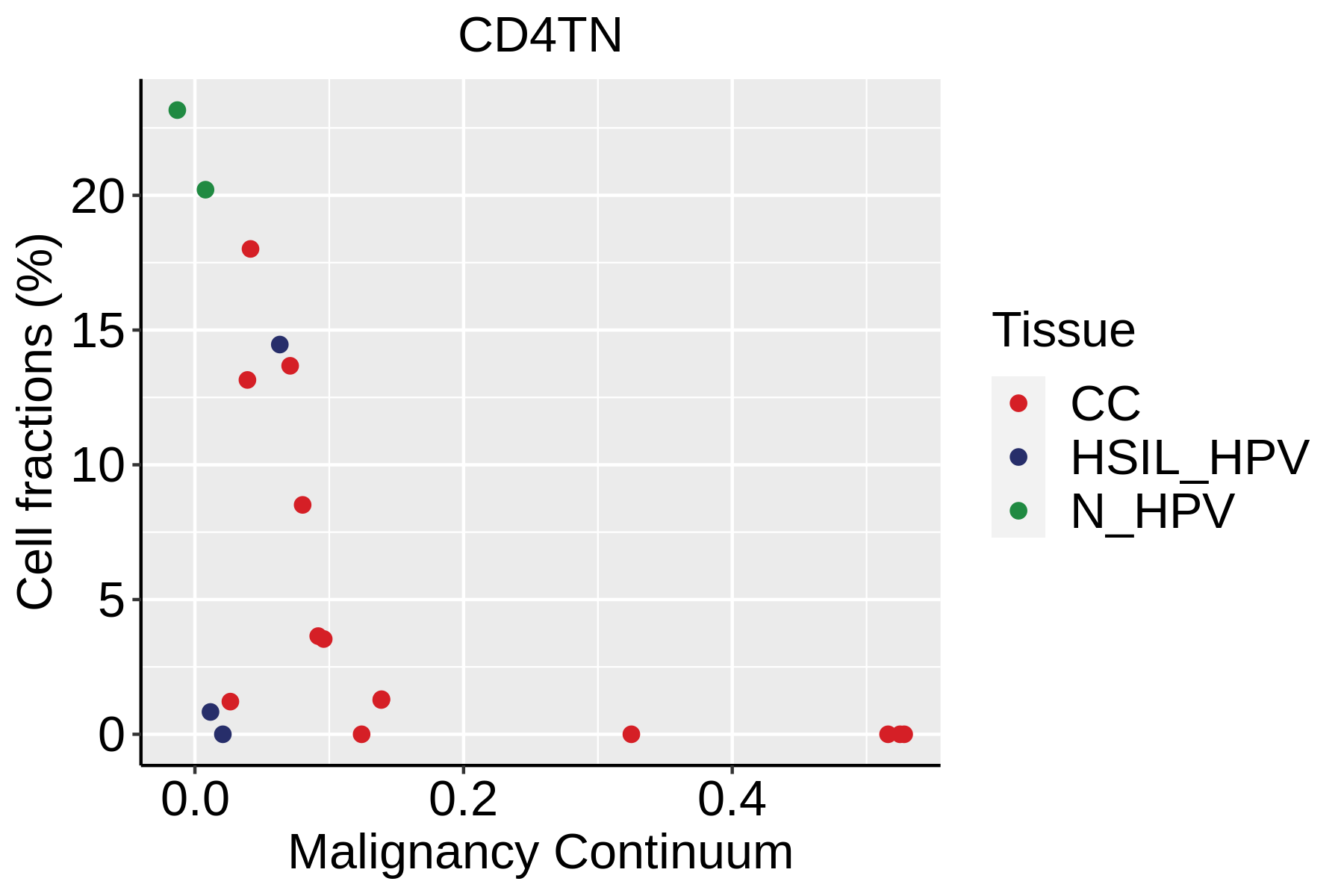 | 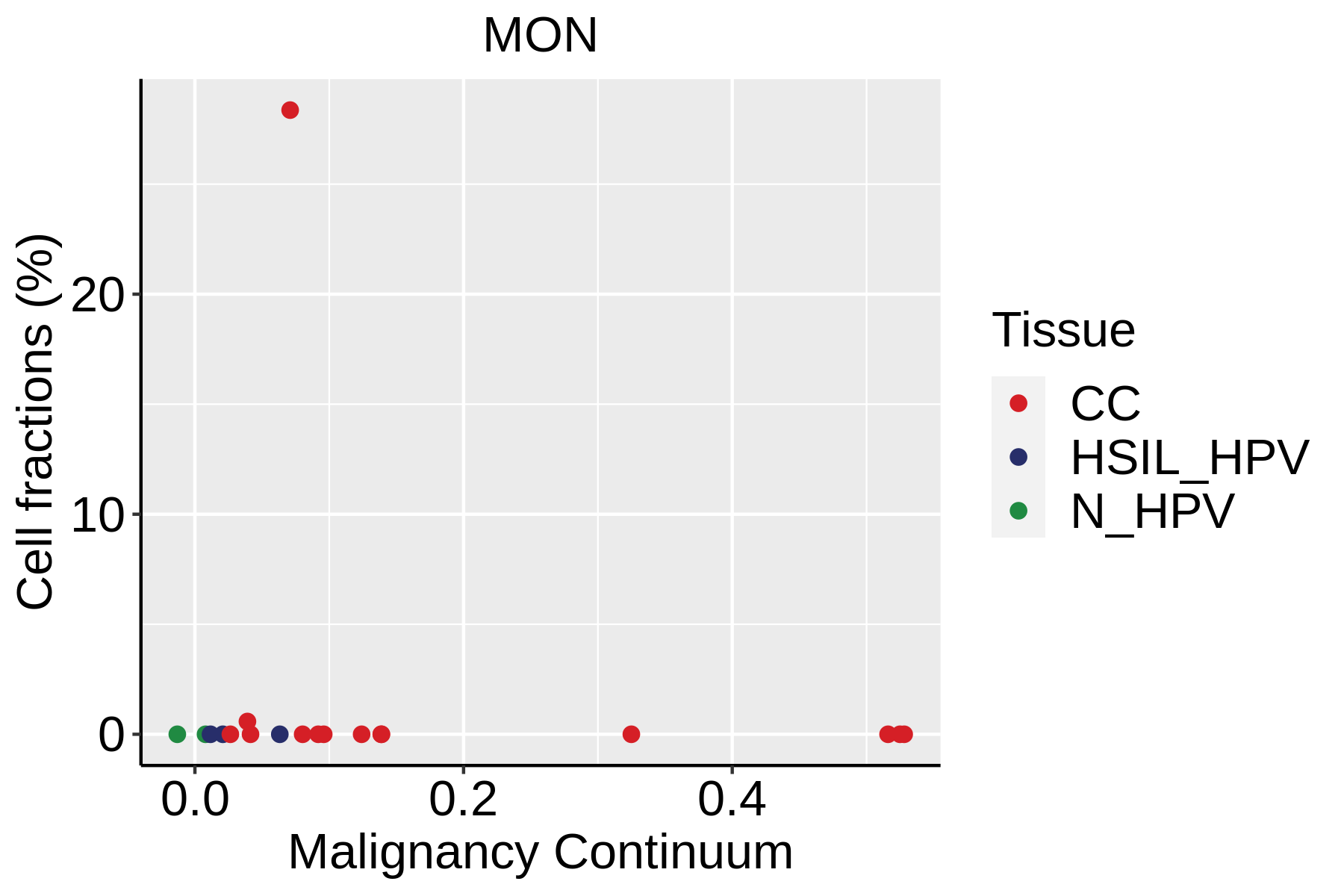 | 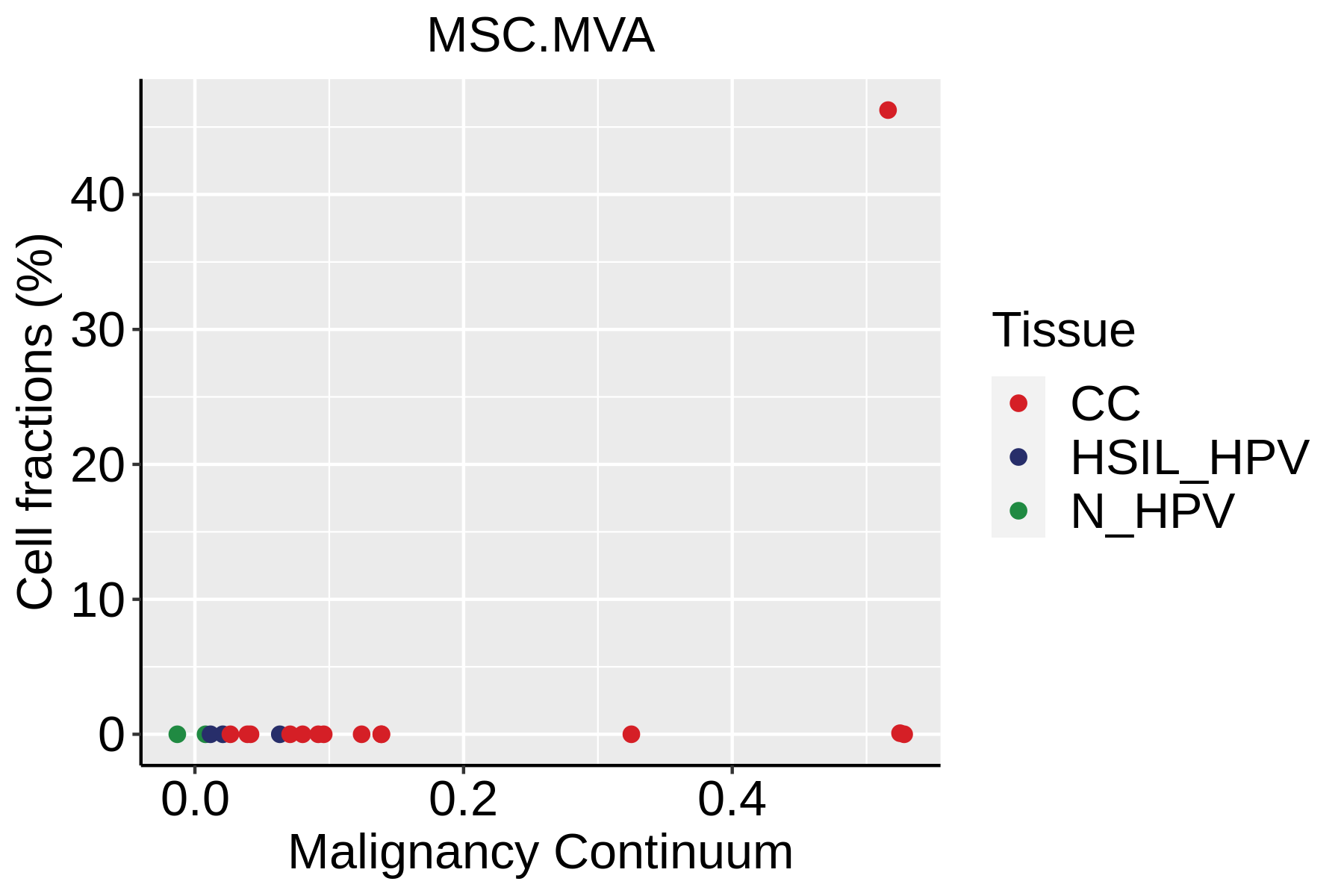 |
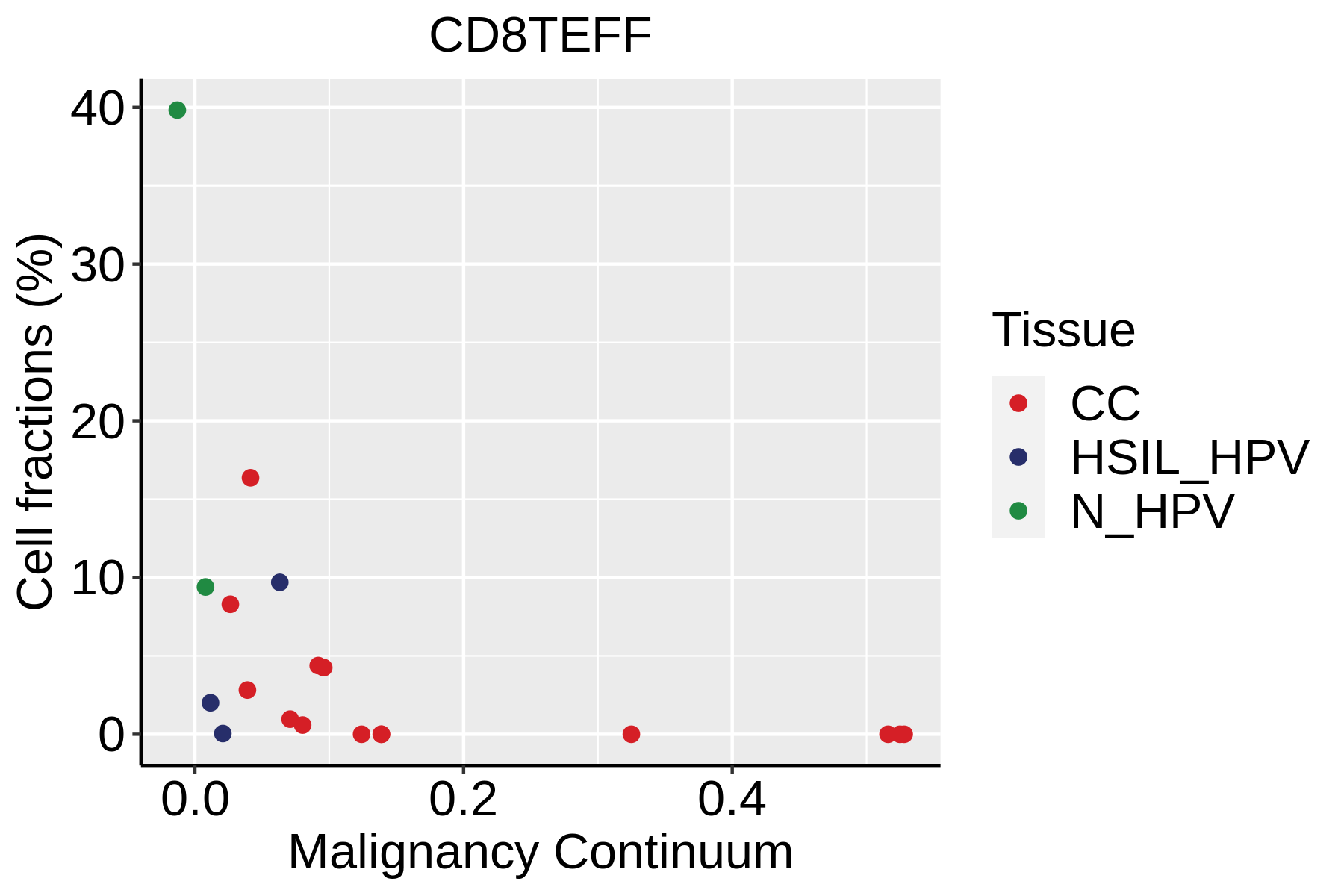
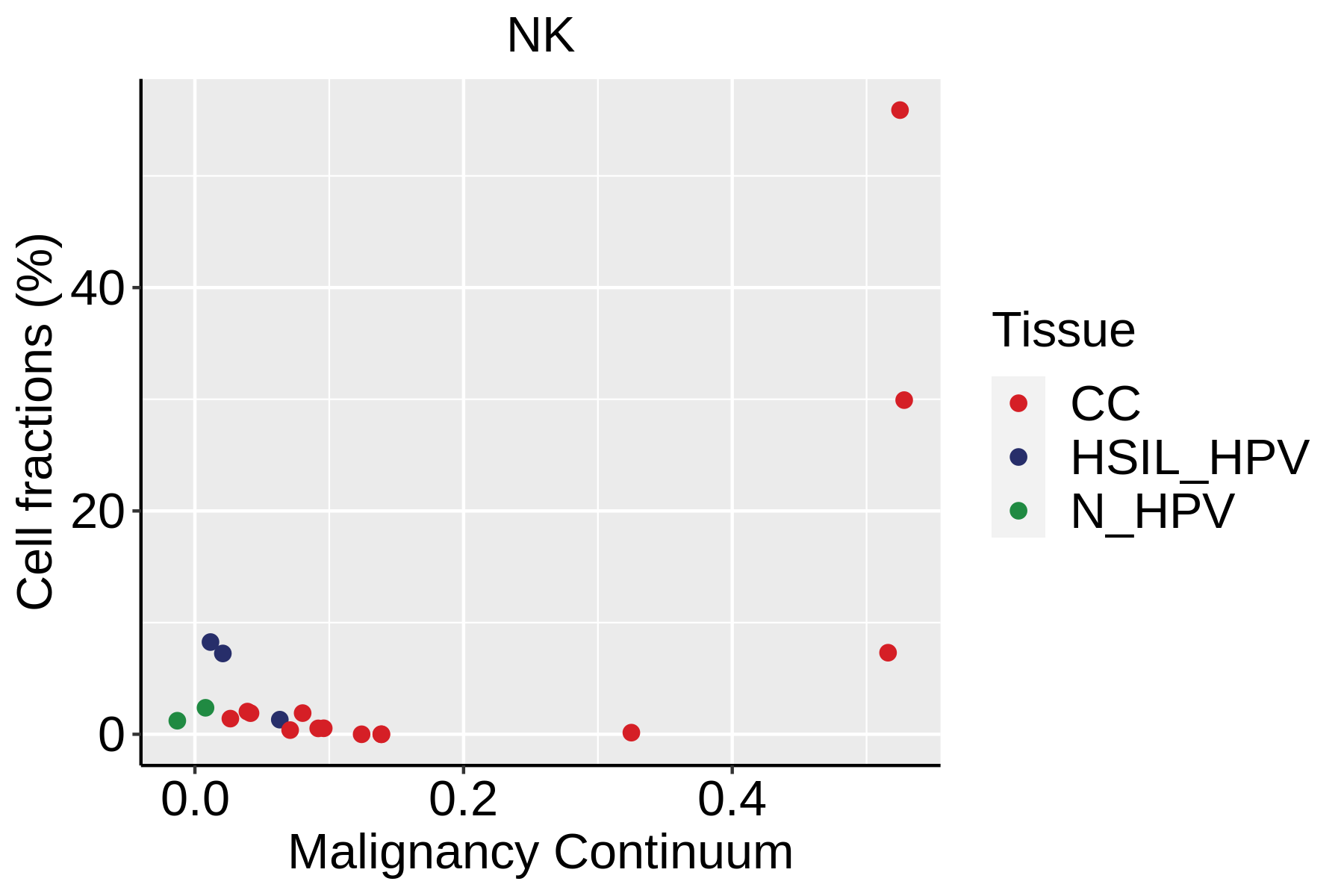
 | 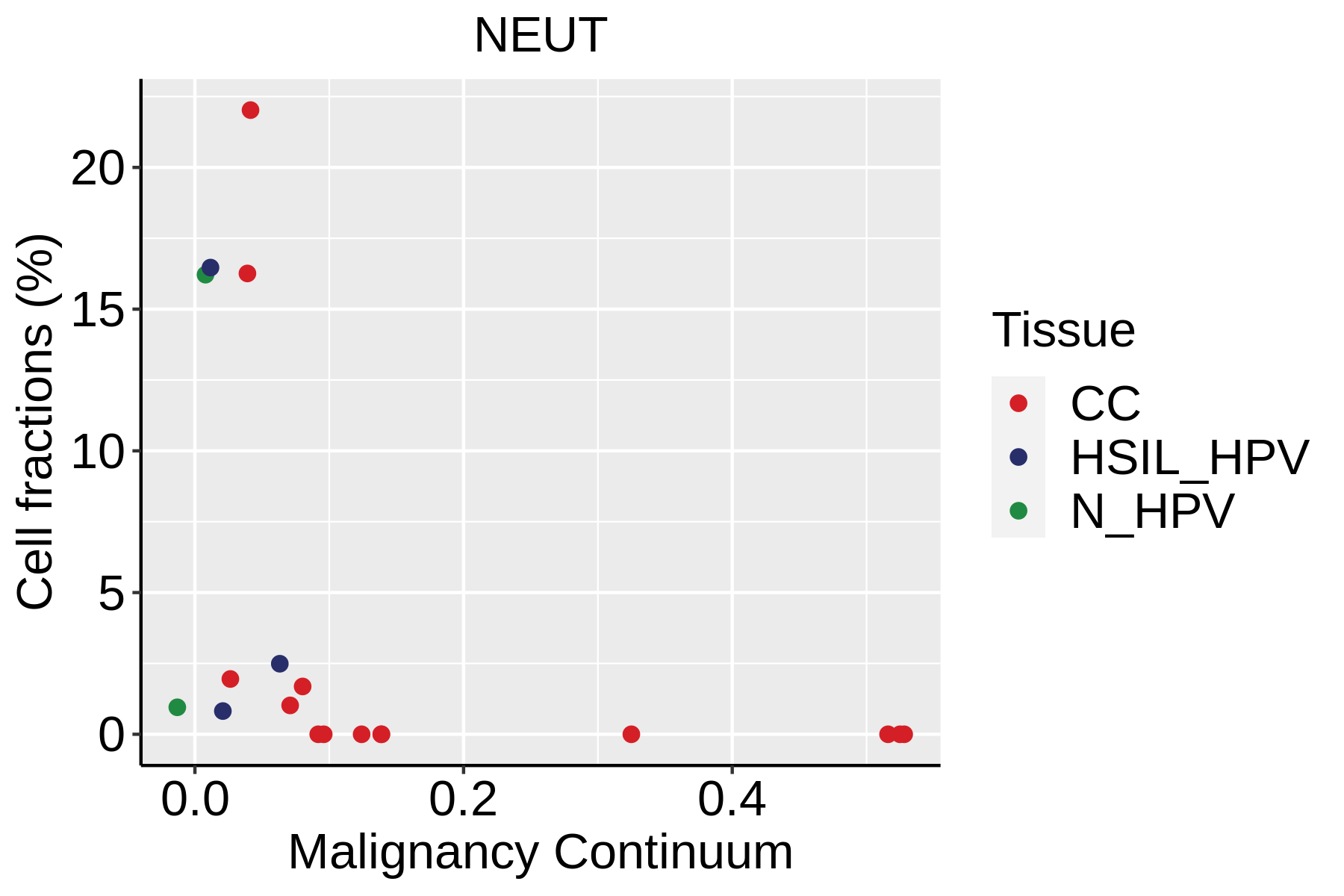 | 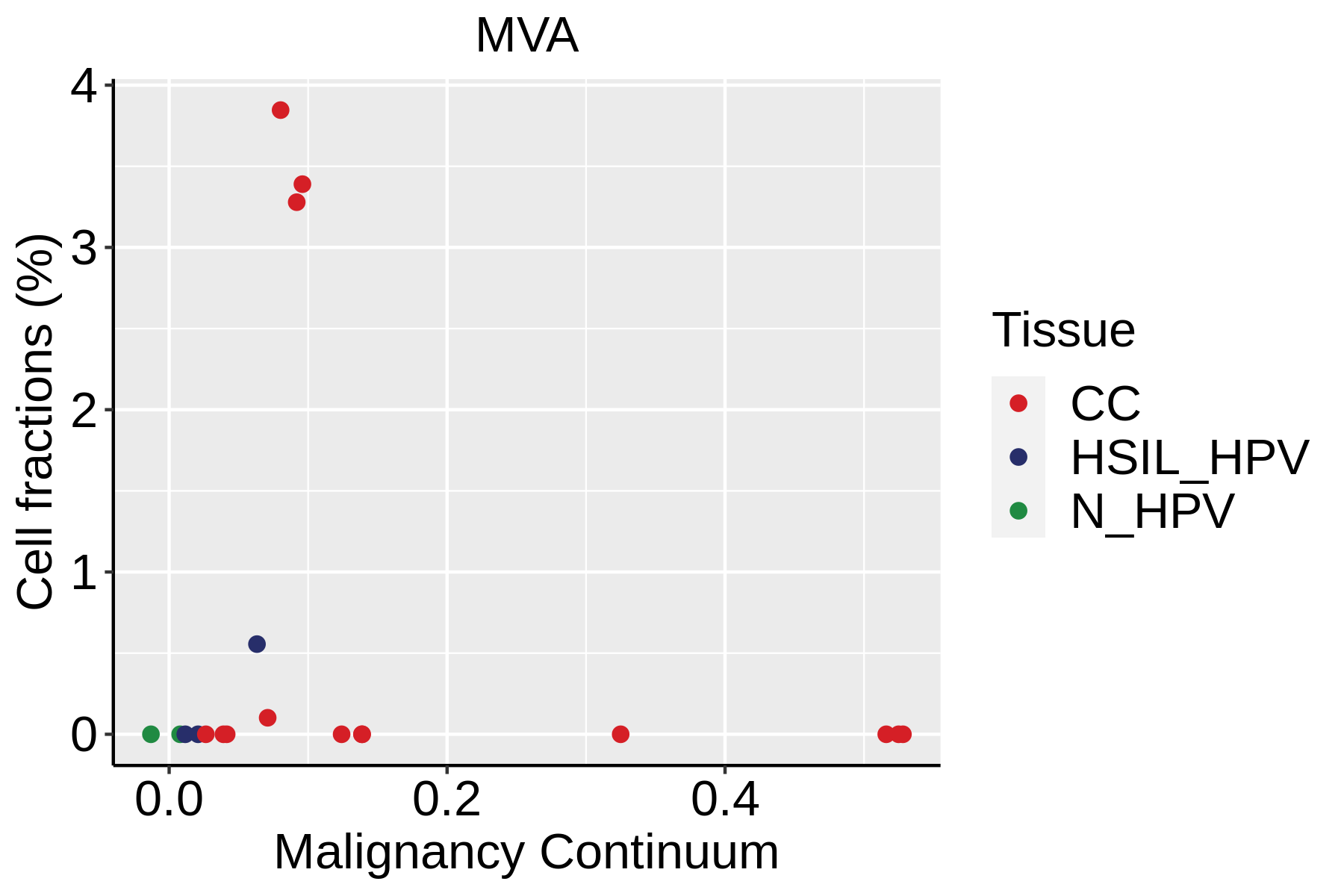 |
 |  | 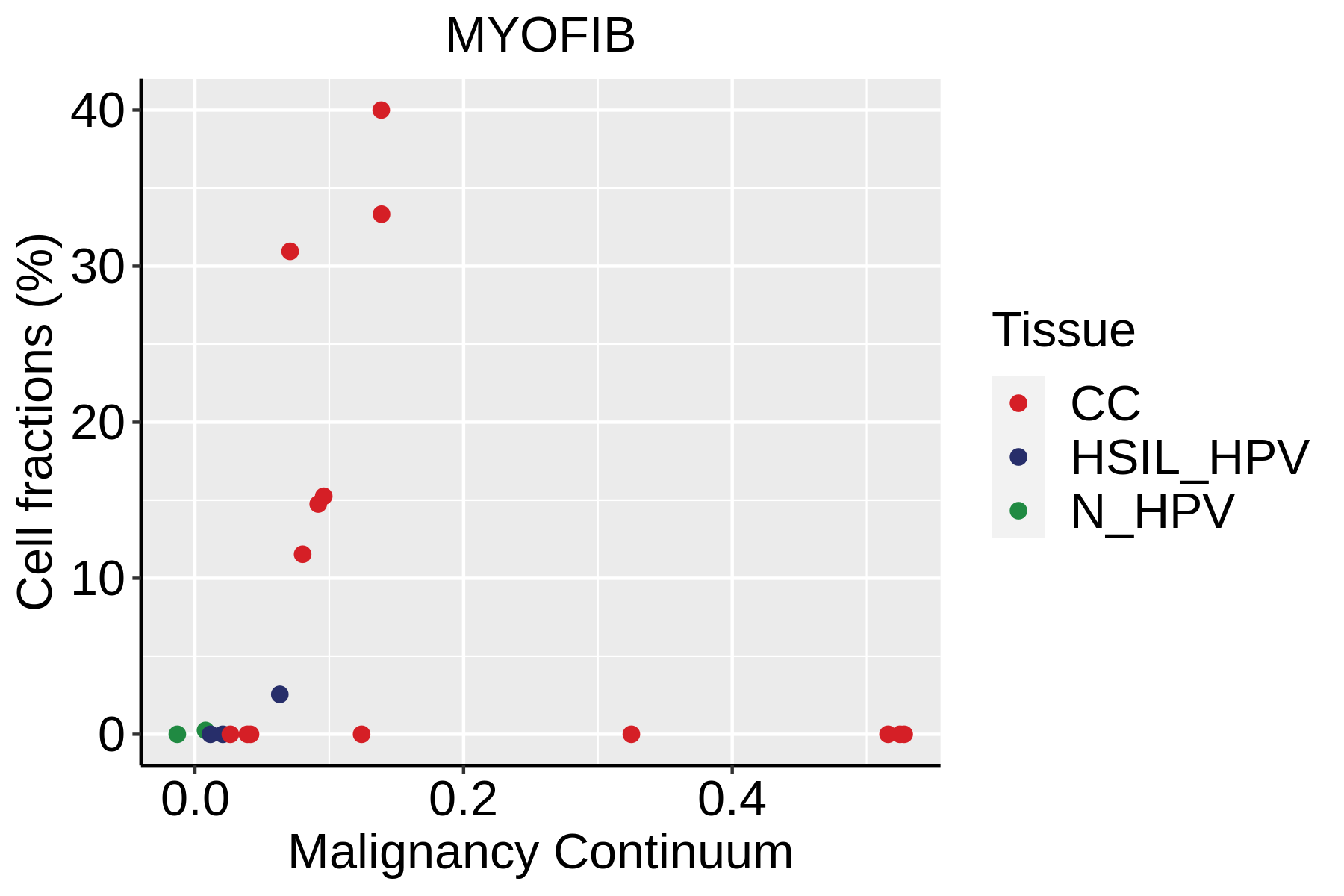 |
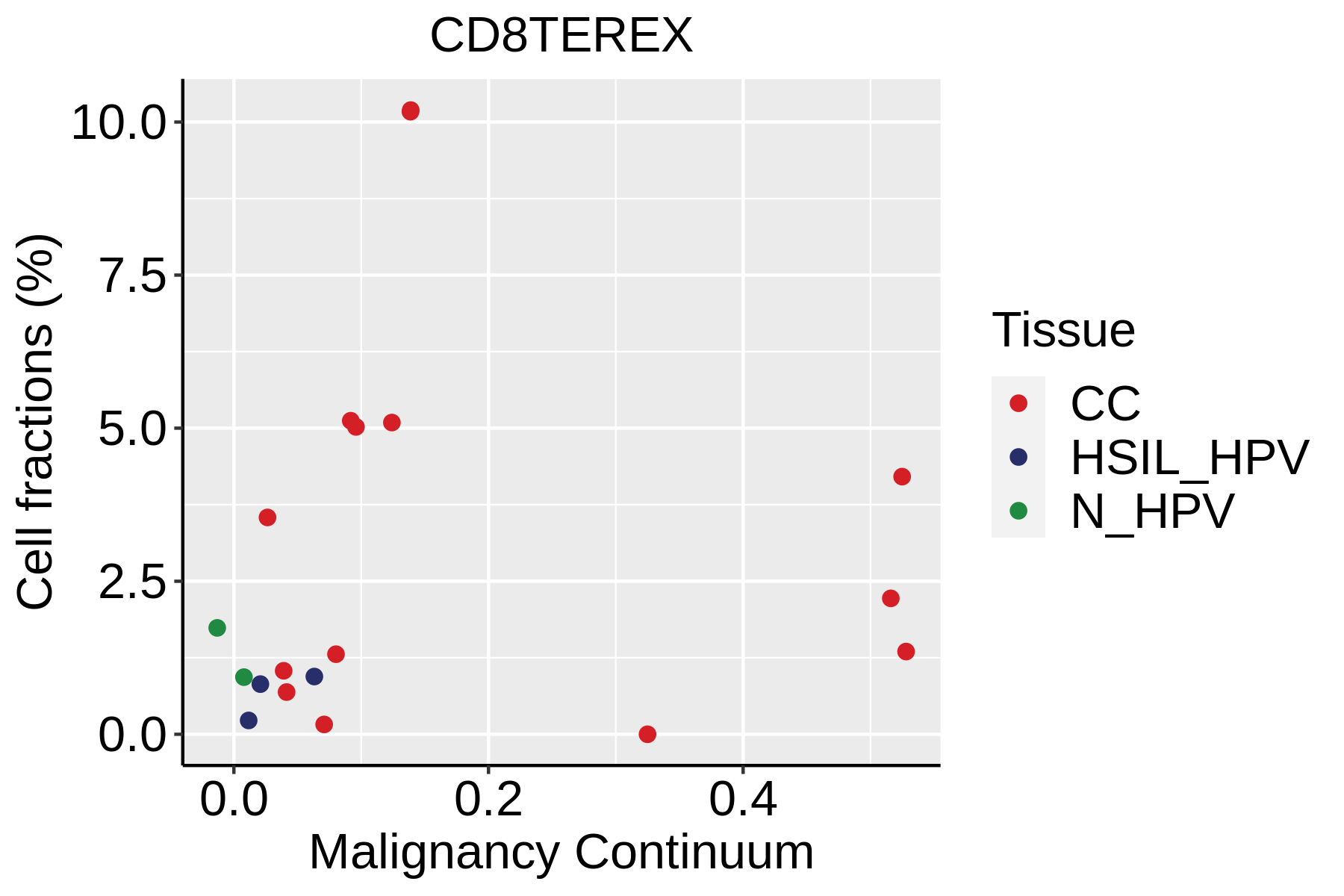 | 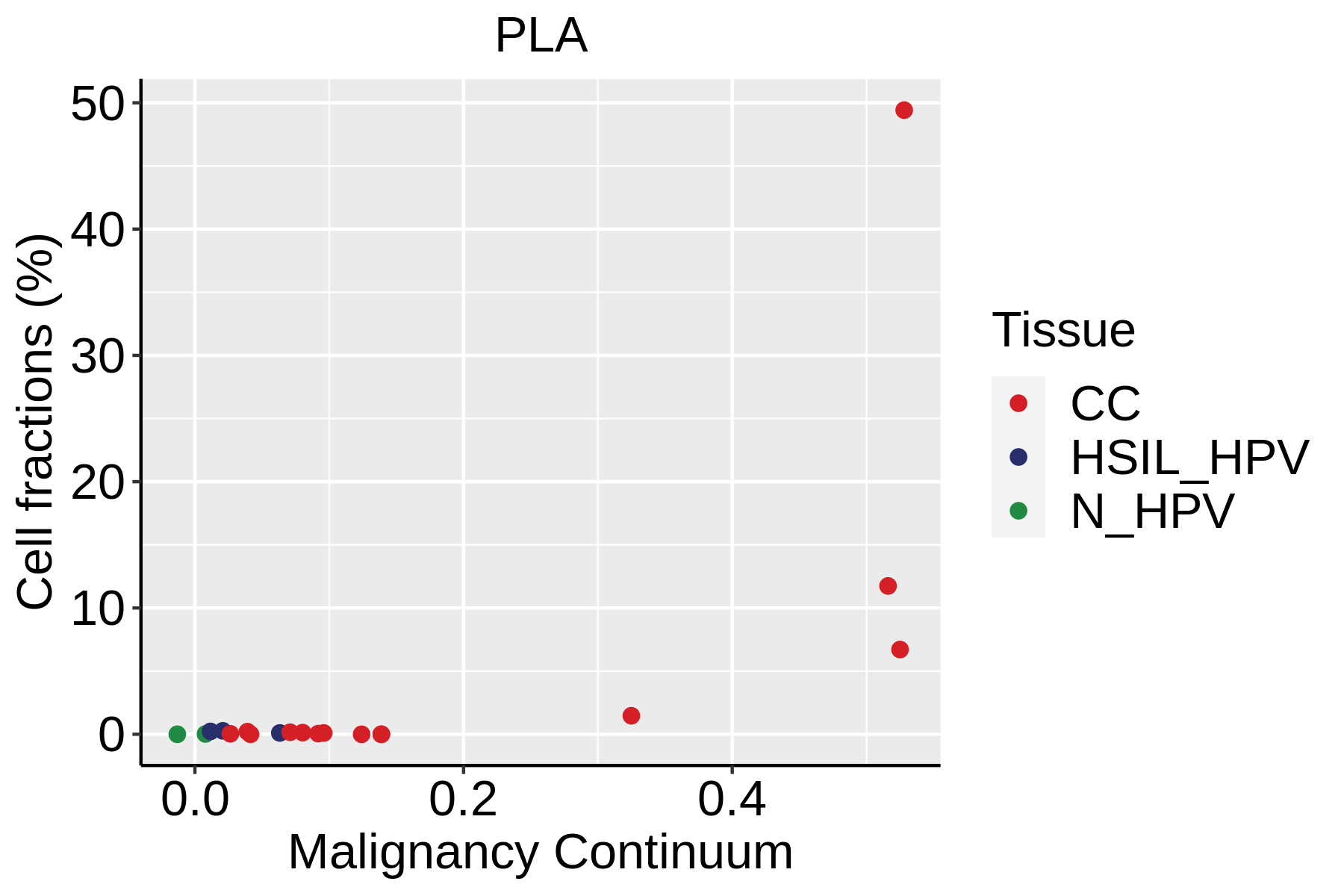 |  |
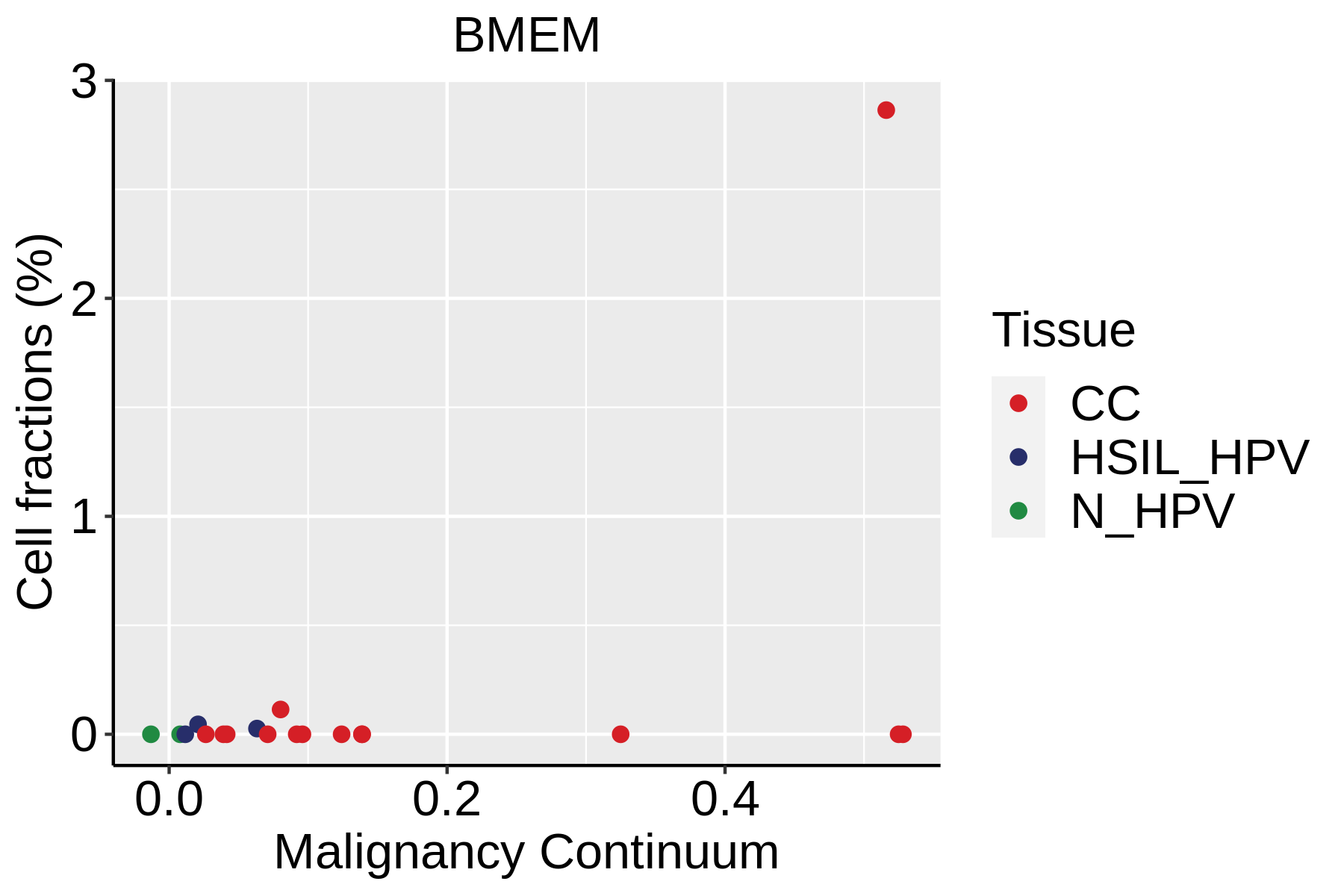
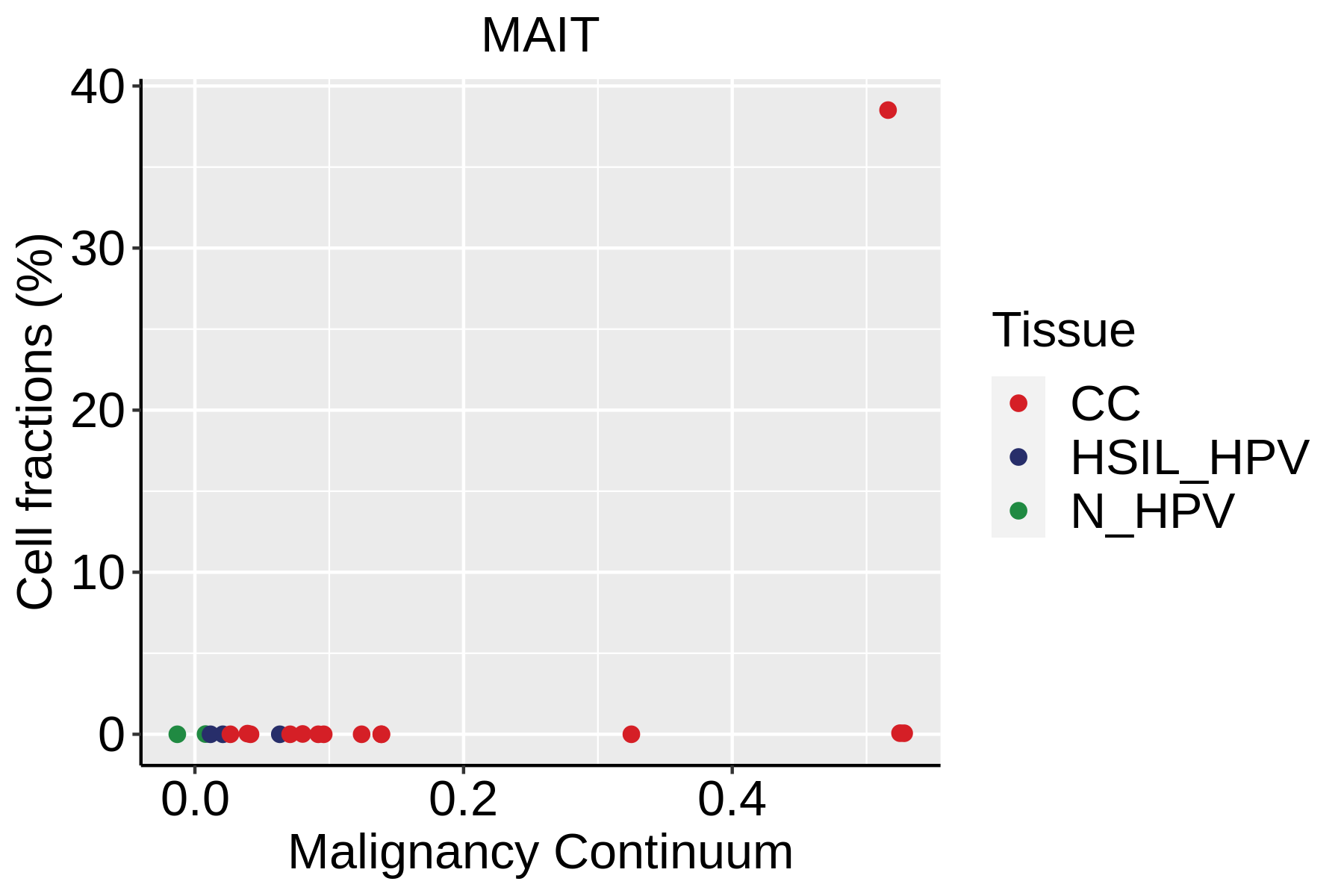
| ∗Fraction of cell type in each scRNA-seq sample plotted against position of the sample in the malignancy continuum for all cell types in Cervix tissue. Samples are colored based on if they are derived from different Disease States. Cell fractions are computed by dividing the number of cells of a given cell type by the total number of cells in the compartment (epithelial versus immune versus stromal). |
| Page: 1 2 3 |
Top |
Cell lineage trajectory inference |
| Disease State | Epithelia | Immune | Stromal |
| Healthy | 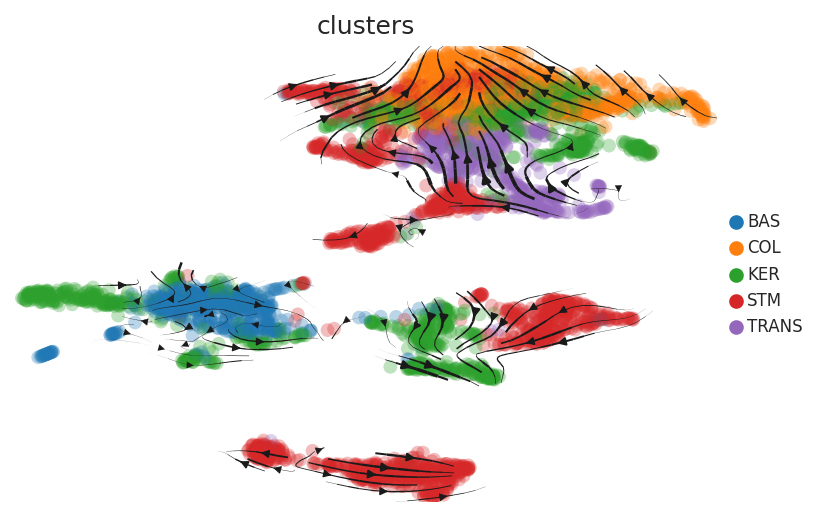 |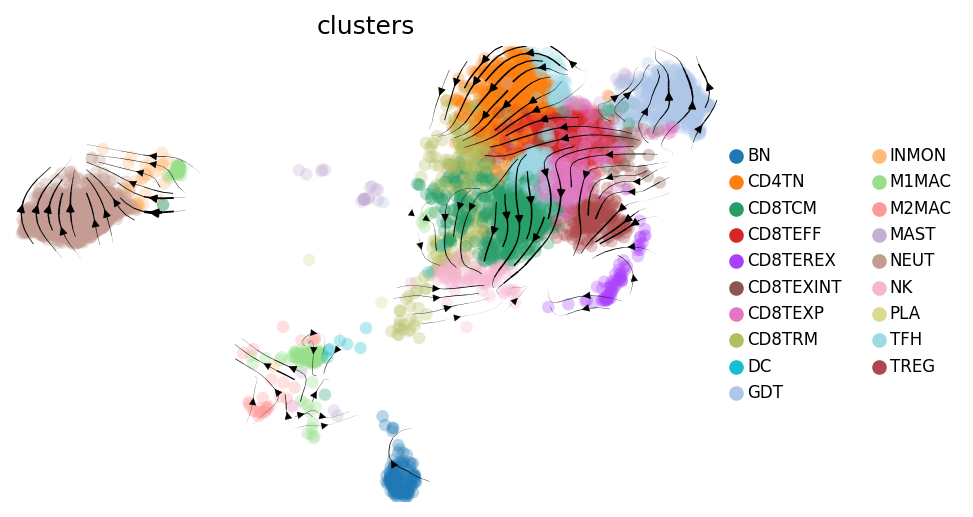  | 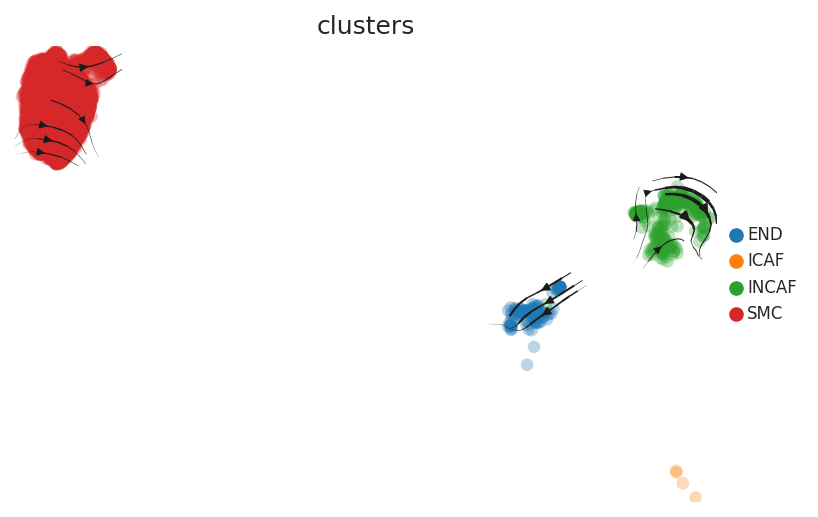 |
| Precancer |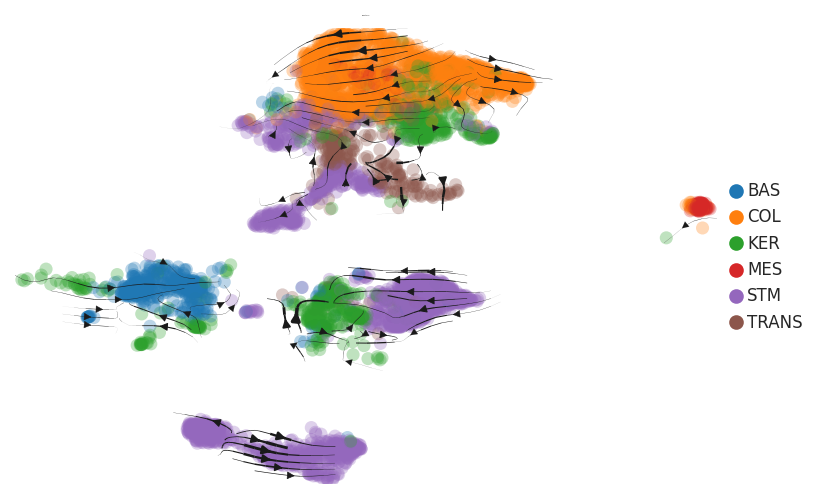  | 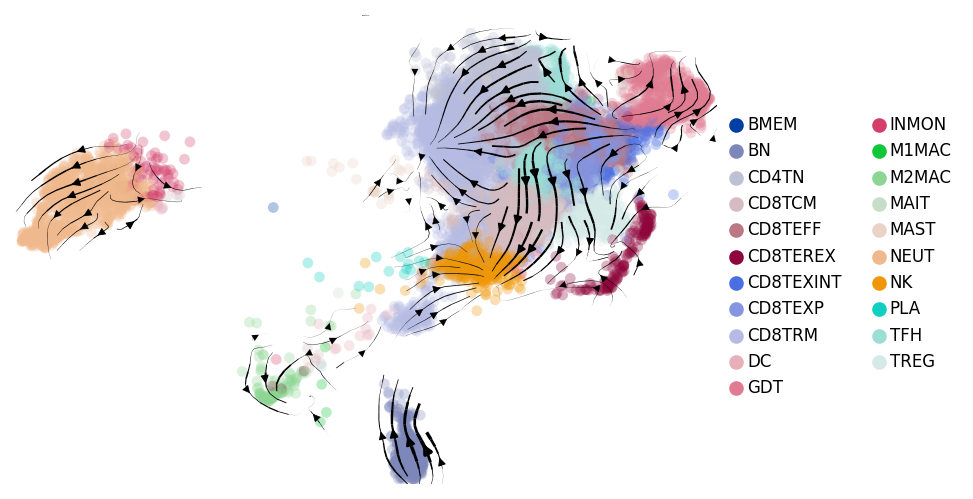 |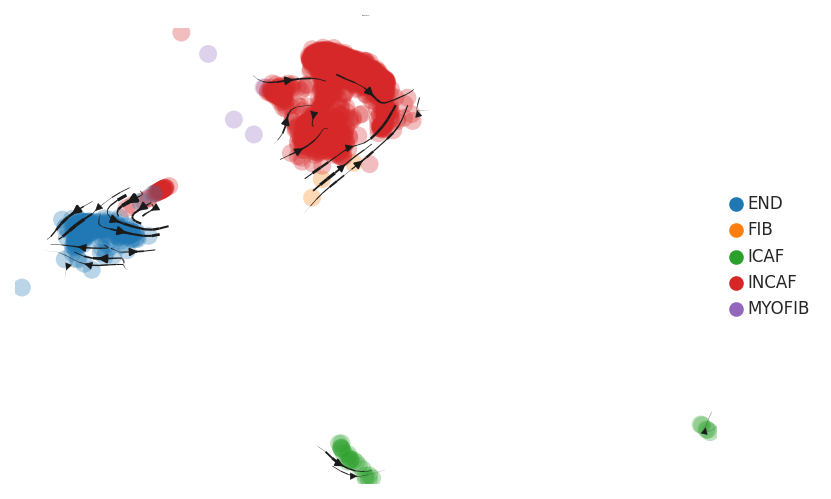  |
| CC | 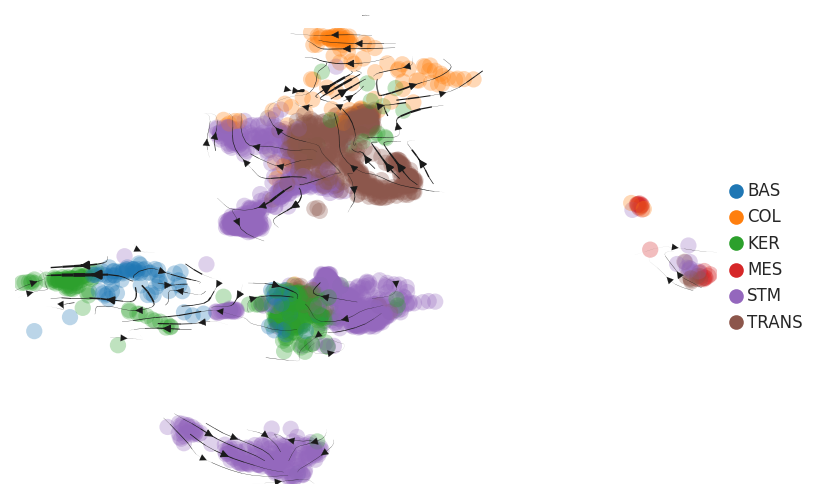 |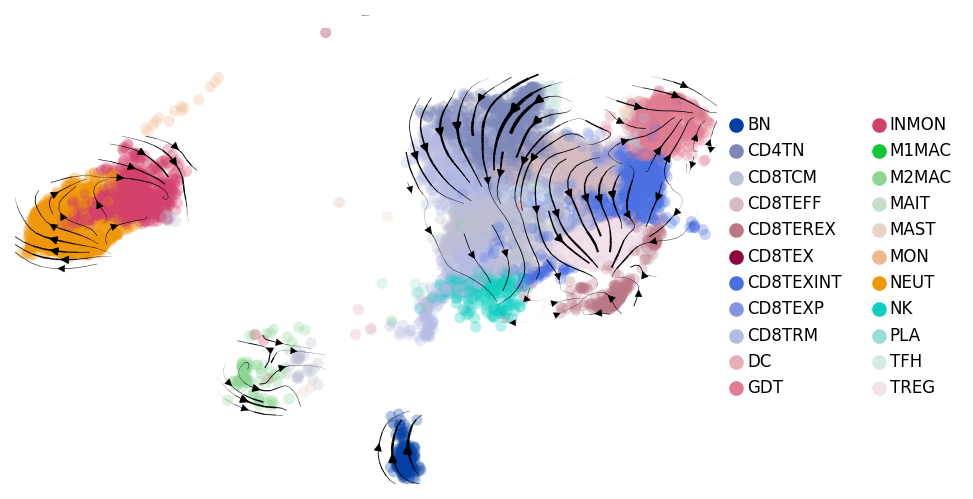  |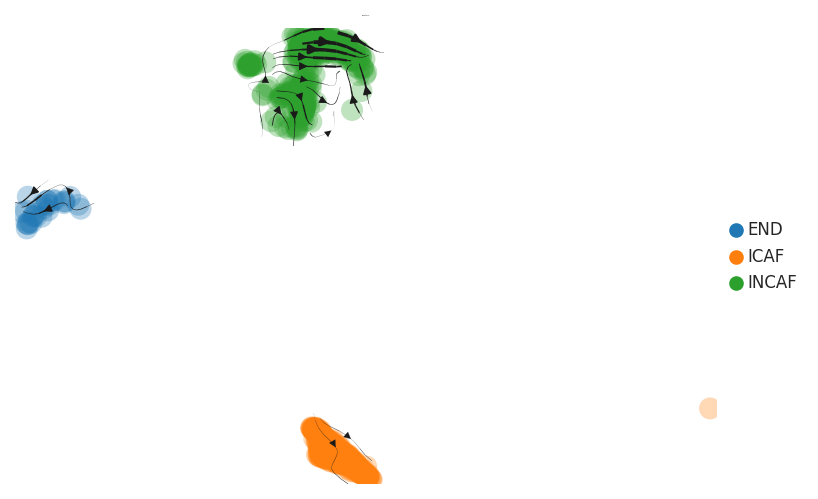  |
| ∗RNA velocity maps for epithelial, immune and stromal compartments of Cervix tissue with different disease states. |
Top |
TF regulatory network analysis |
| Disease State | Epithelia | Immune | Stromal |
| Healthy | 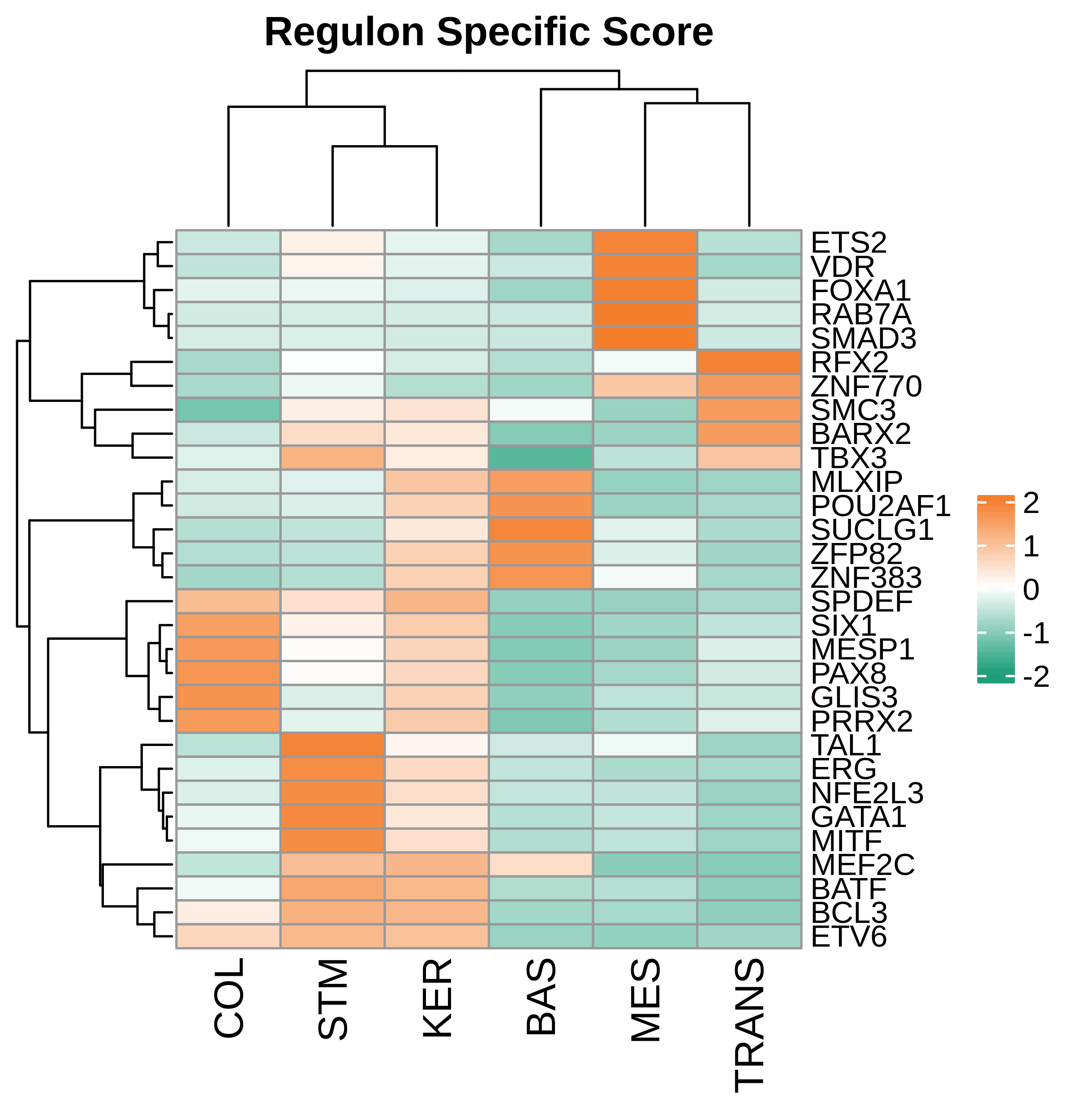 | 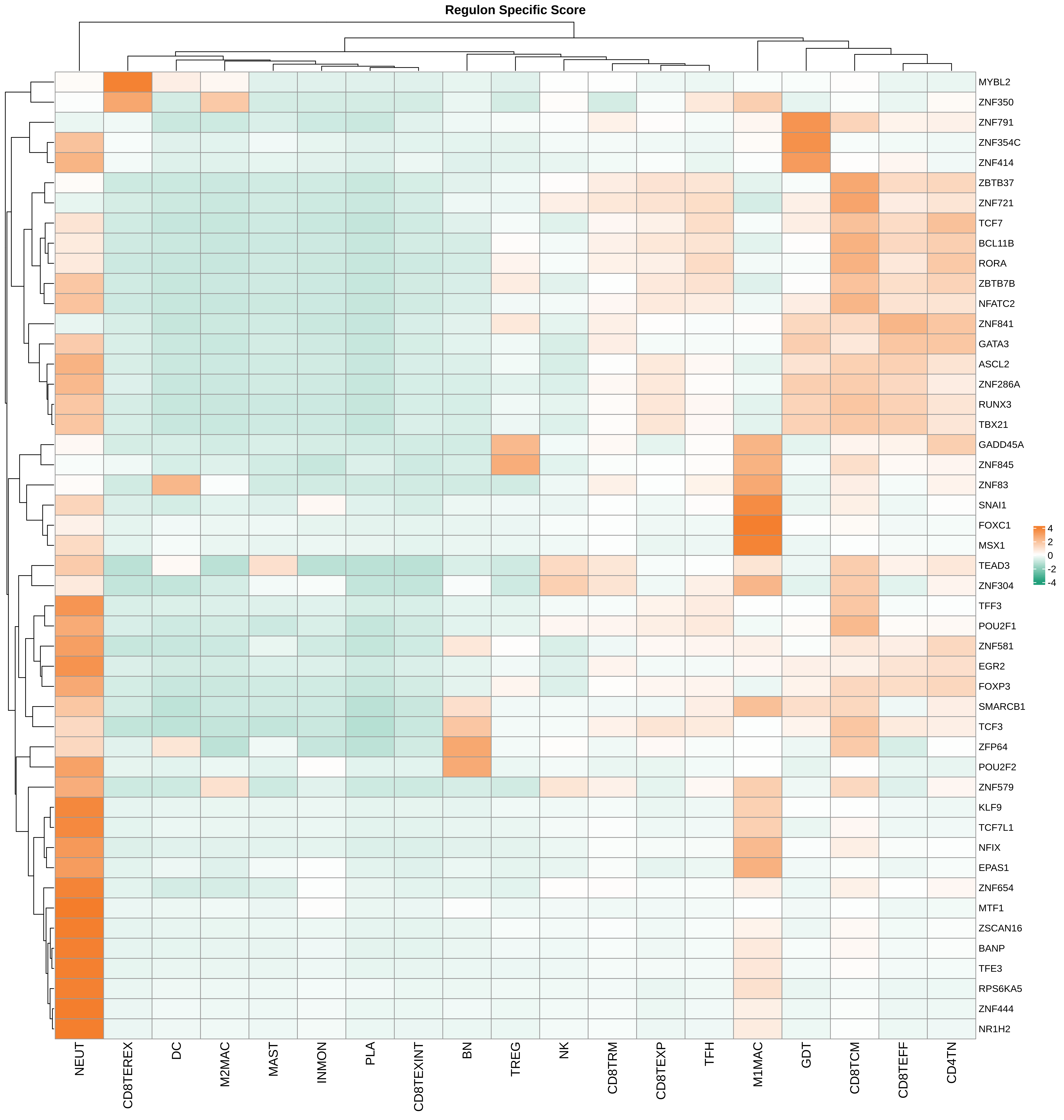 | 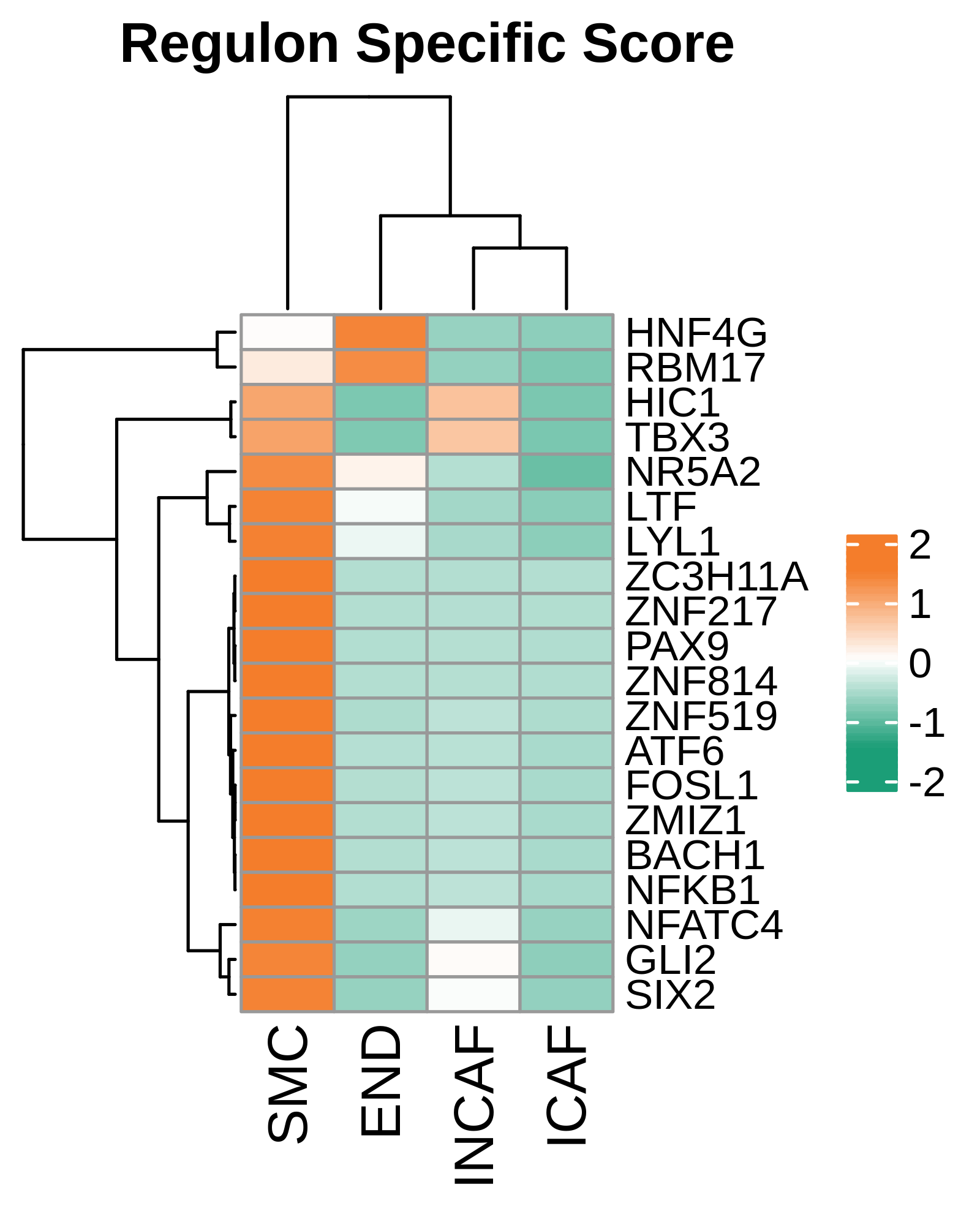 |
| TF target network | TF target network | TF target network | |
| ADJ | 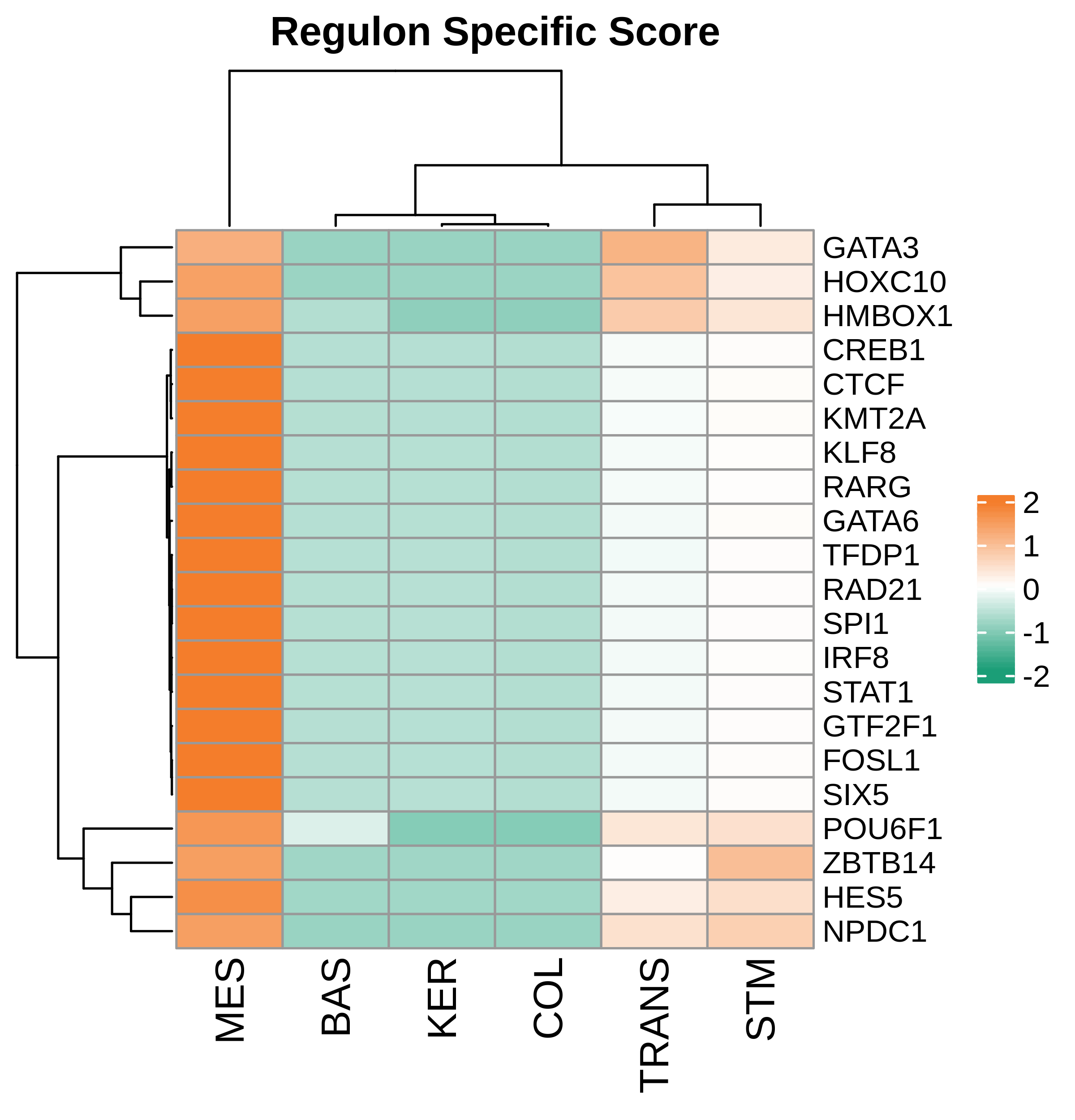 | 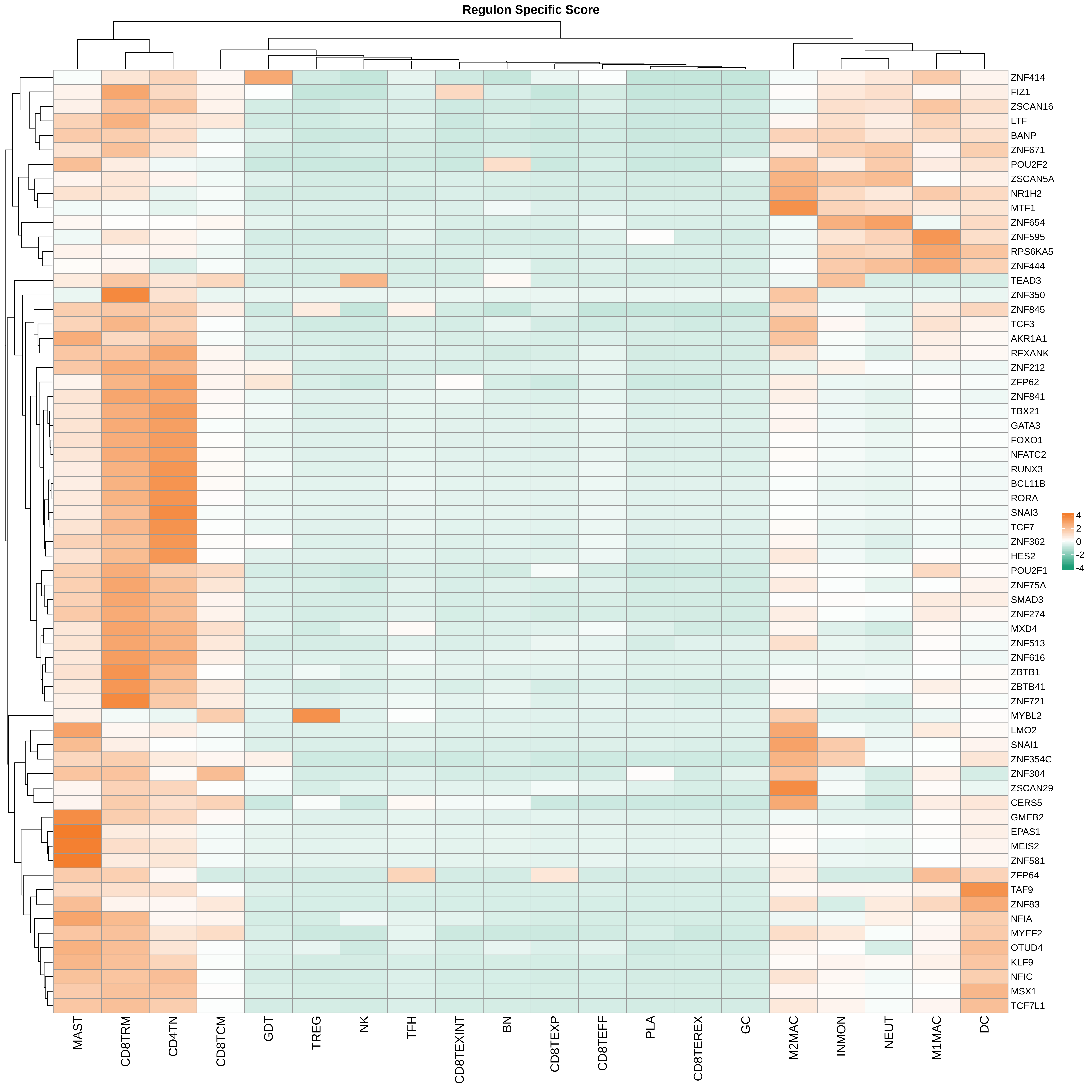 | 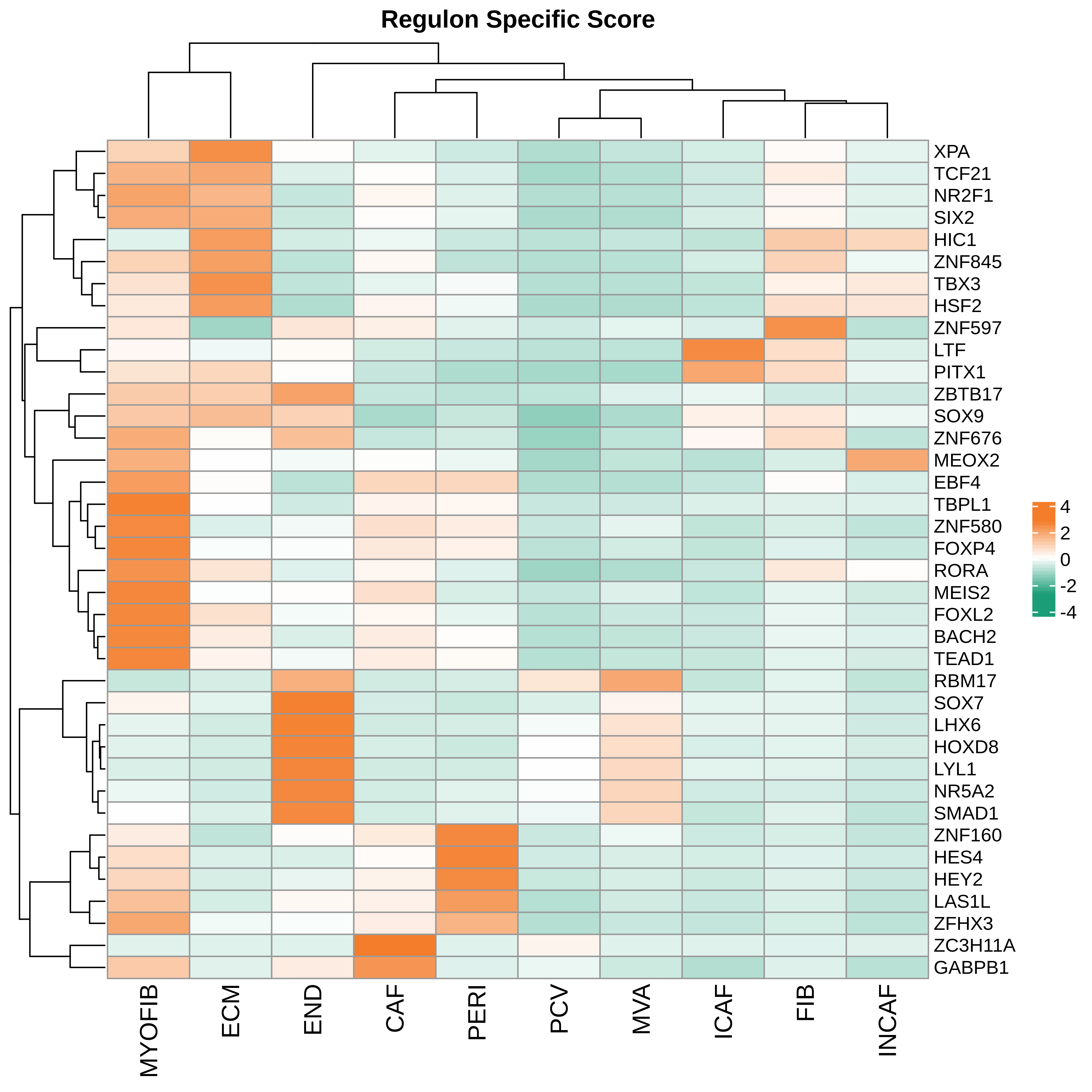 |
| TF target network | TF target network | TF target network | |
| Precancer | 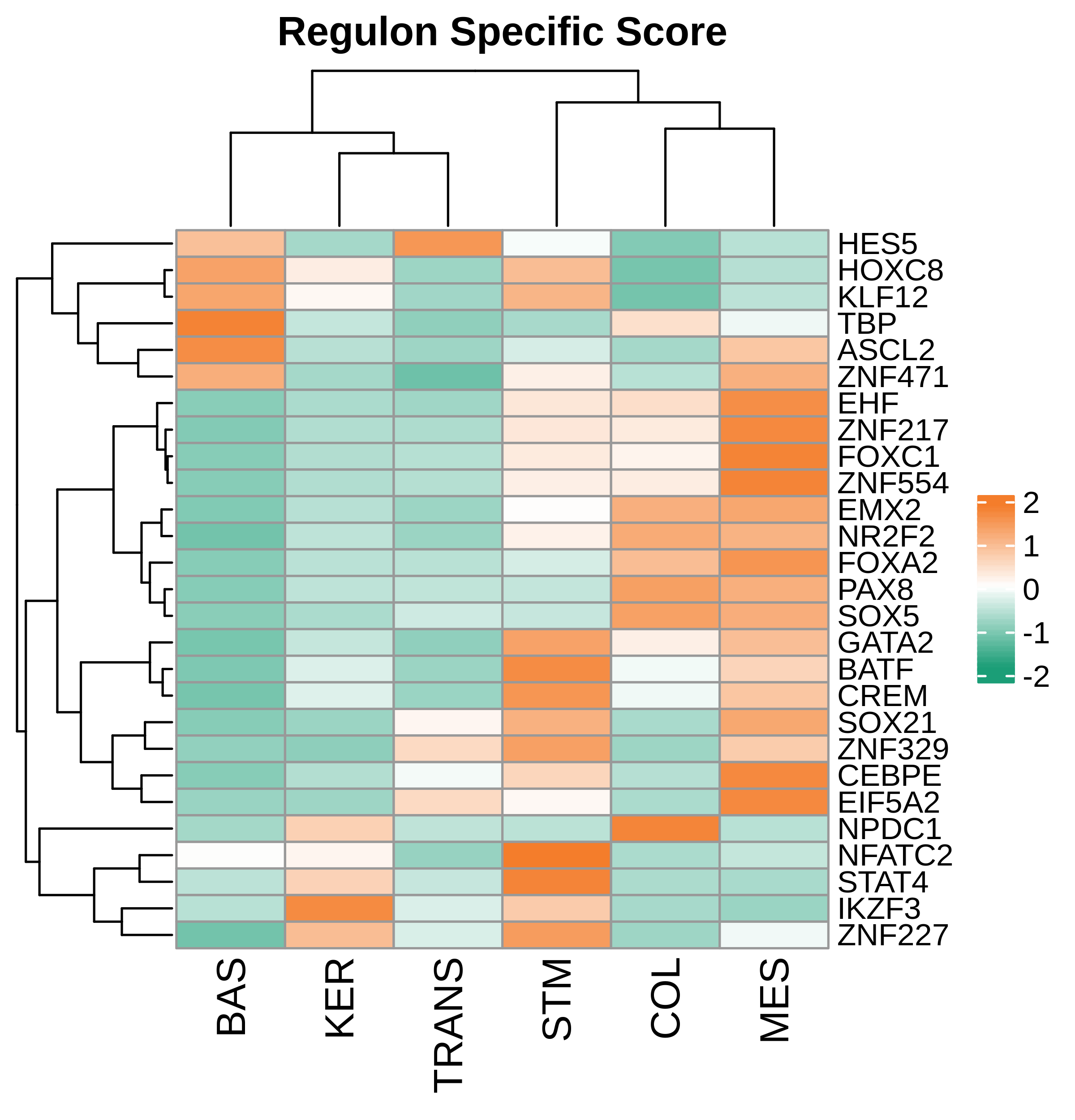 | 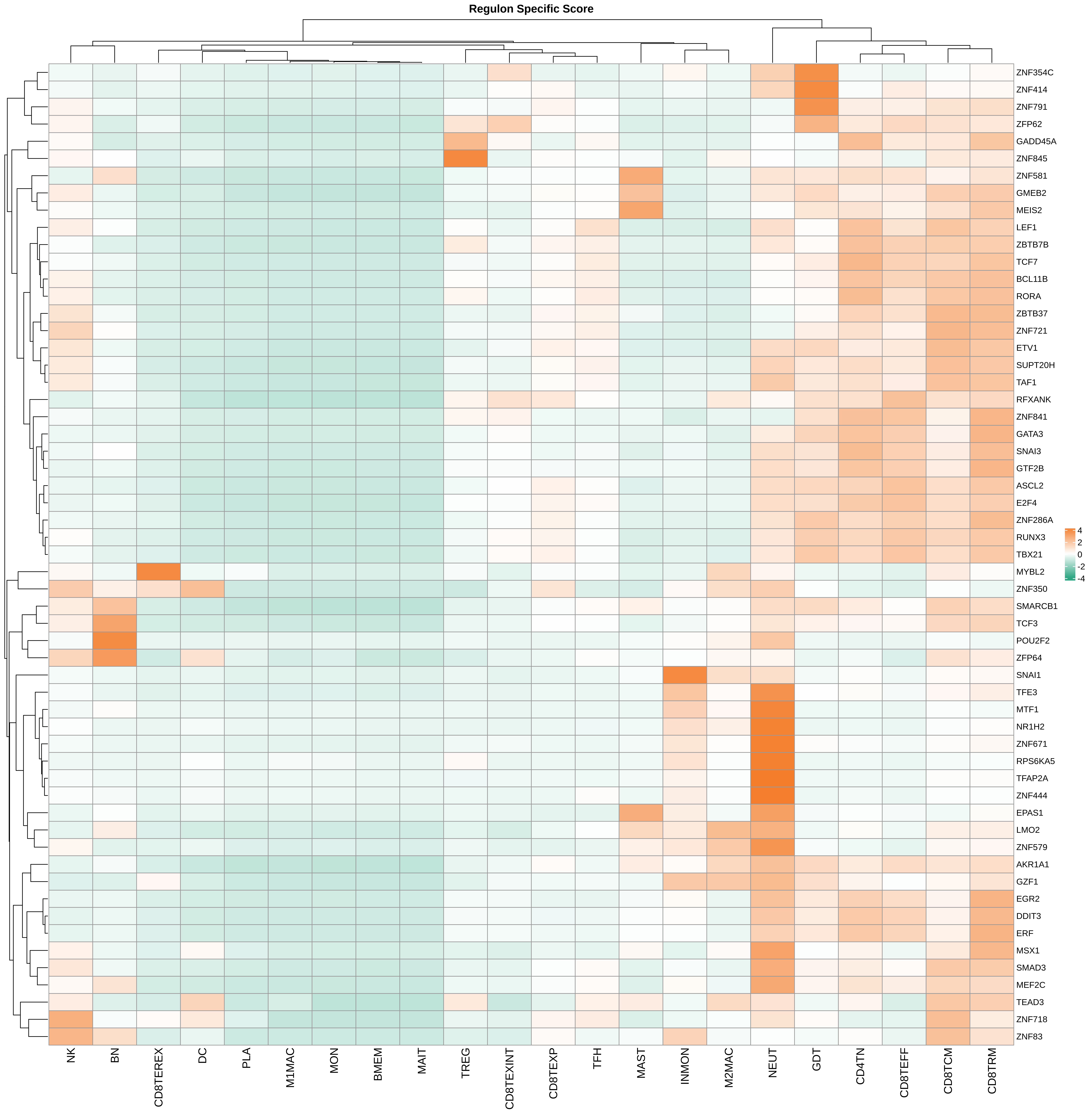 | 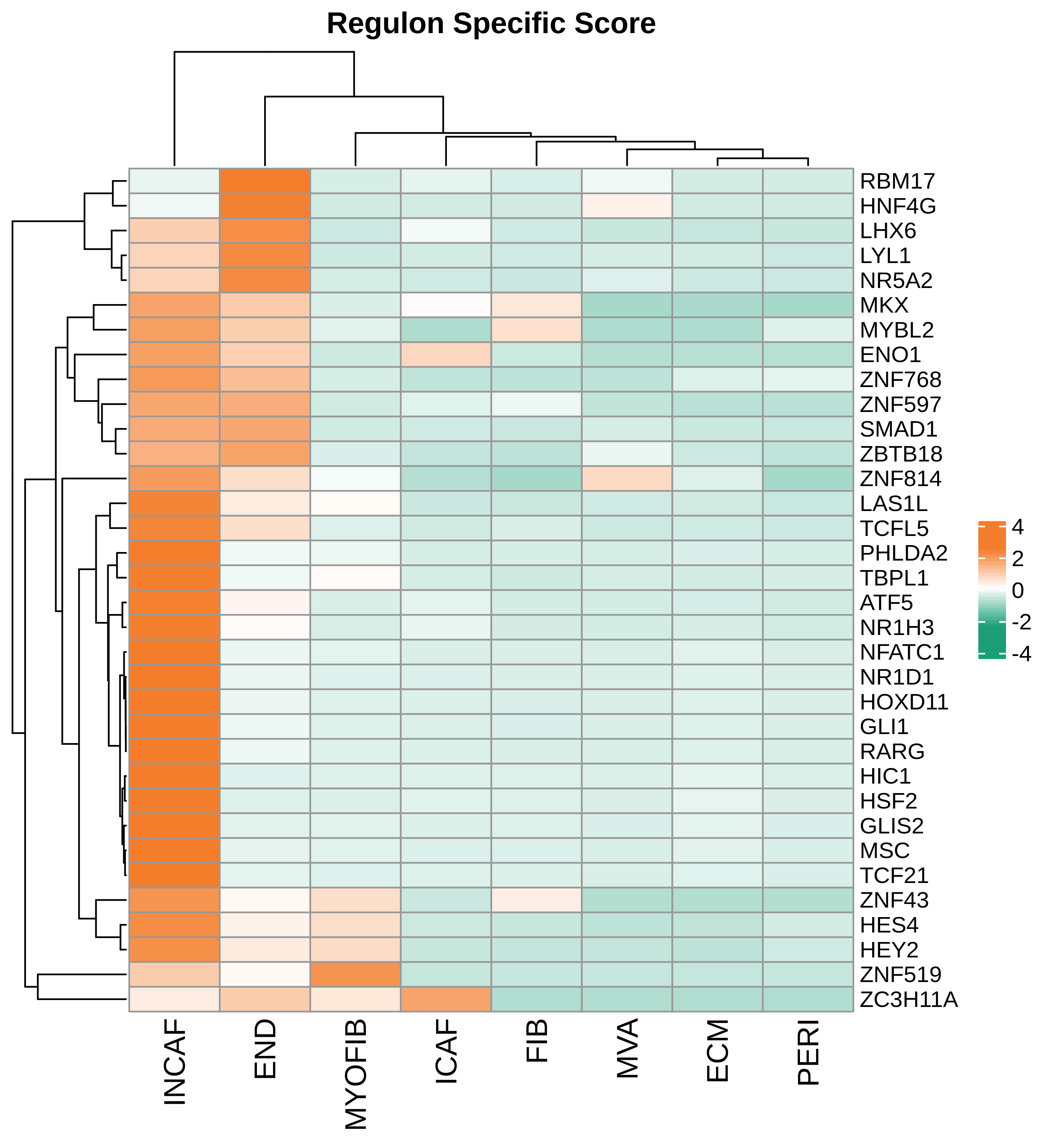 |
| TF target network | TF target network | TF target network | |
| CC | 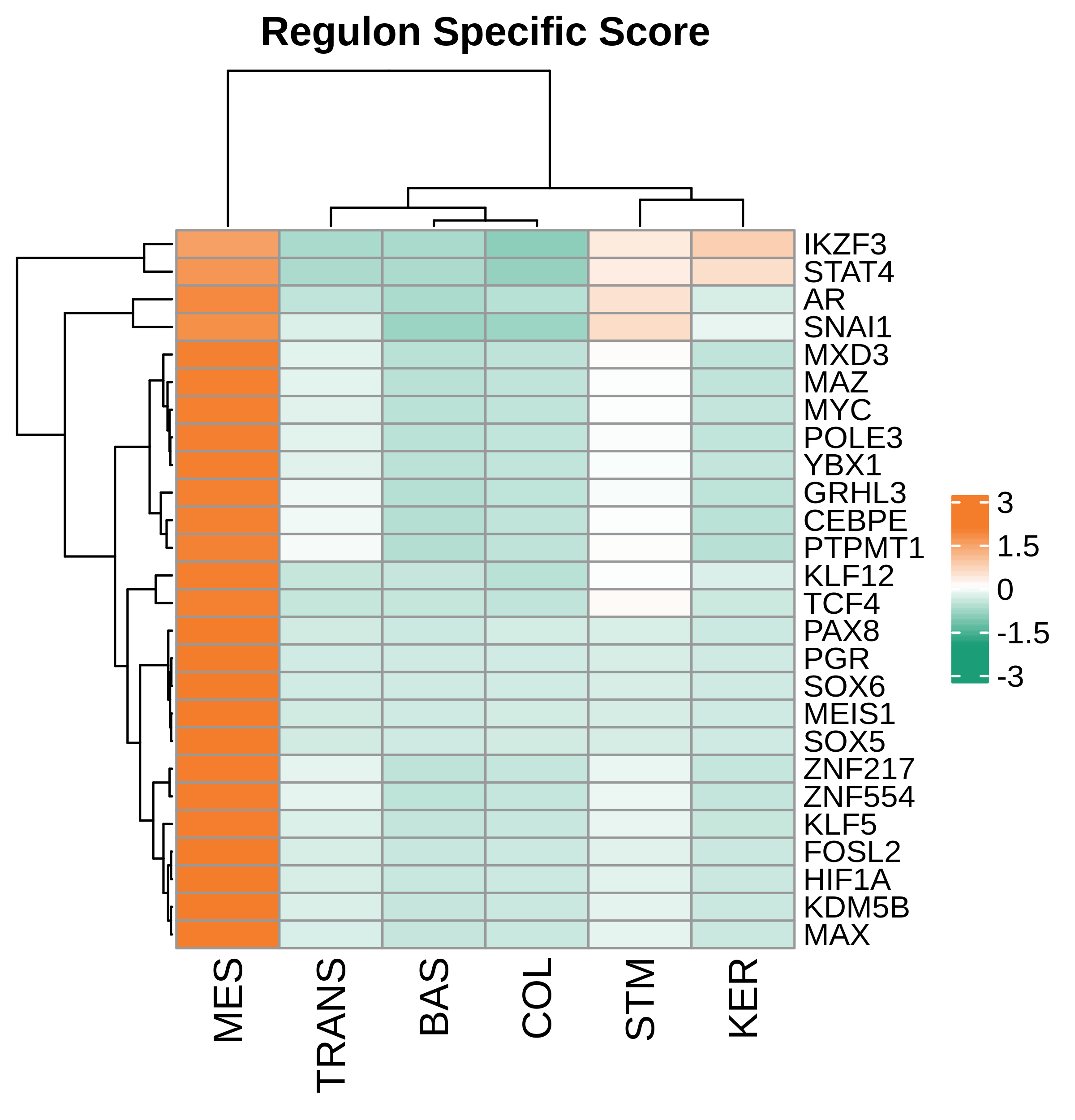 | 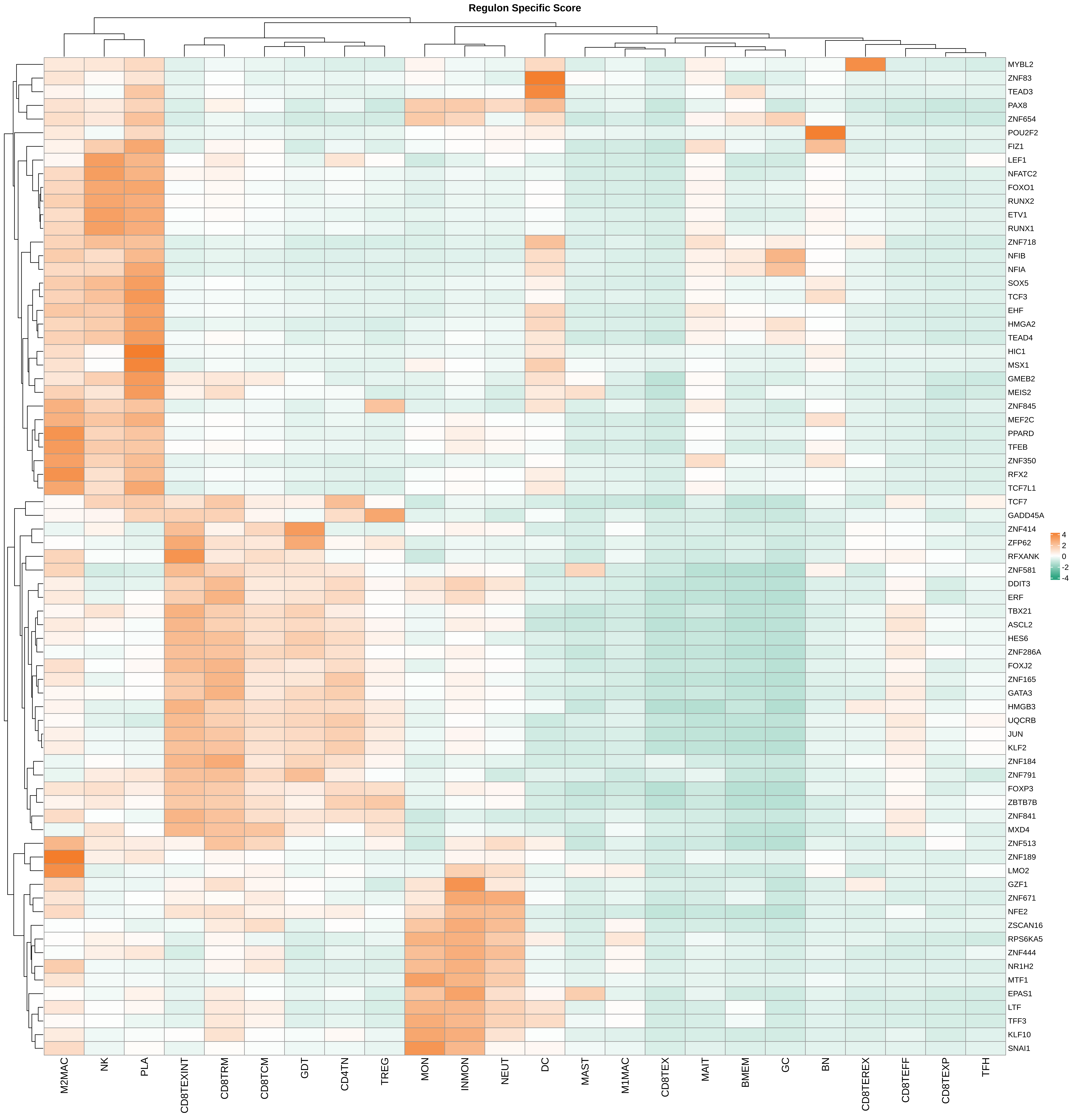 | 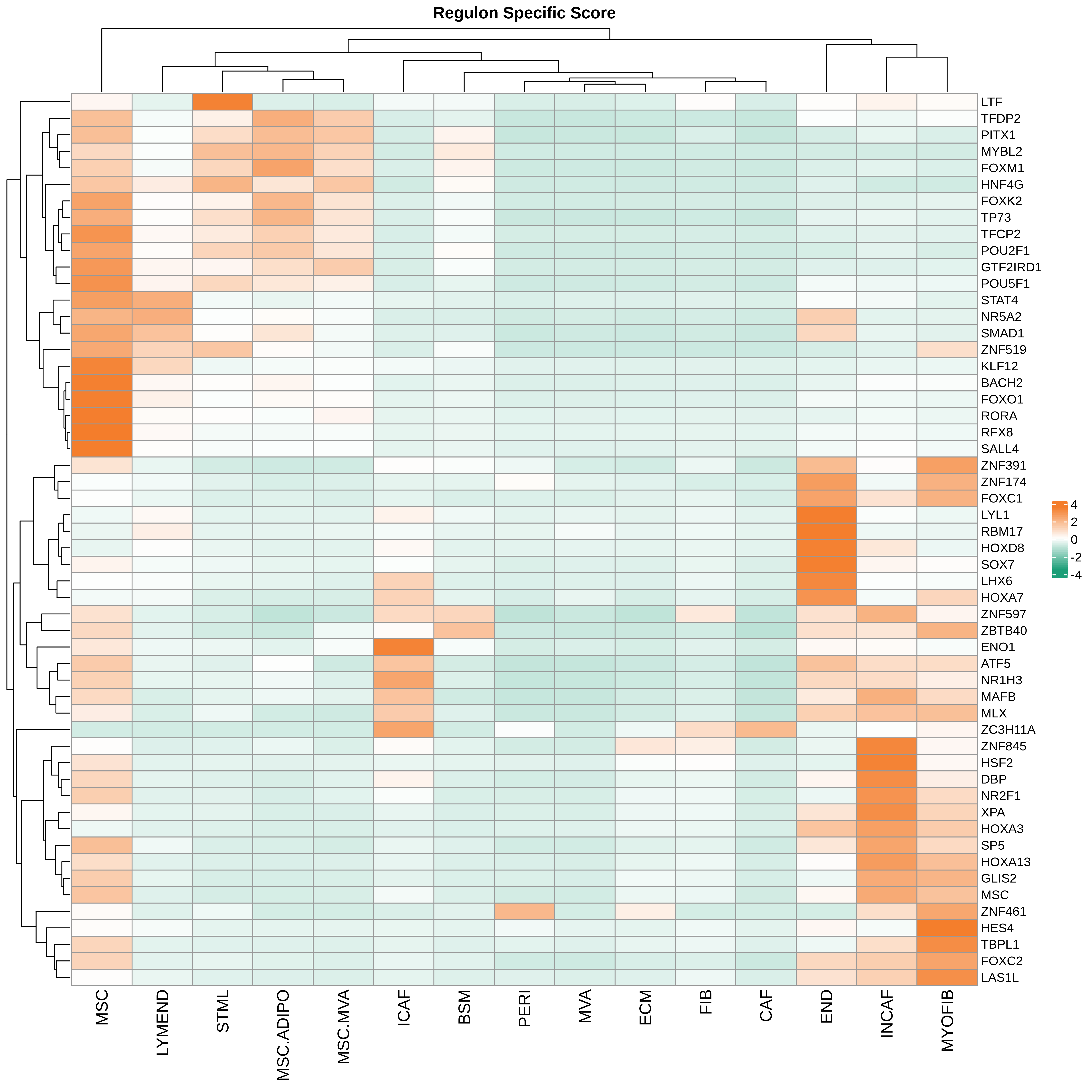 |
| TF target network | TF target network | TF target network |
| ∗Heatmap: Heatmap representation of significantly different TFs among all cell types of epithelial compartment in Healthy-derived samples of Cervix tissue by comparing their average AUC by using pySCENIC in Python. Regulon specific score for each cell type is colored. |
| ∗Network: TF target network created from Healthy-derived samples of Cervix tissue using Top 50 predicted target genes of each regulon. Edge lengths are the inferred TF-target weightings. |
Top |
Cell-cell interaction analysis |
| Disease State | Cell Type | Circle | Source | Target |
| Healthy | BAS | 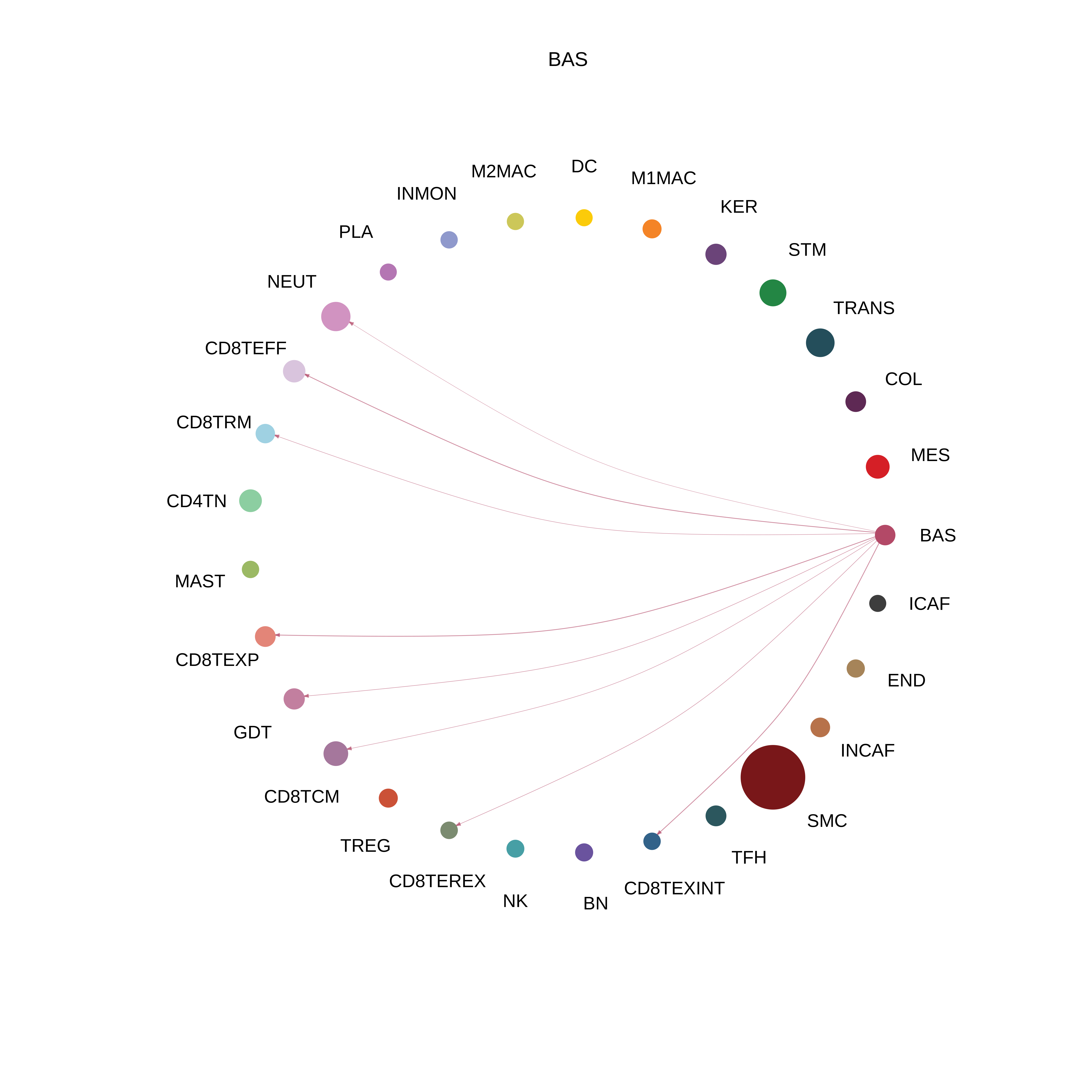 | 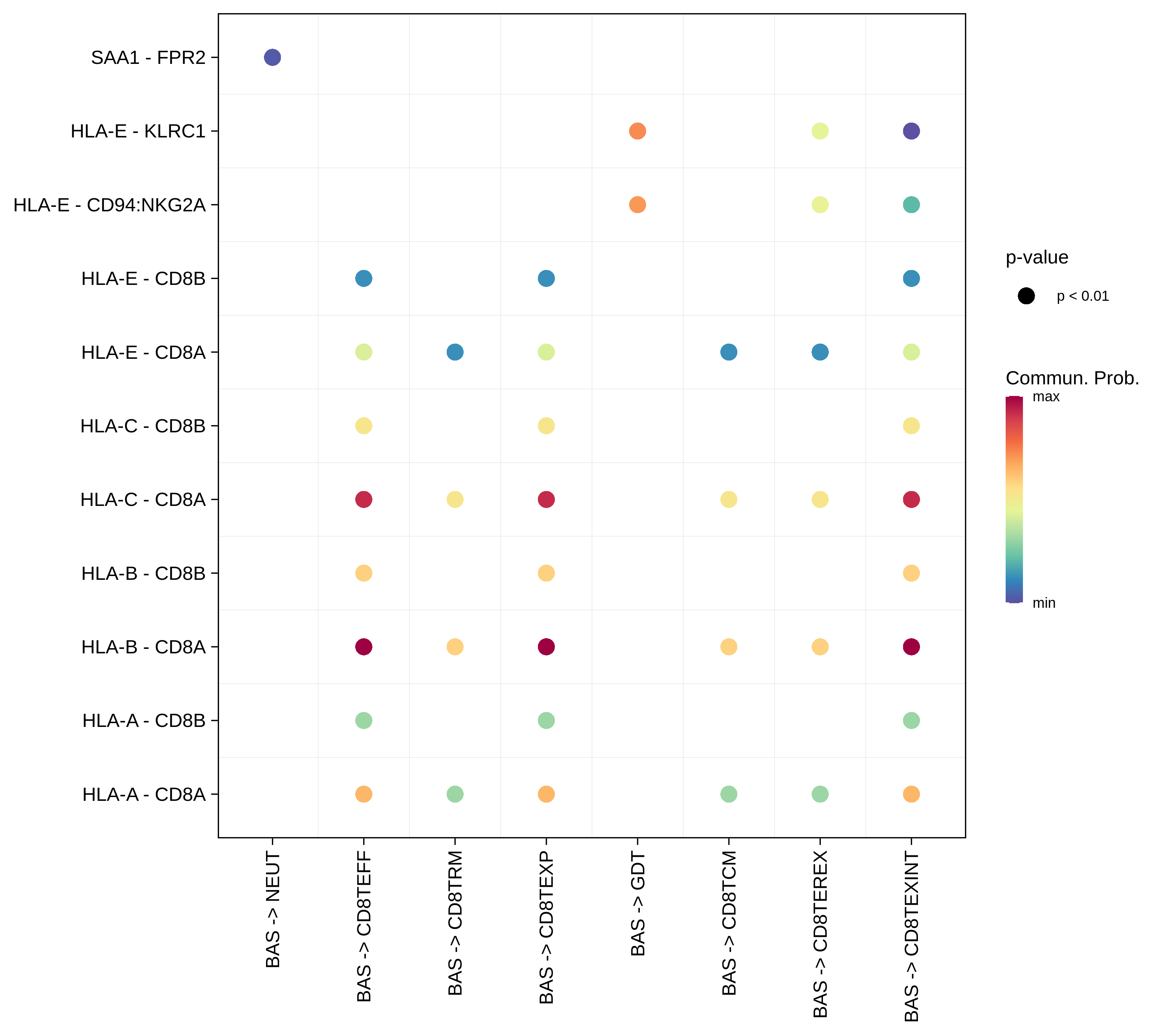 | 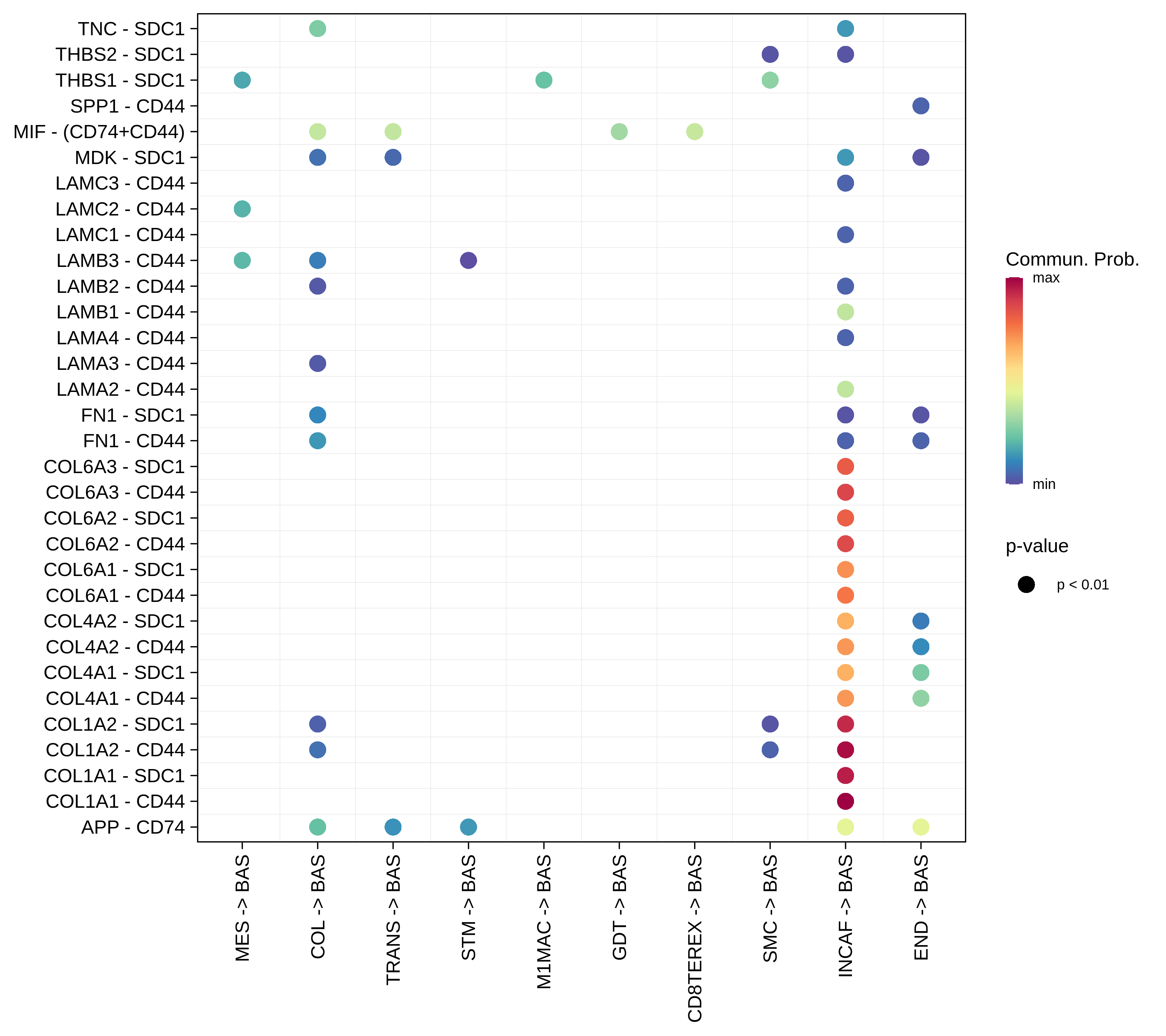 |
| BN | 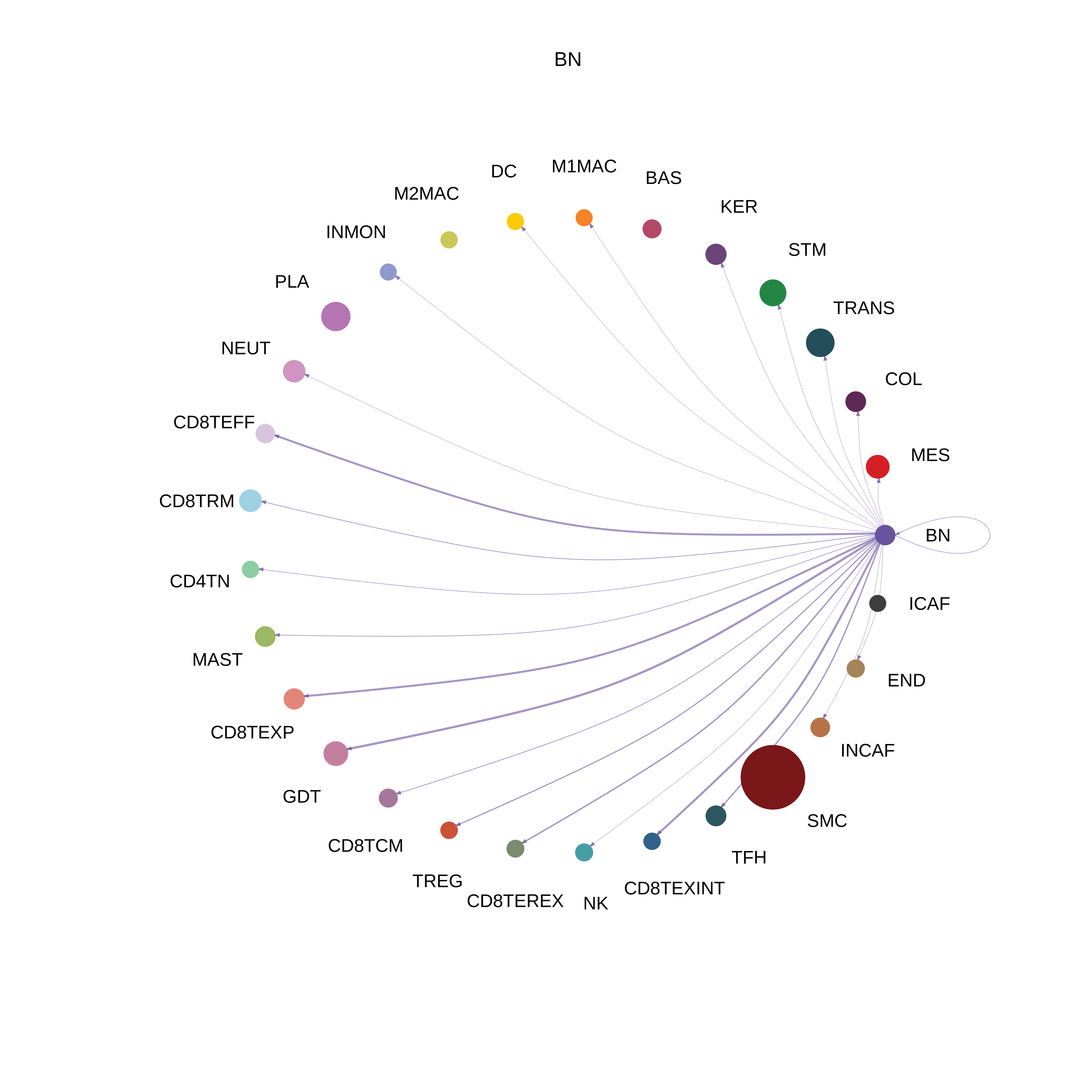 | 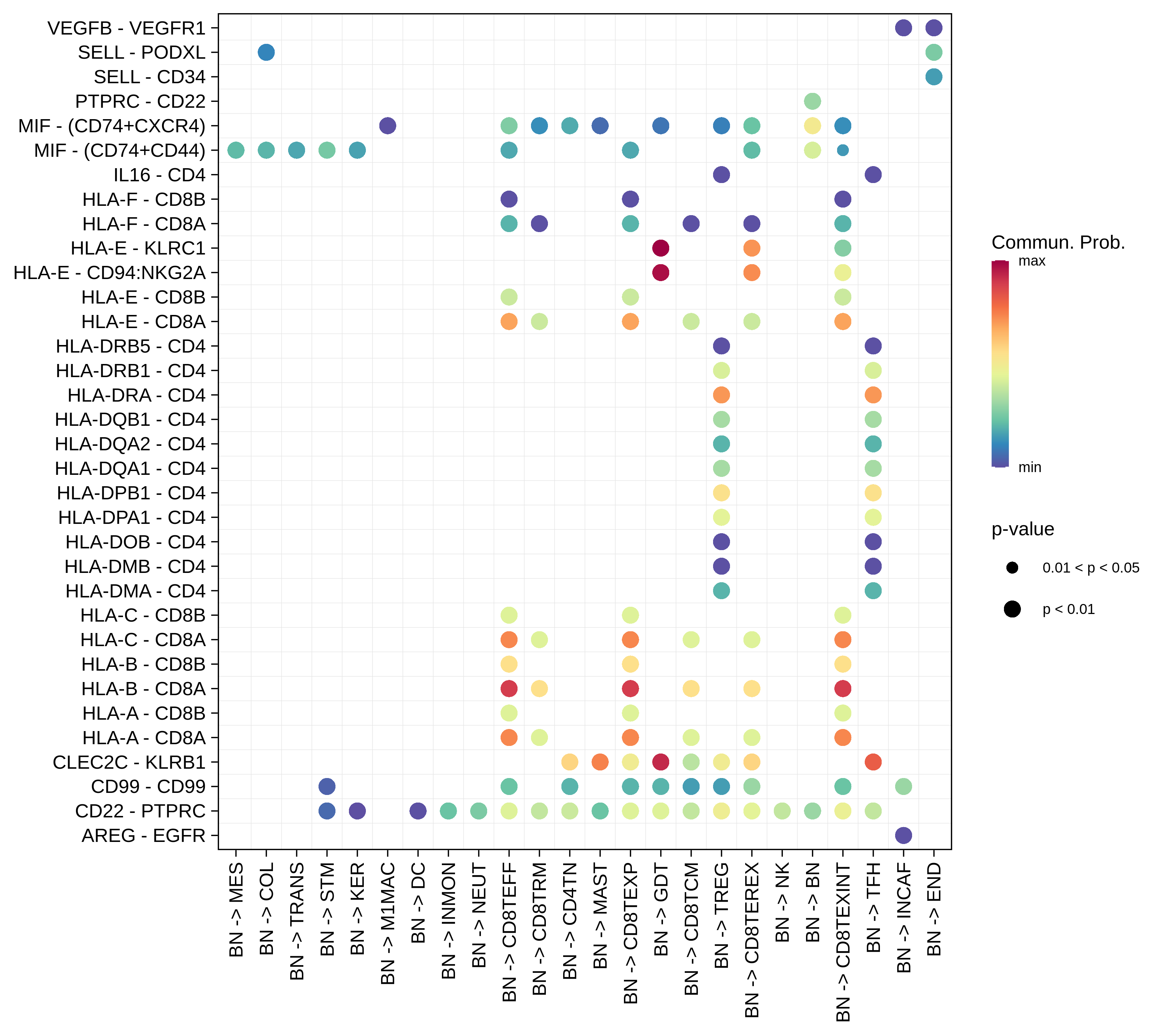 | 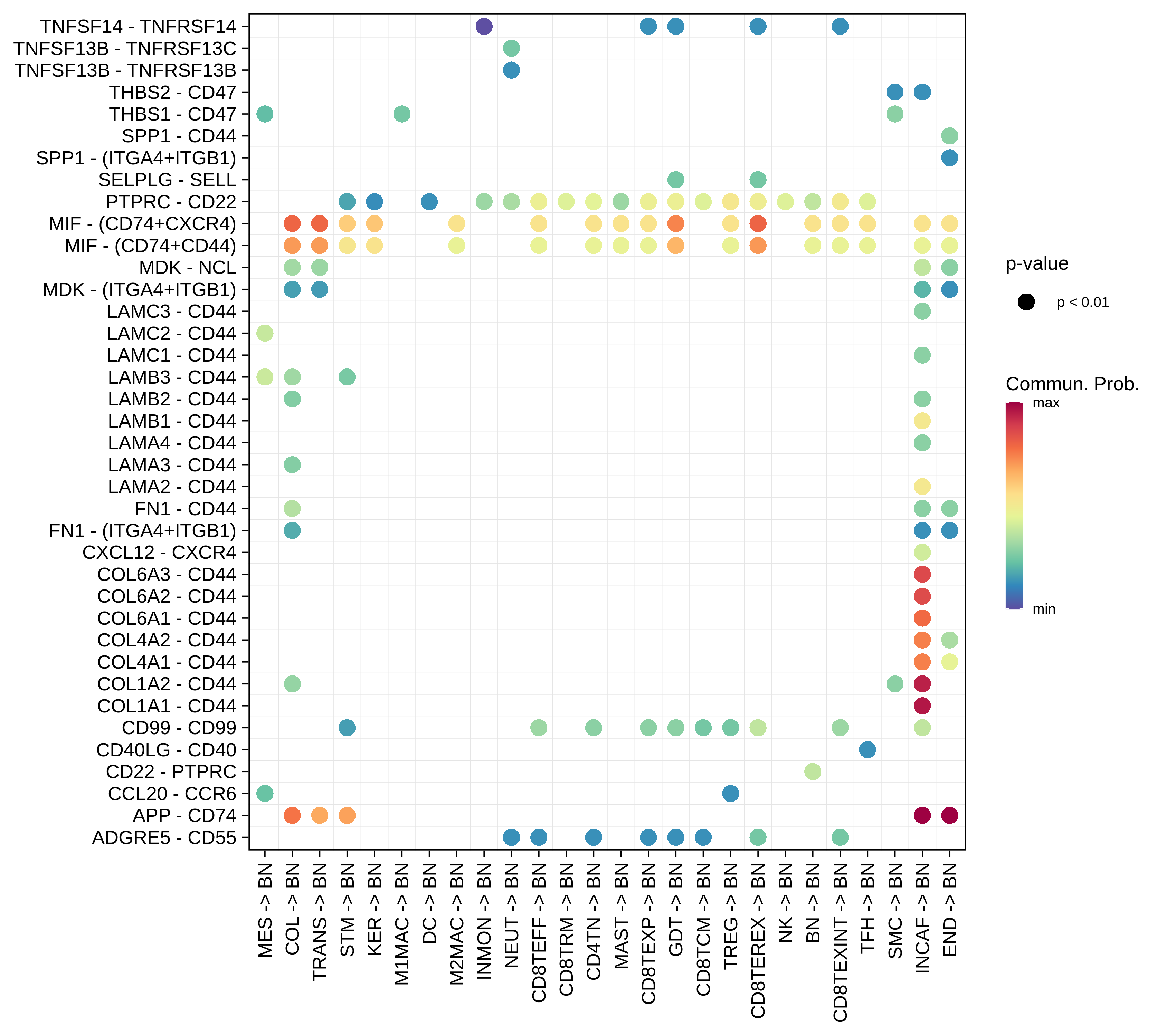 |
| Page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
| Disease State | Cell Type | Circle | Source | Target |
| ADJ | BAS | 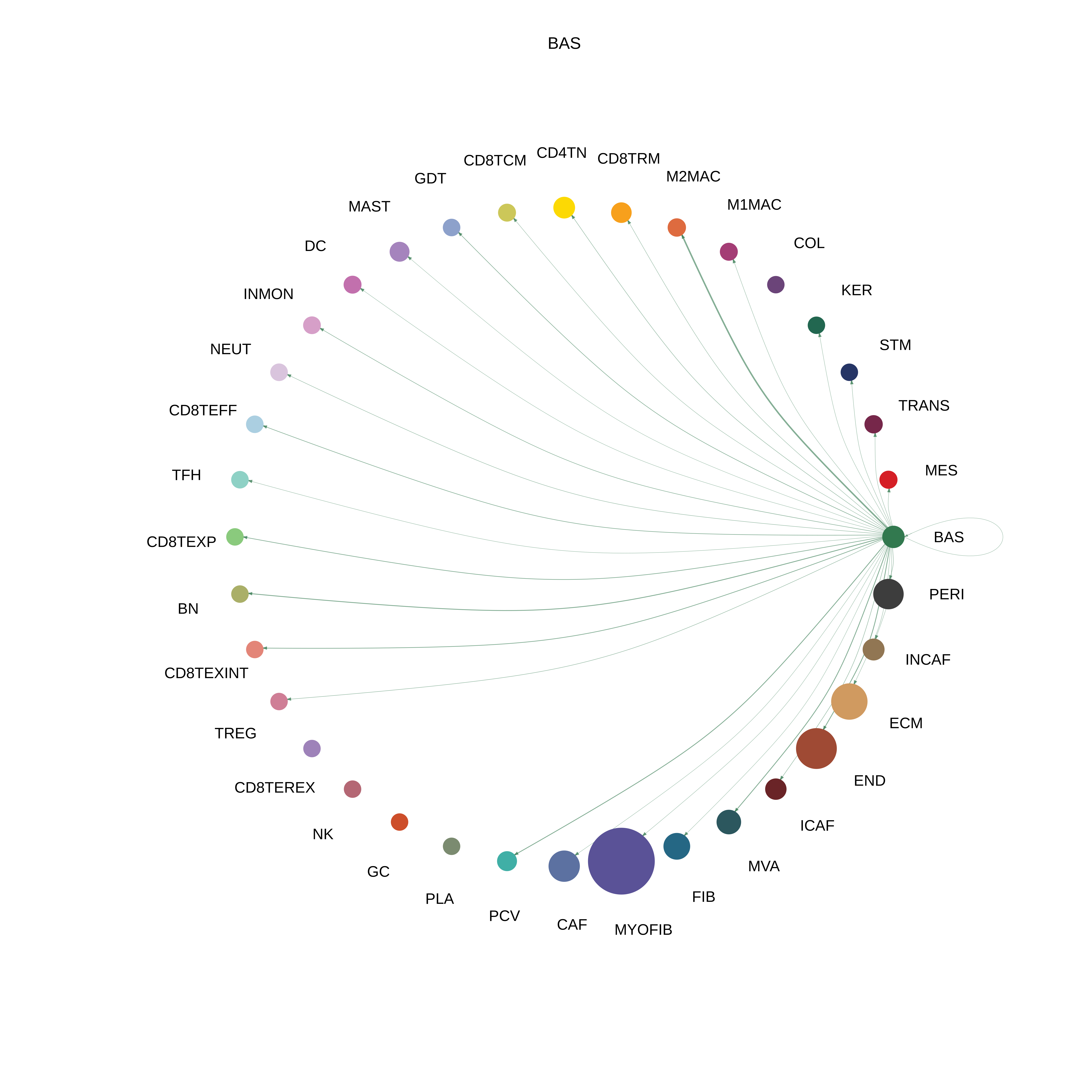 | 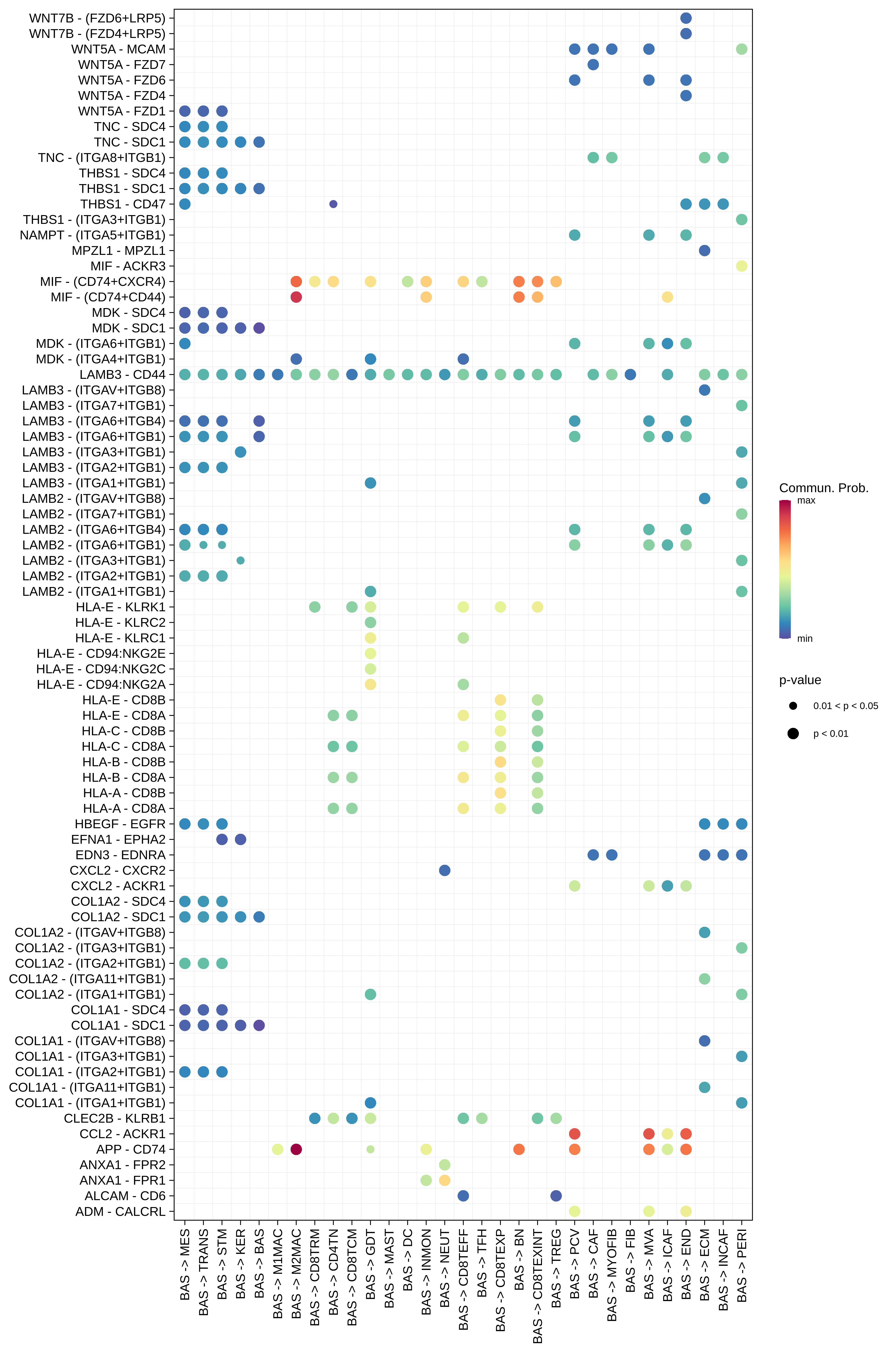 | 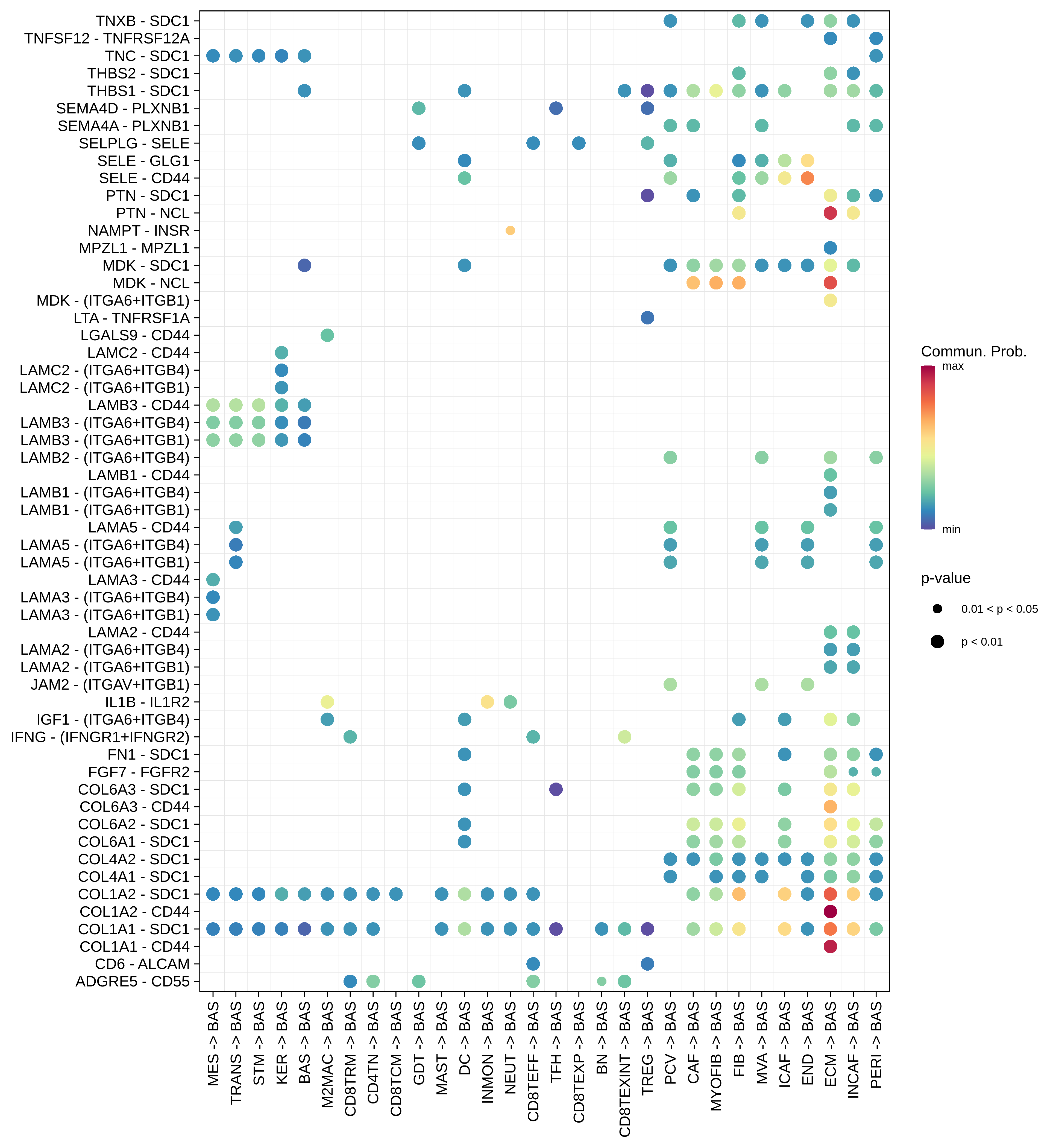 |
| BN | 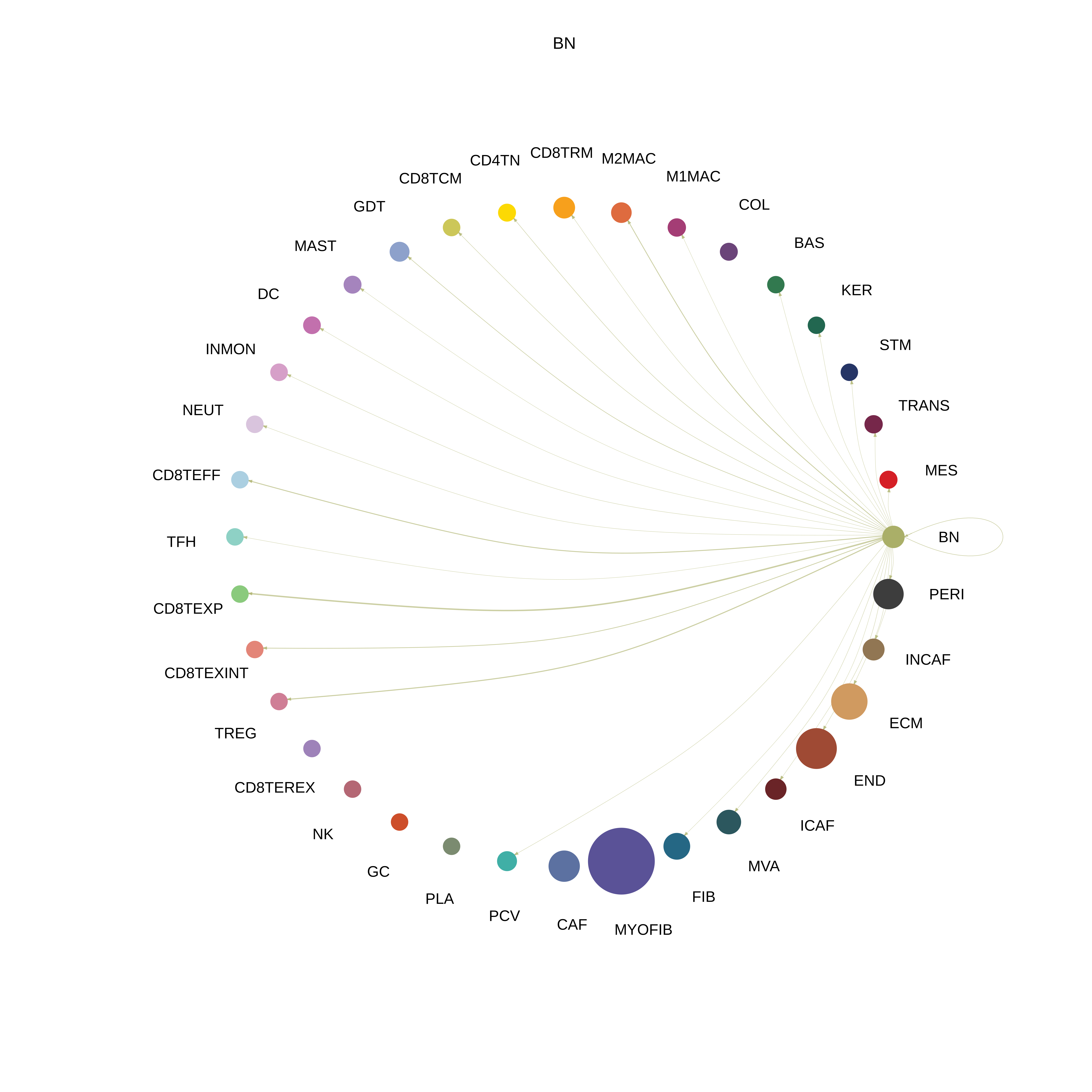 | 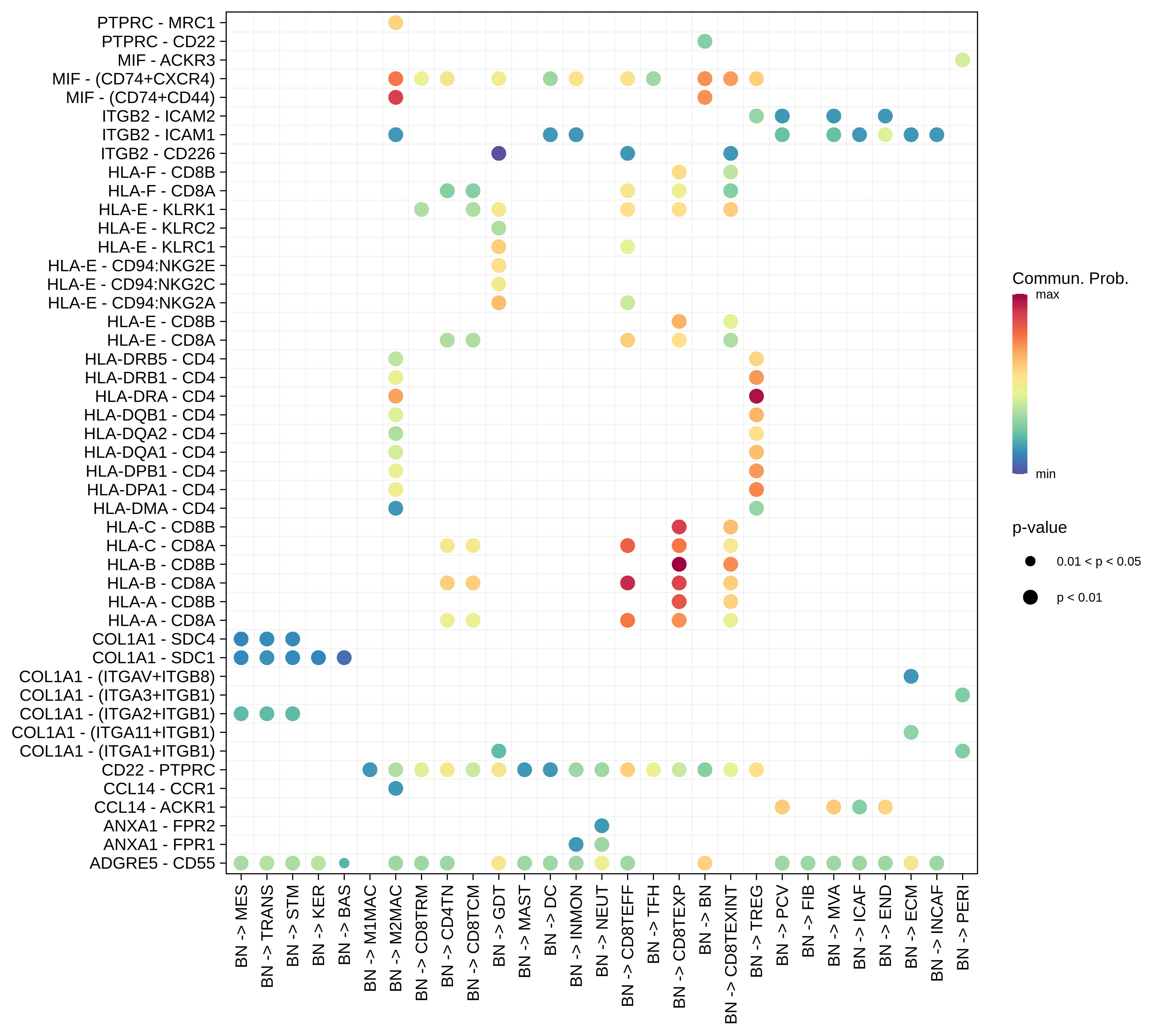 | 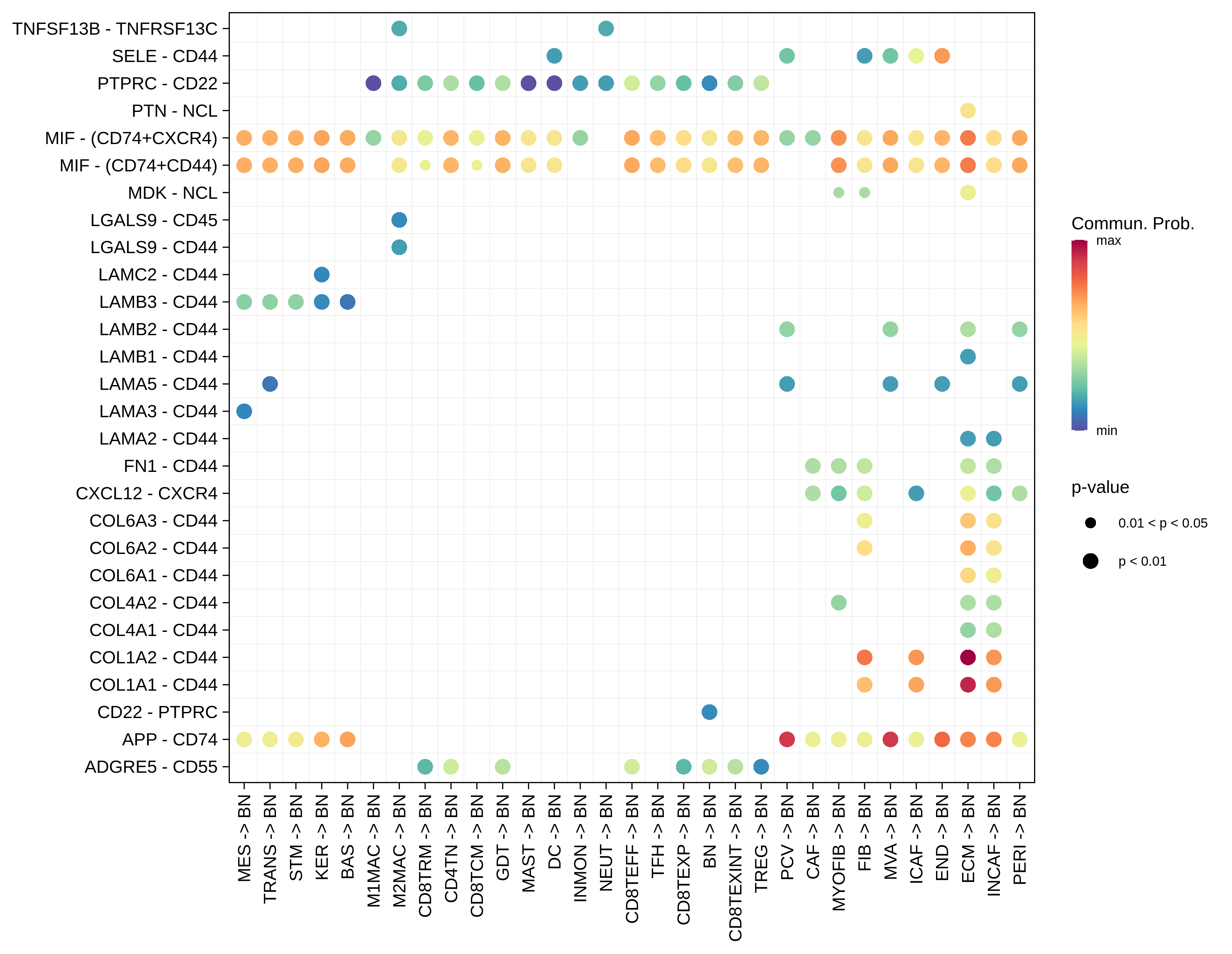 |
| Page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
| Disease State | Cell Type | Circle | Source | Target |
| Precancer | BAS | 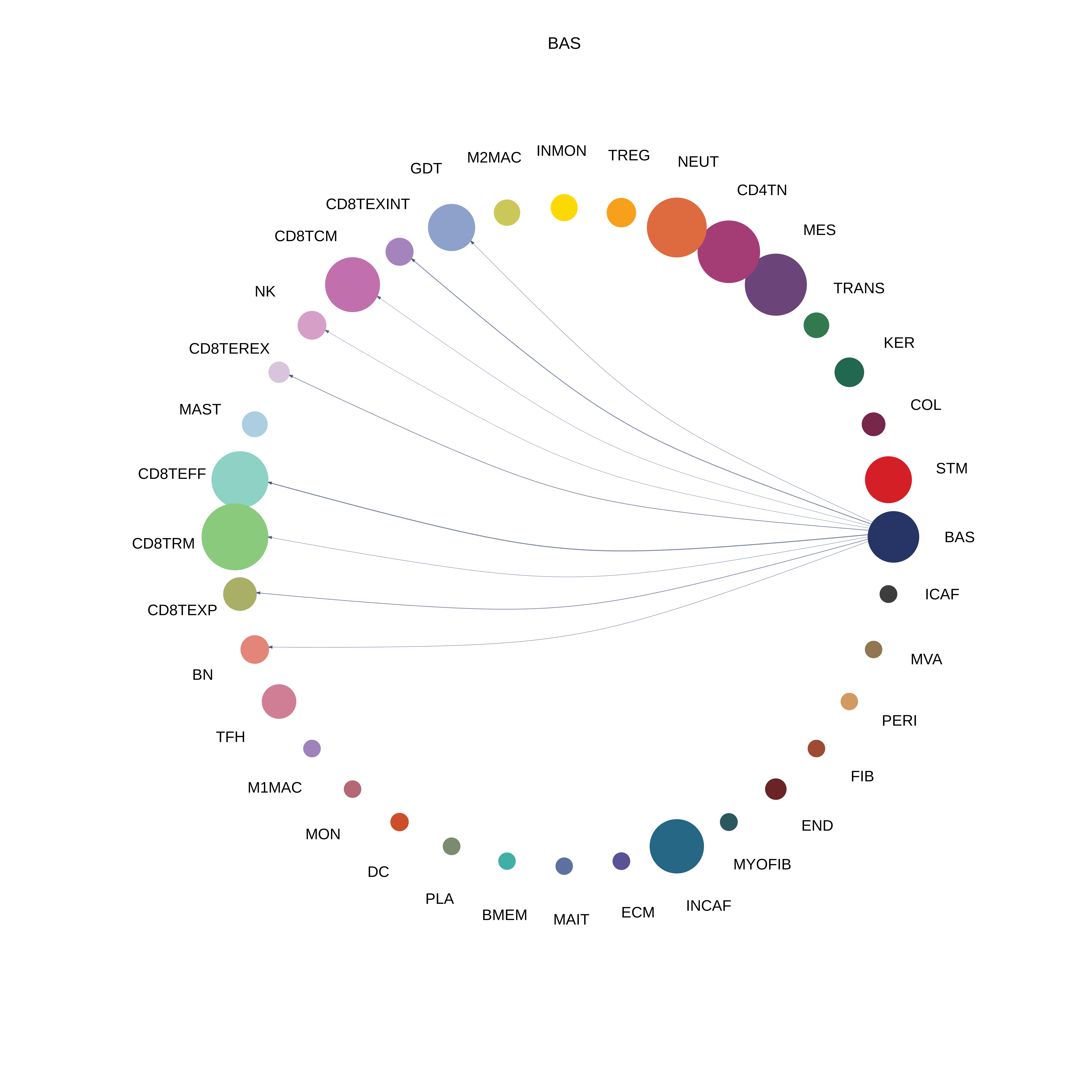 | 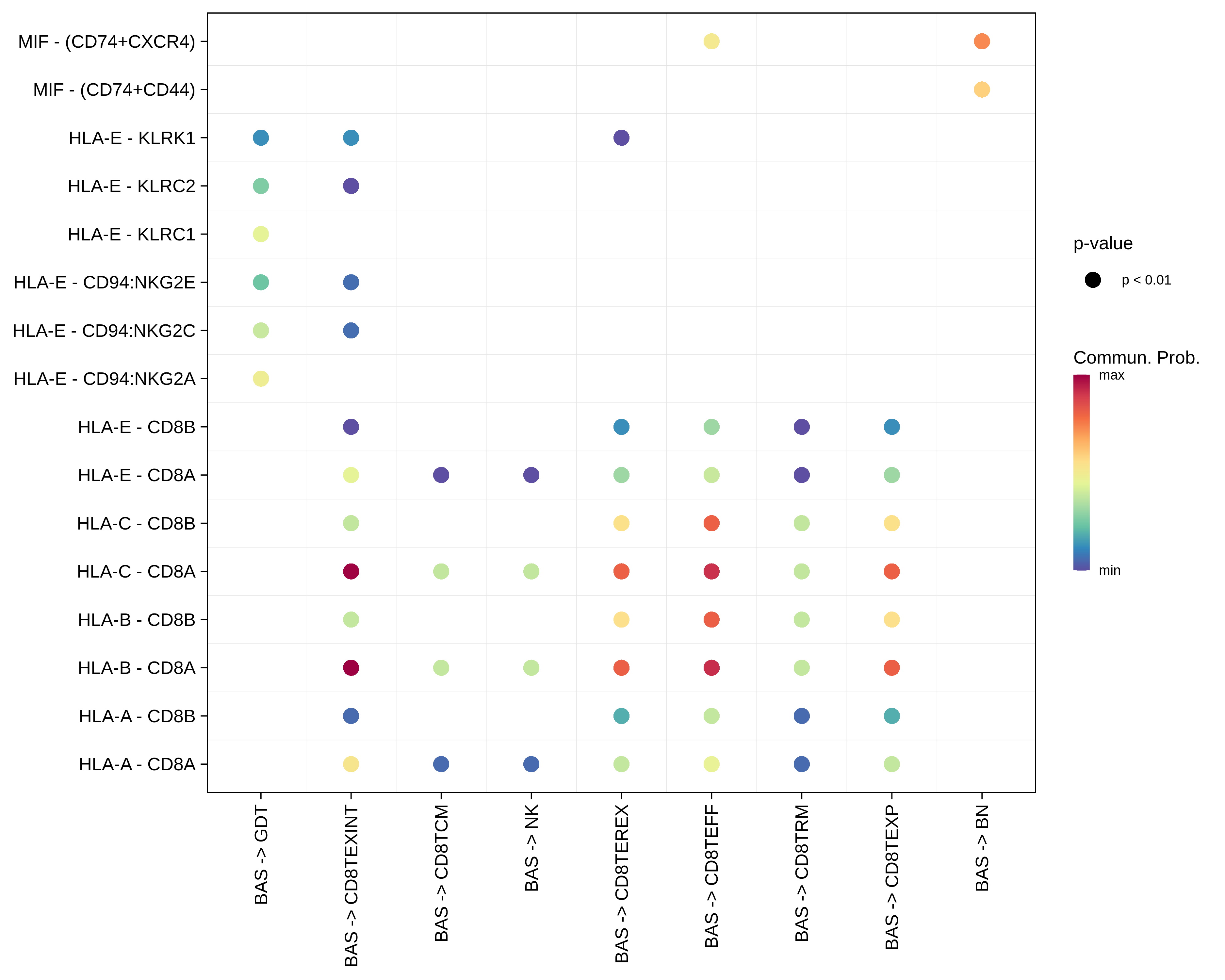 | 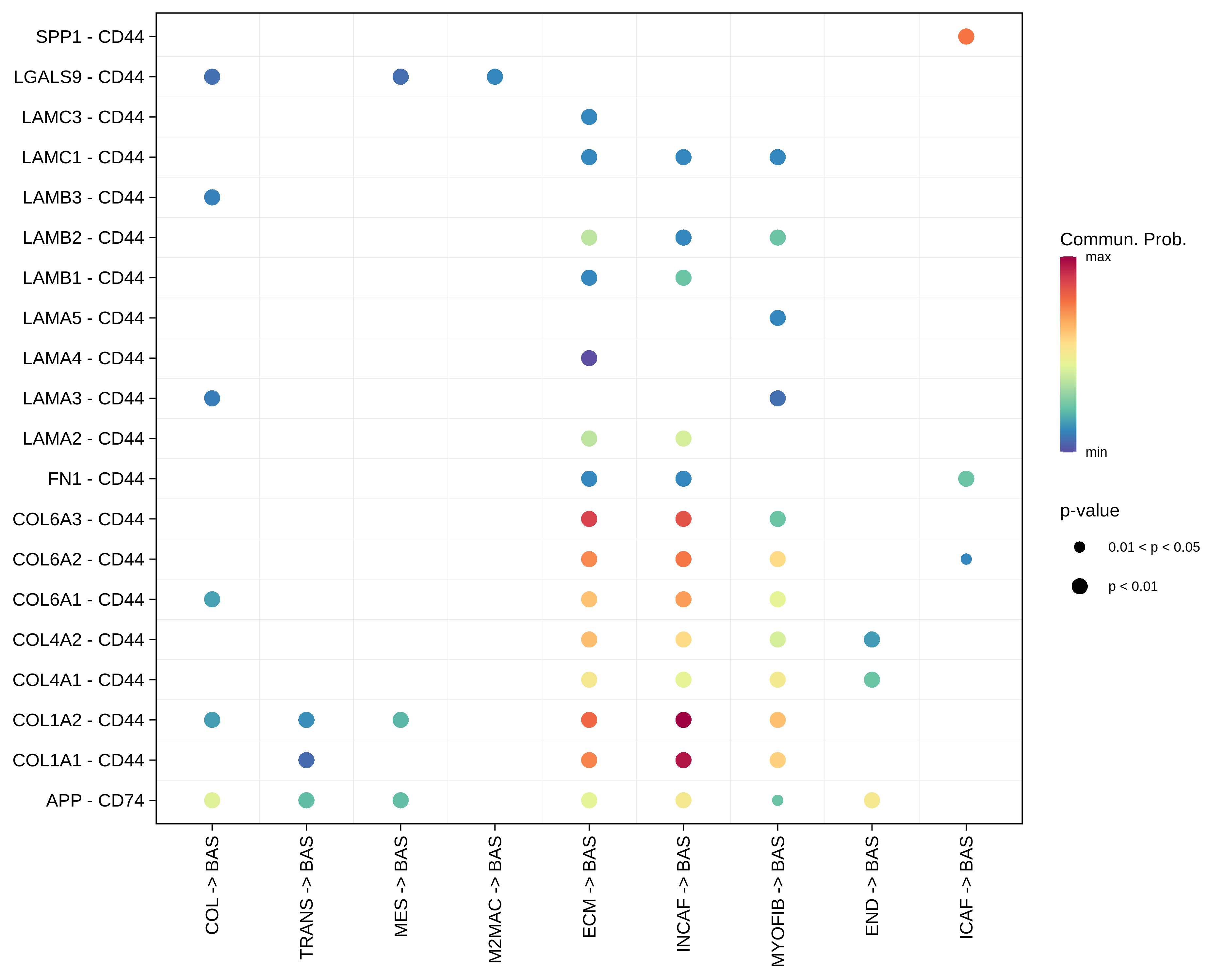 |
| BN | 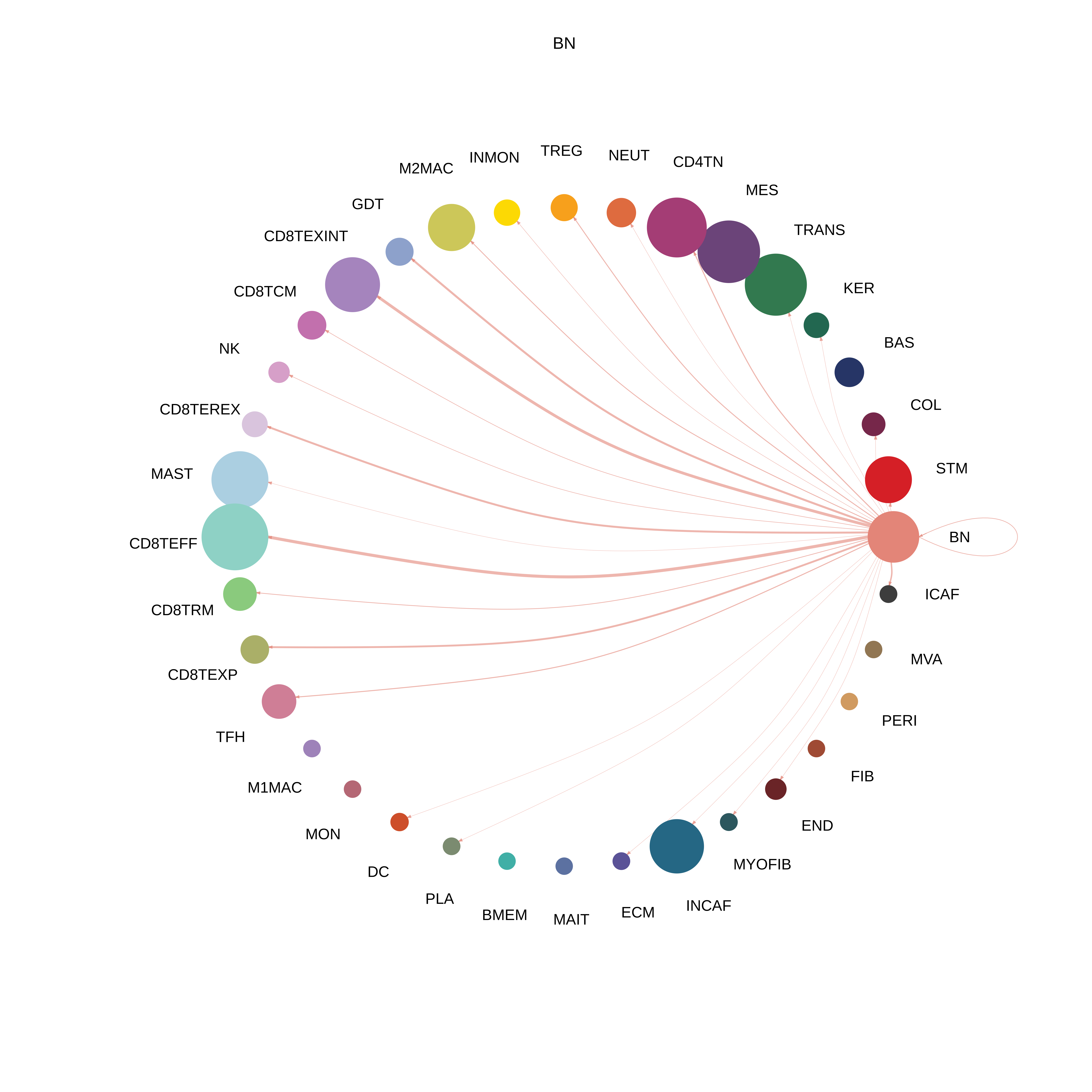 | 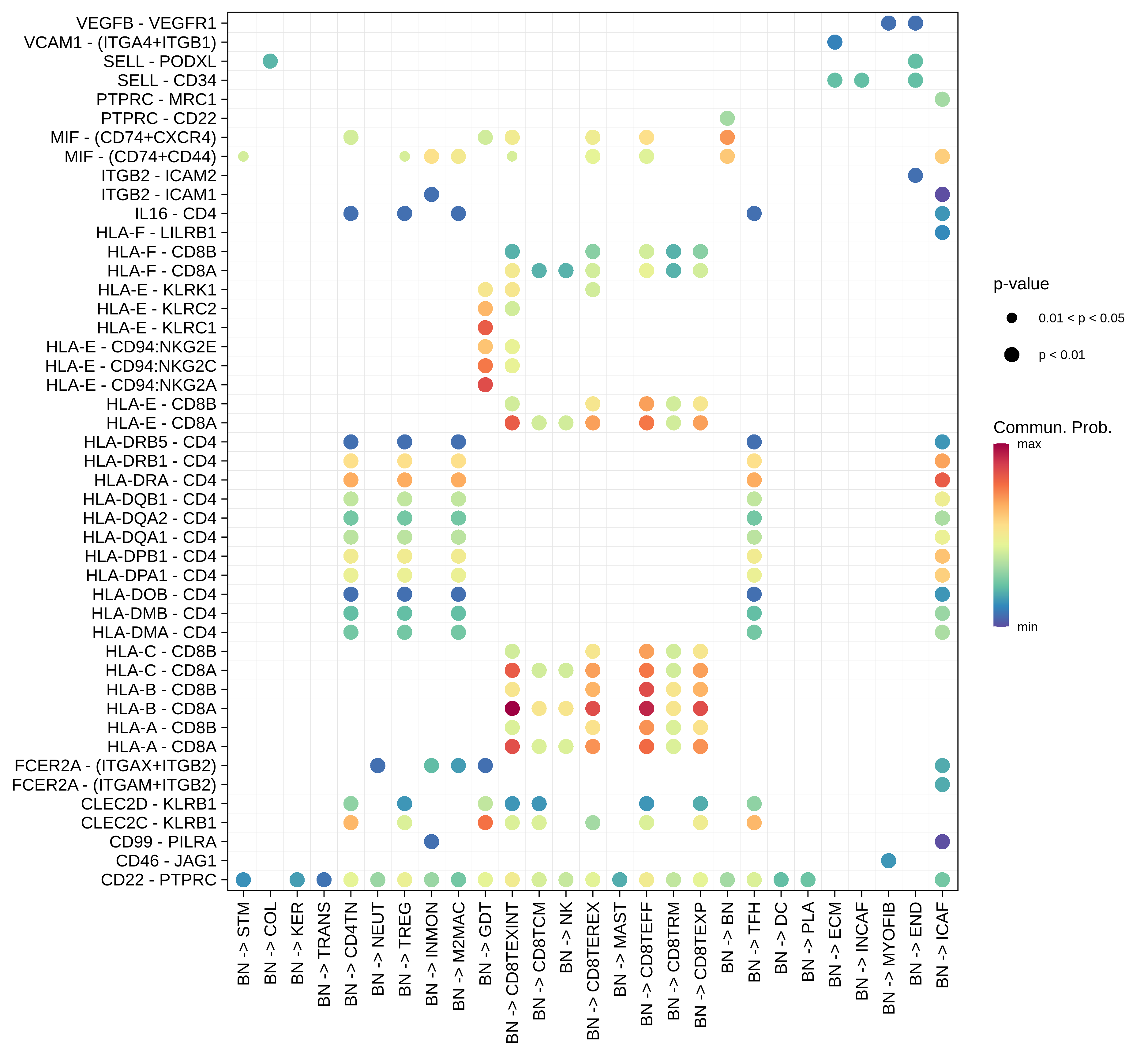 | 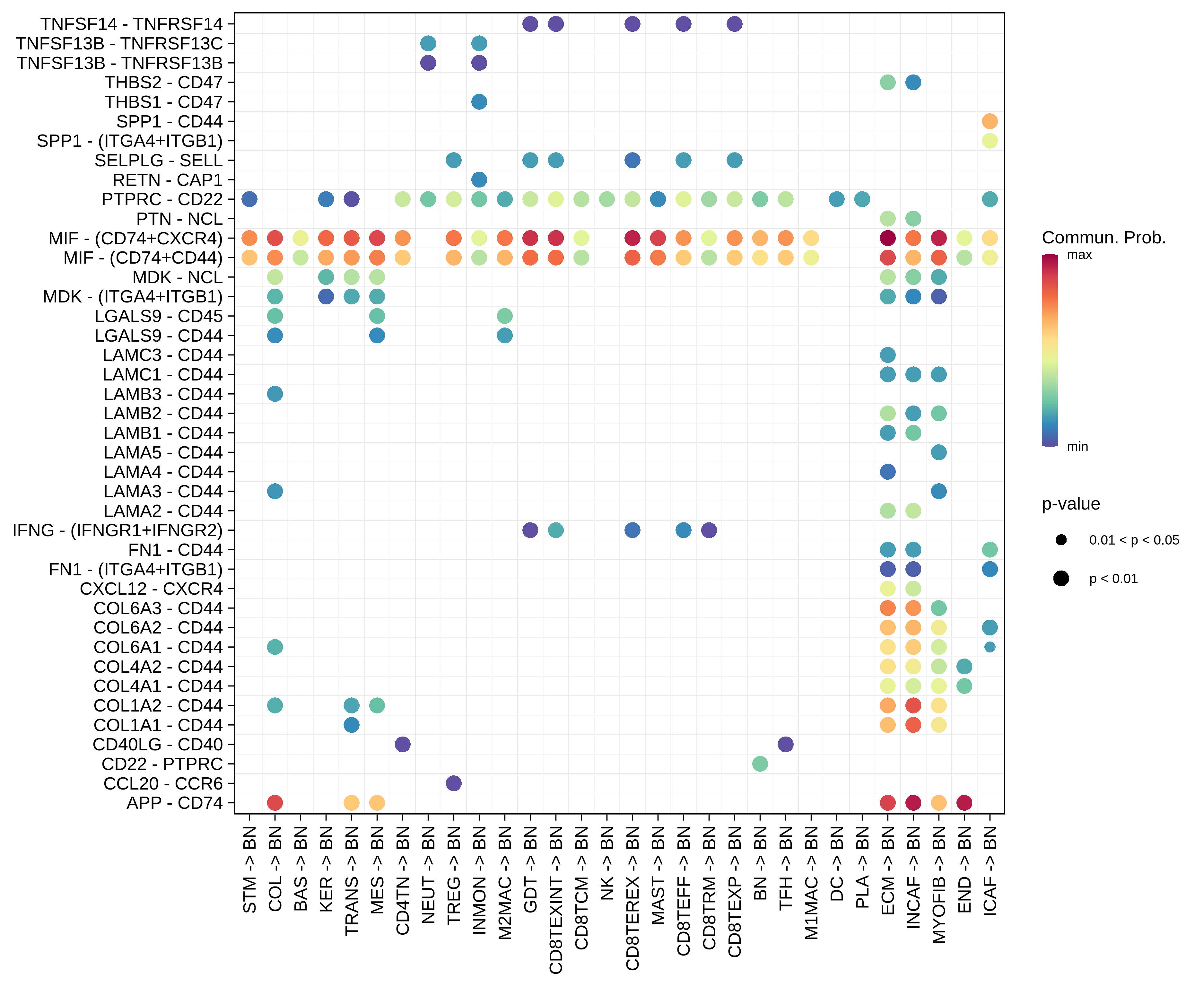 |
| Page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
| Disease State | Cell Type | Circle | Source | Target |
| CC | BAS | 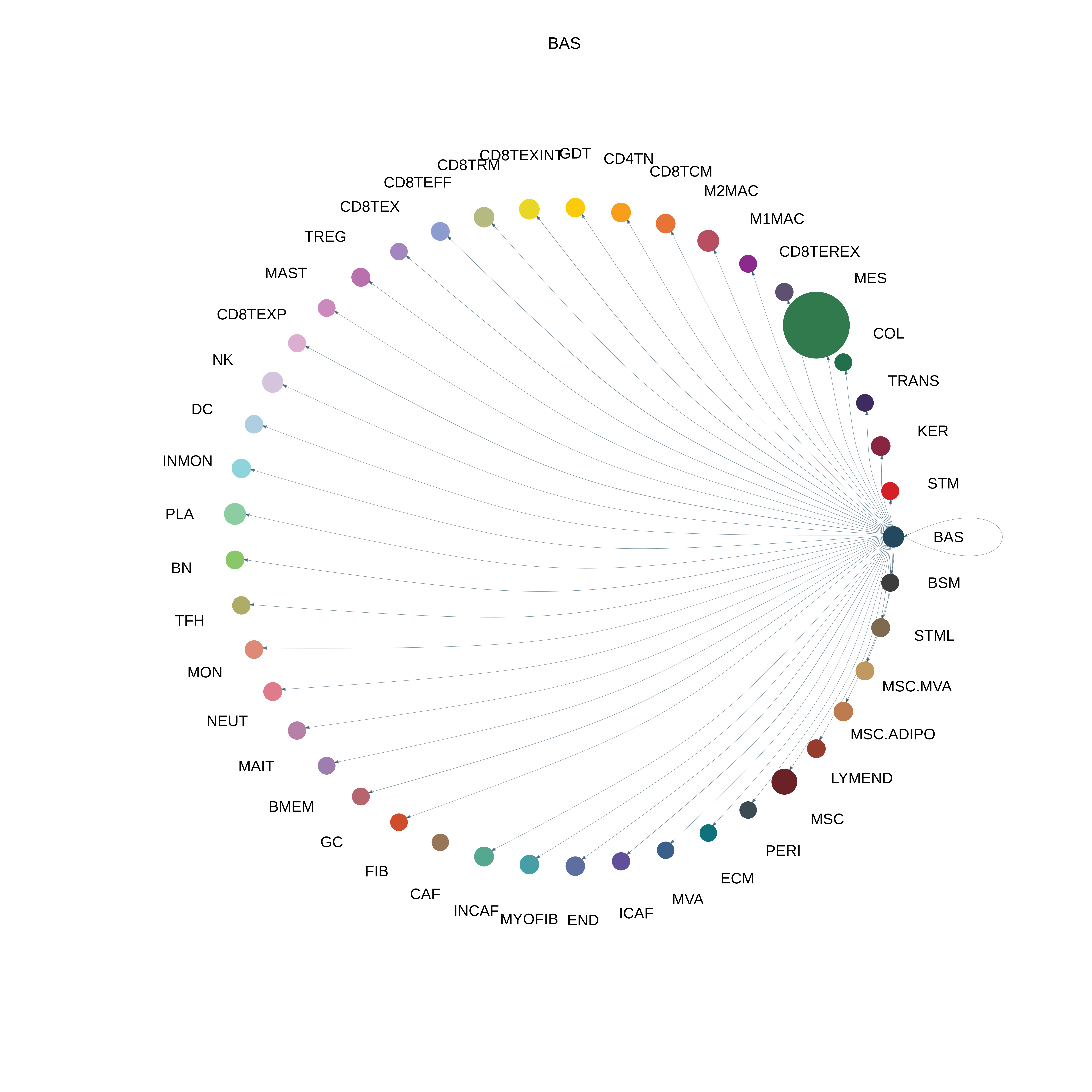 | 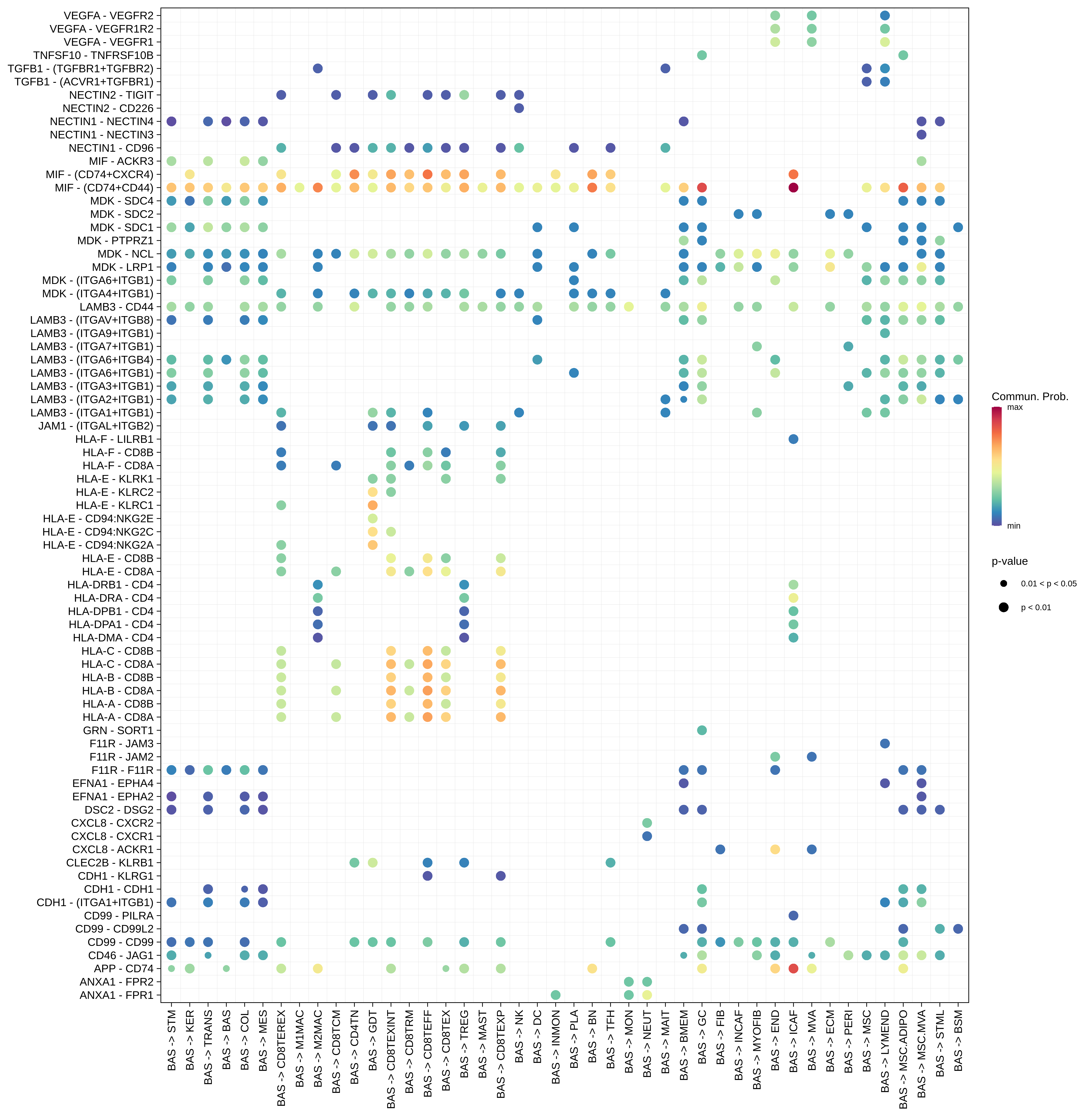 | 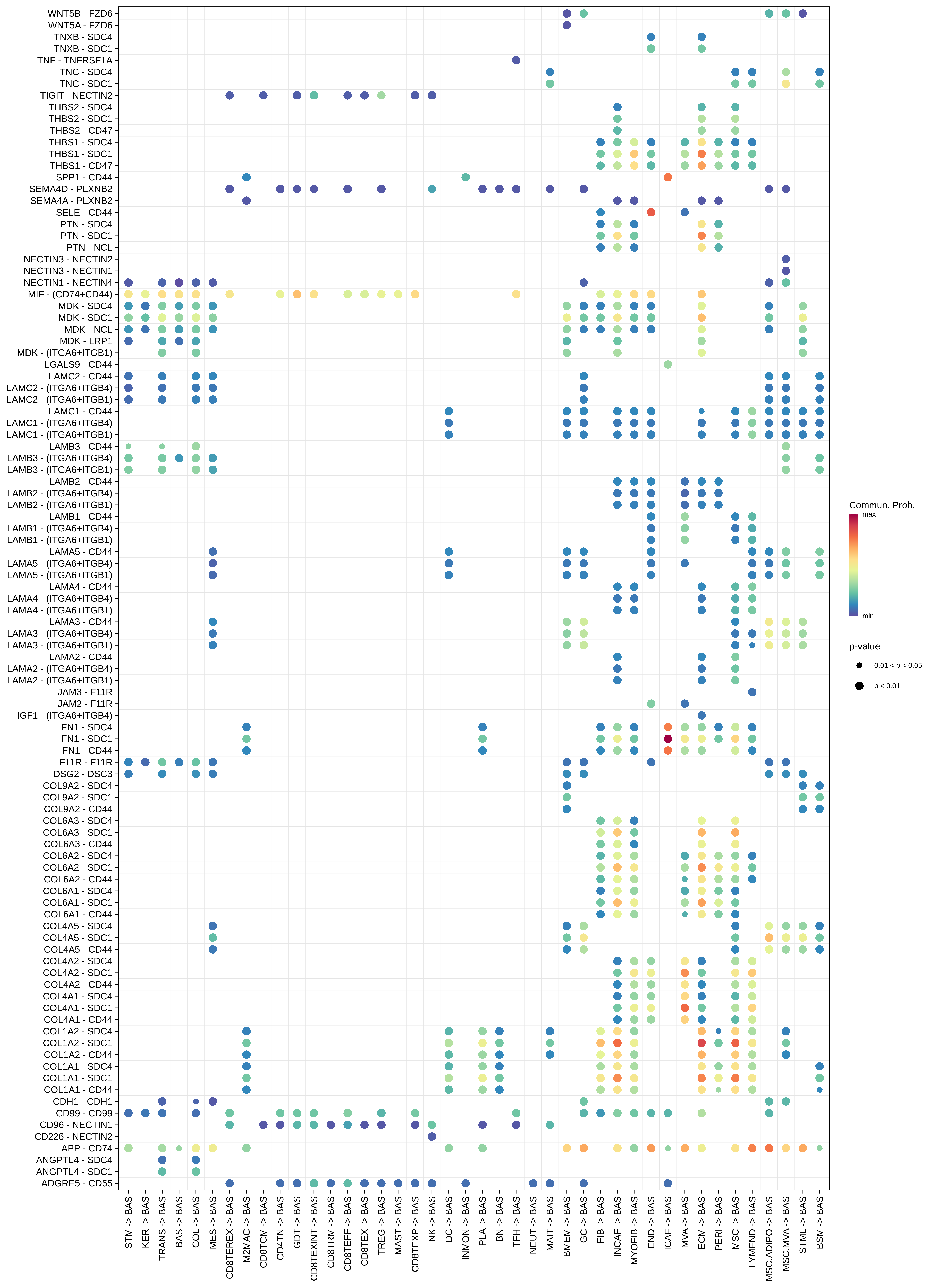 |
| BMEM | 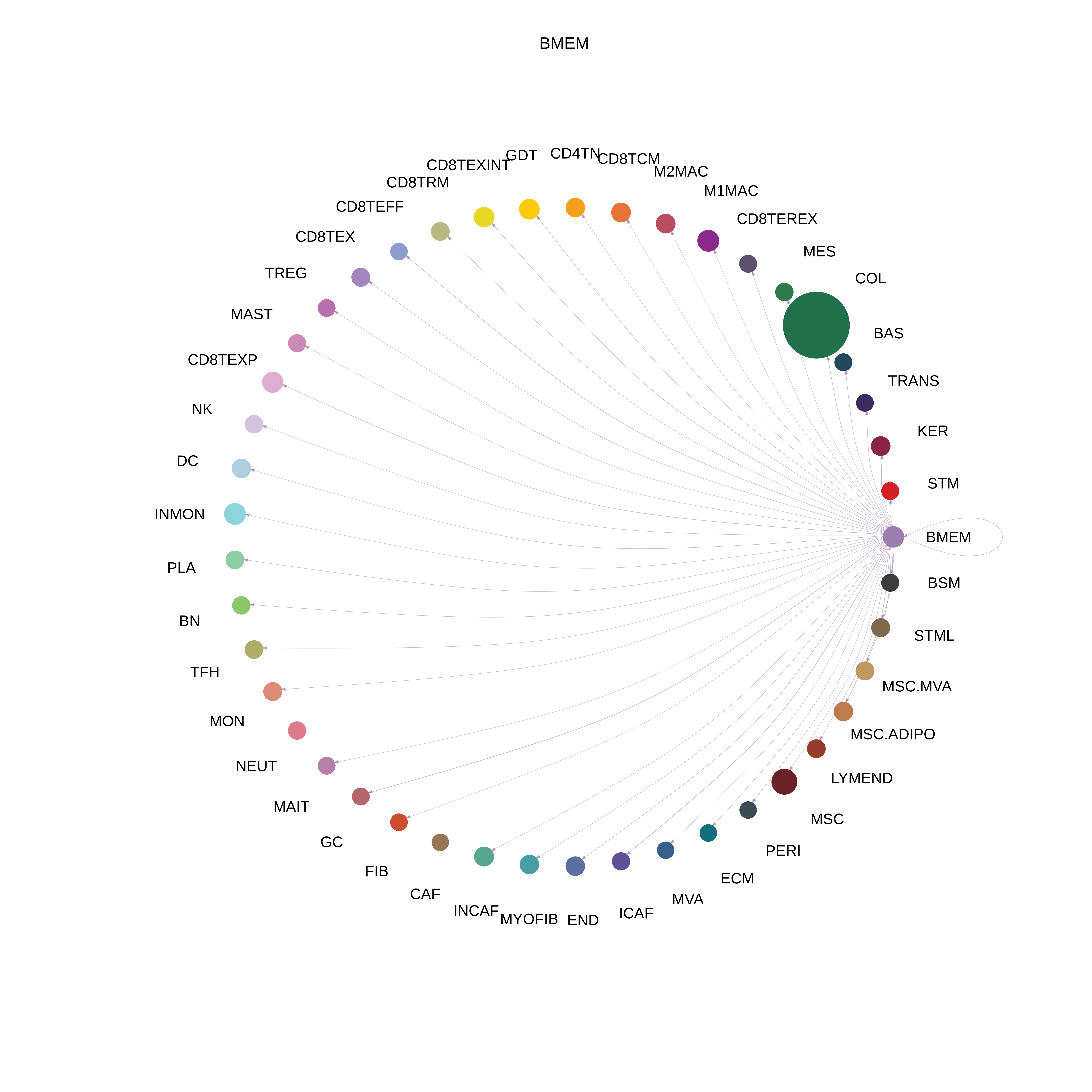 | 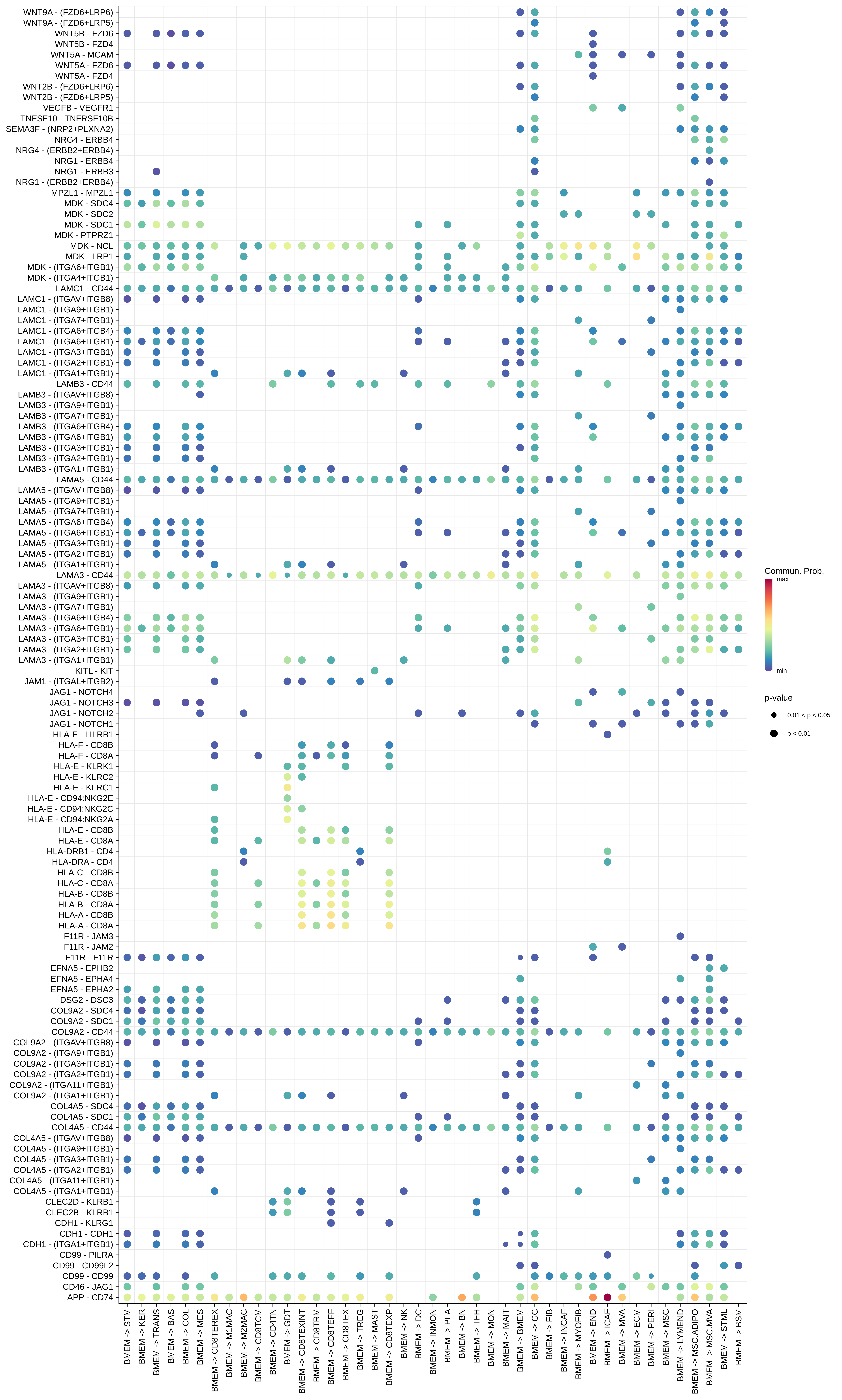 | 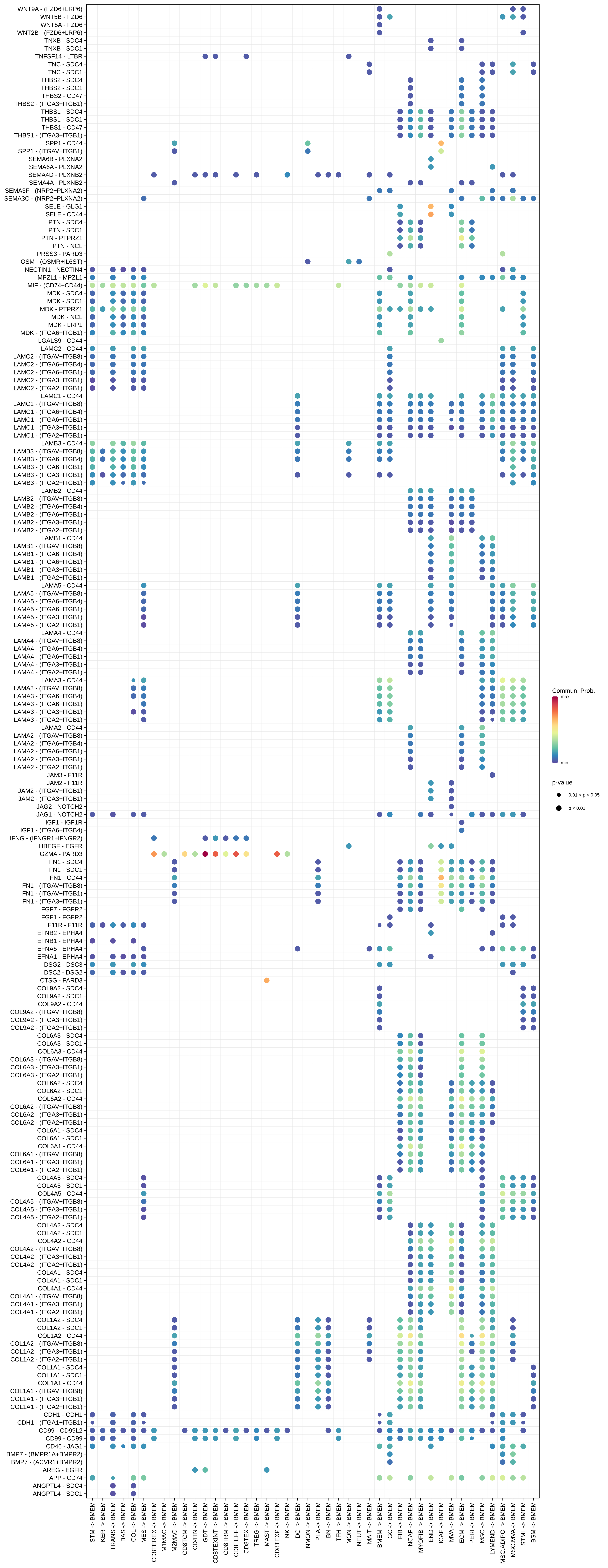 |
| ∗The cell-cell communications between each two interacting cell types in different states-derived samples of Cervix tissue. Different colors in the circle plot represent different cell groups and the edge width is proportional to the indicated number of ligand-receptor pairs. |
| ∗Bubble plot of proportion to the communication probability in significant signaling pathways between this cell type and its source and target cell population. Each row represents the significant ligand and receptor gene pairs. |
| Page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
Top |
Stemness, Senescence, Metaplasia and NeoTCR signature analysis |
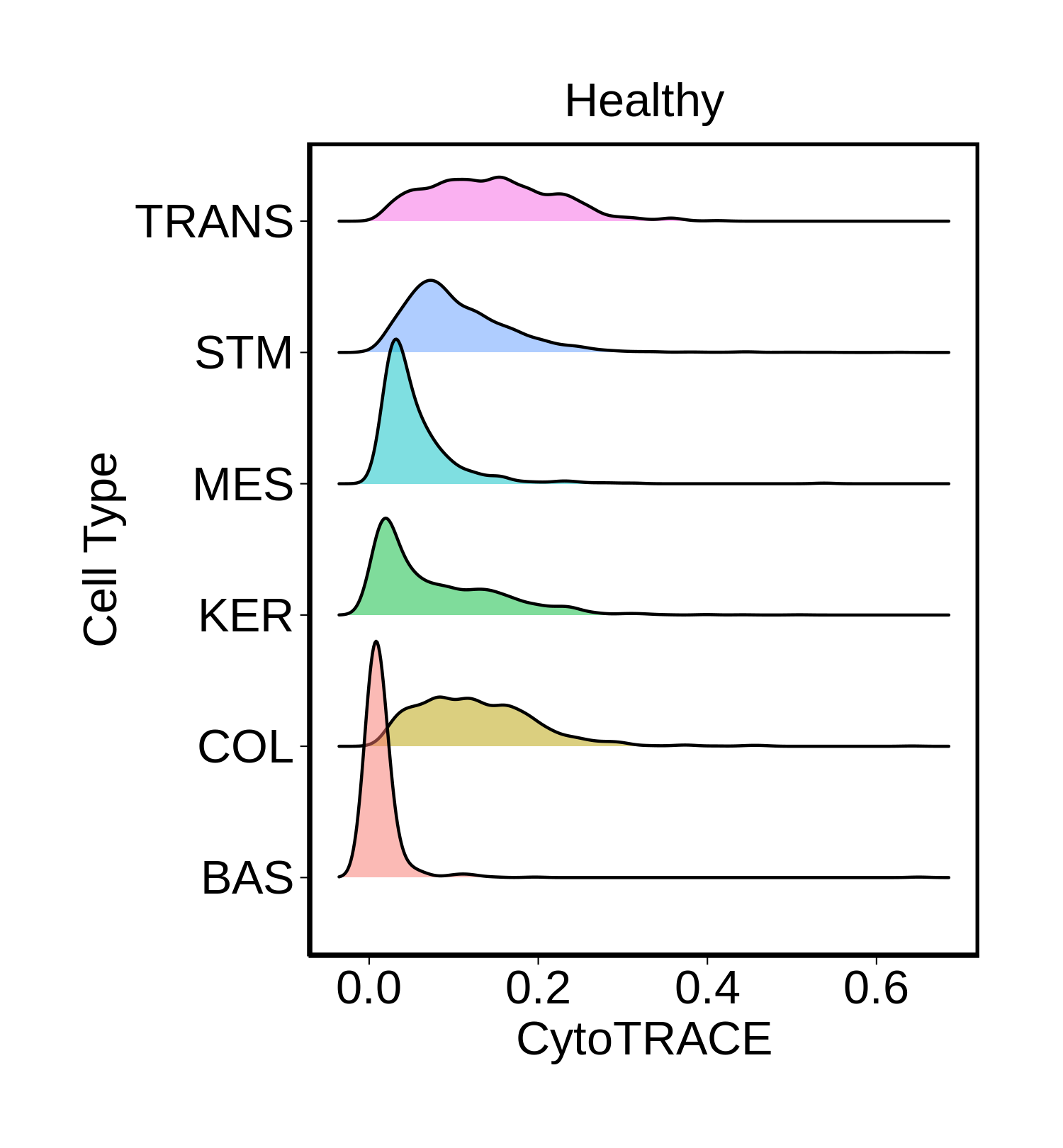 | 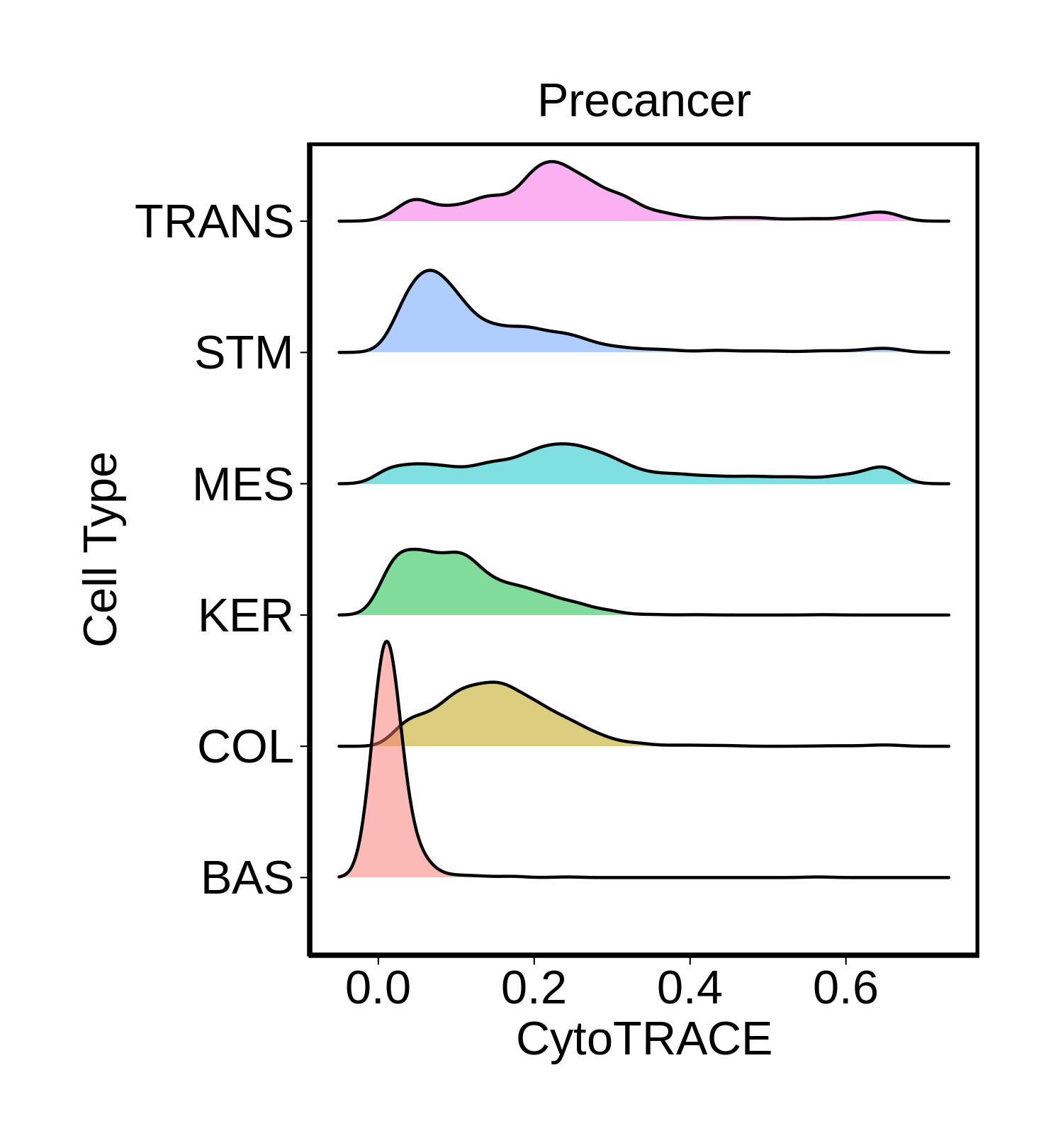 | 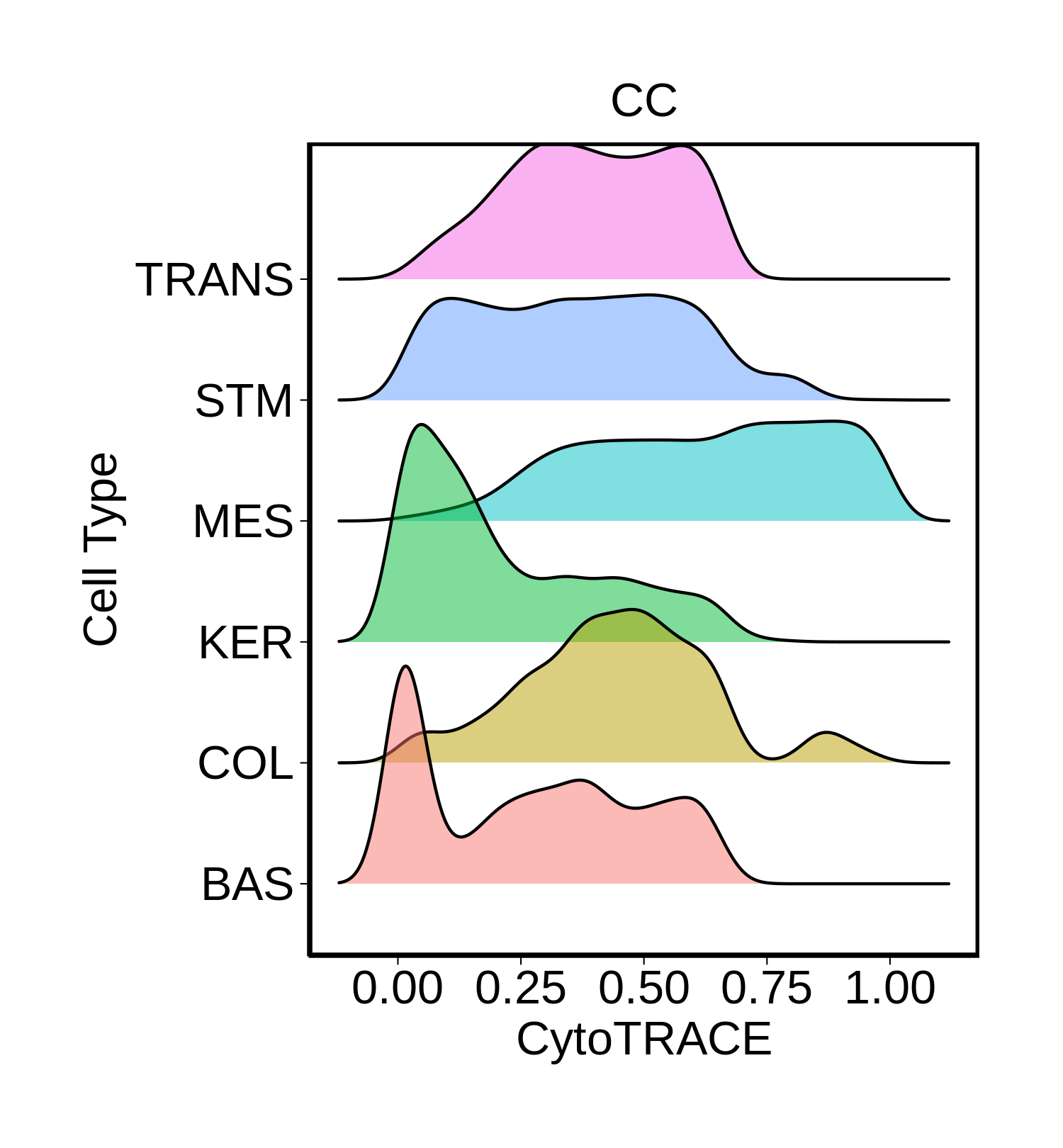 |
| ∗Ridge plots of CytoTRACE score distributions for epithelial cells. |
| Disease State | Epithelia | Immune | Stromal |
| Healthy | 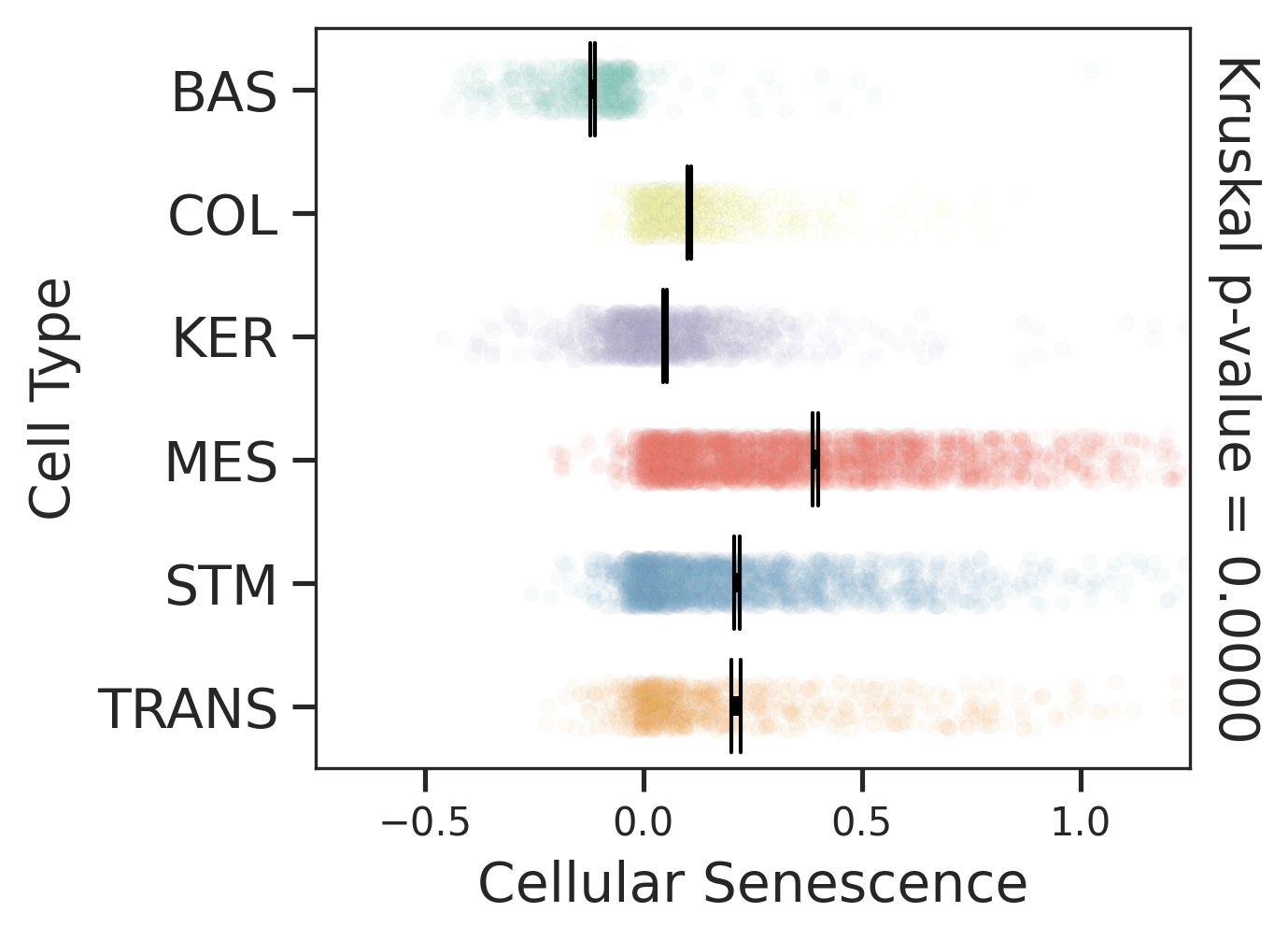 | 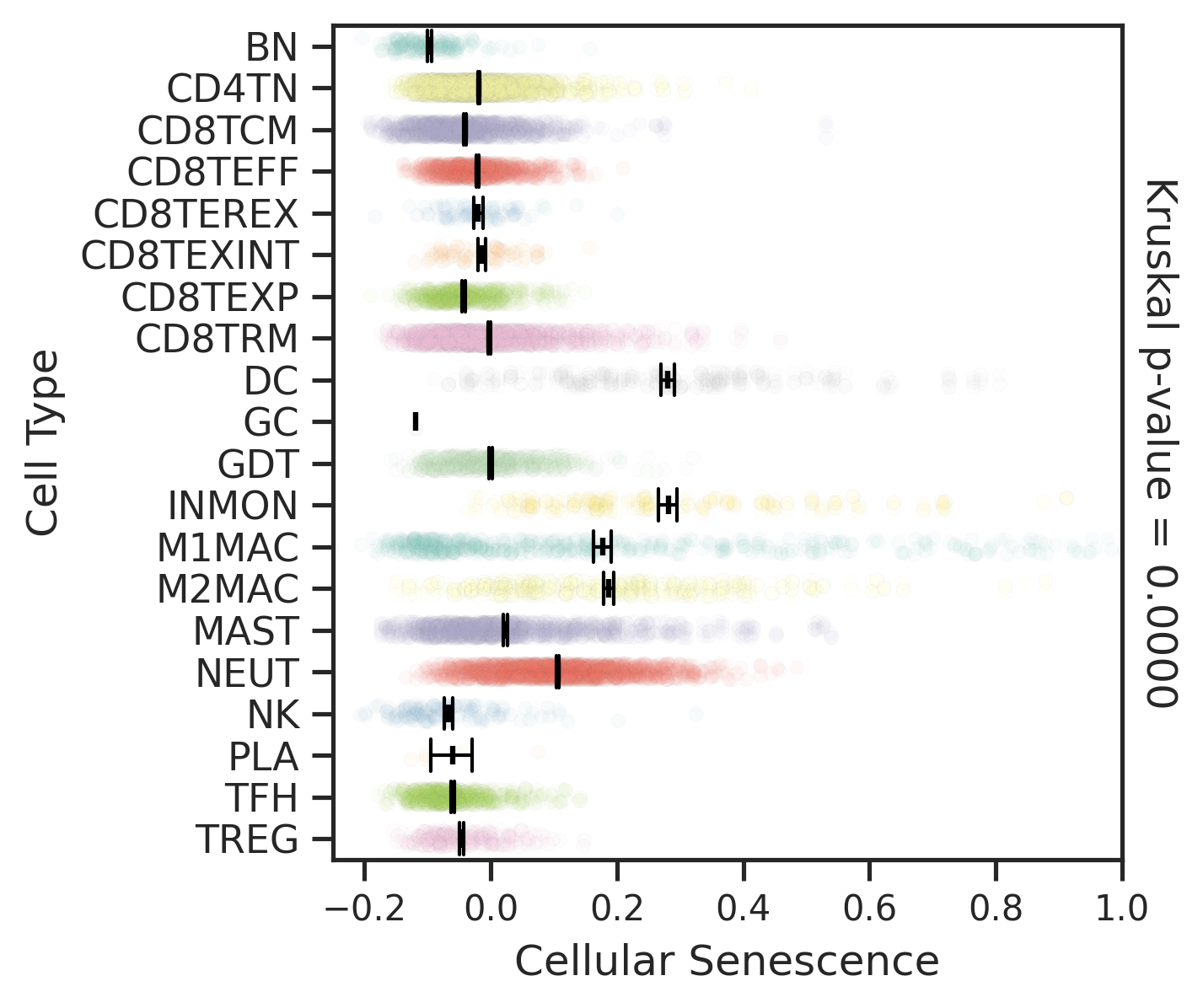 | 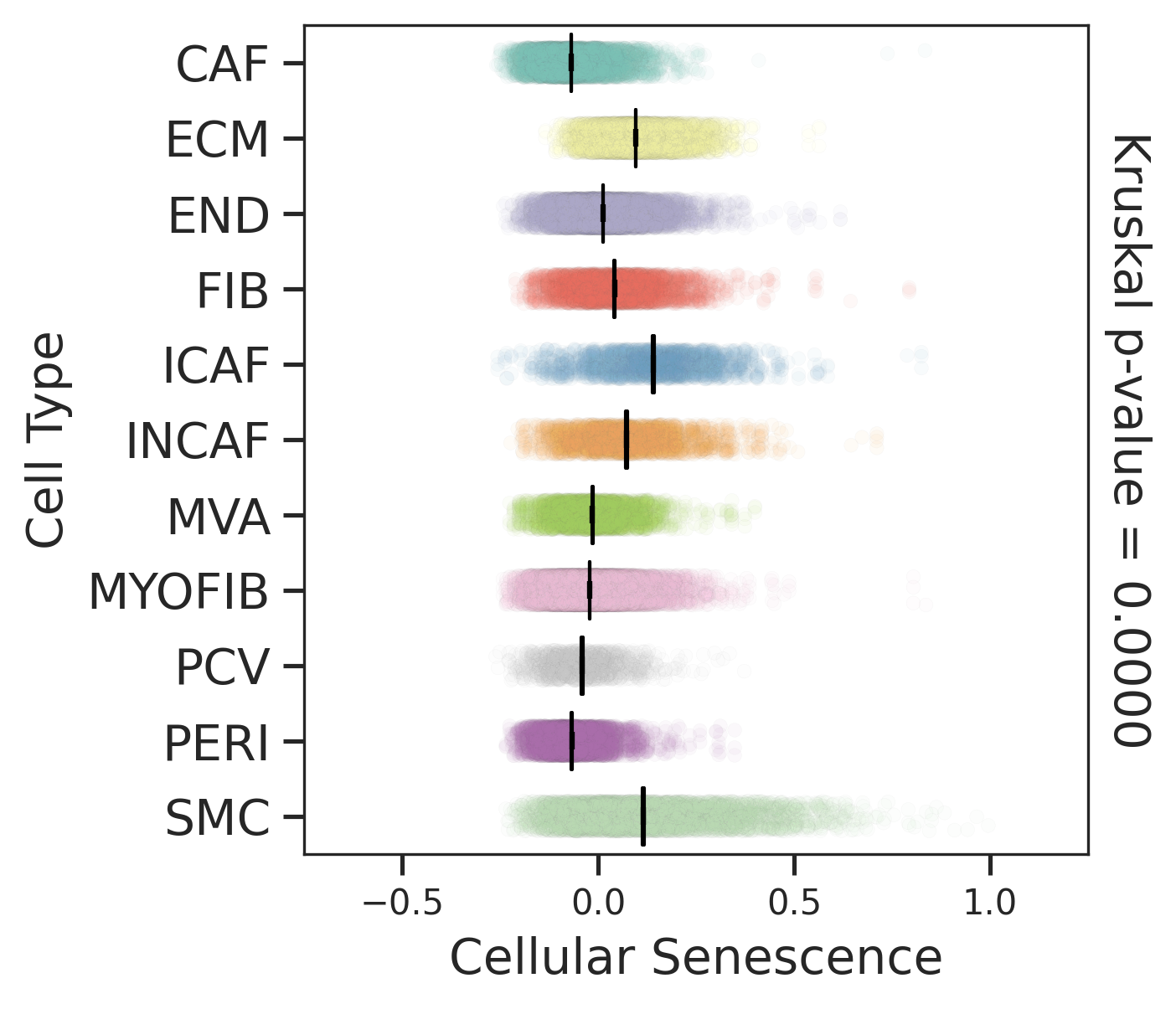 |
| Precancer | 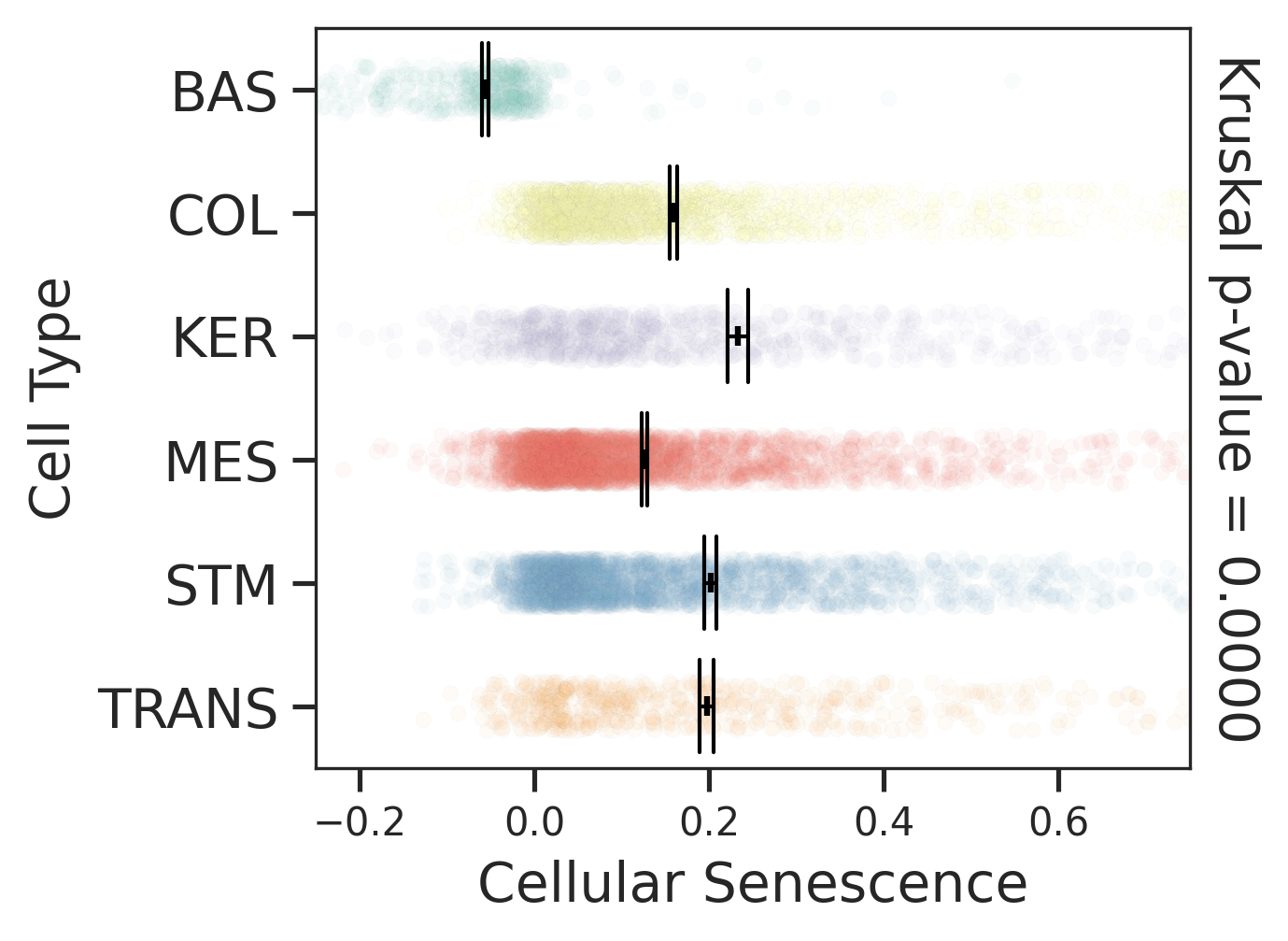 | 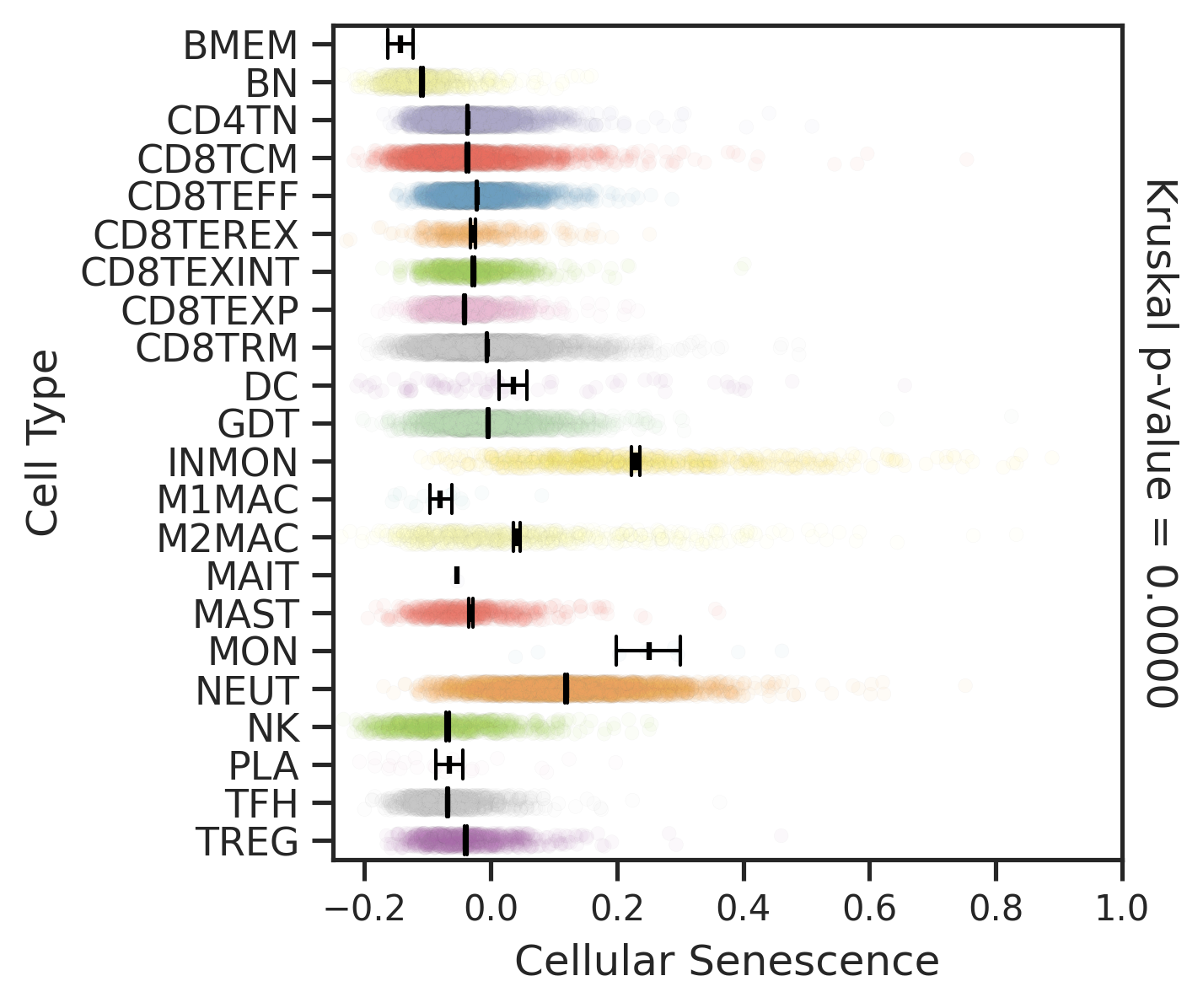 | 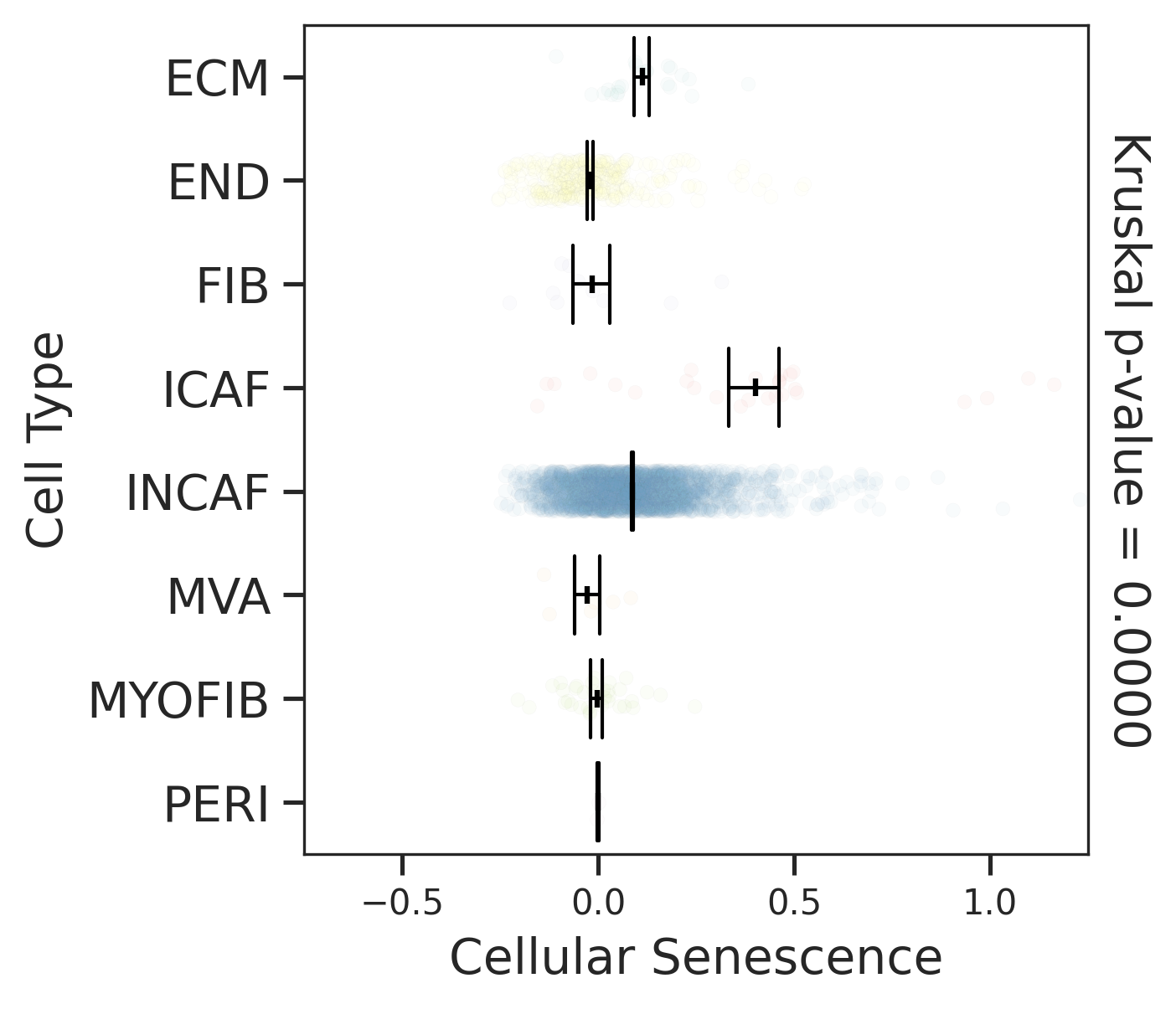 |
| CC | 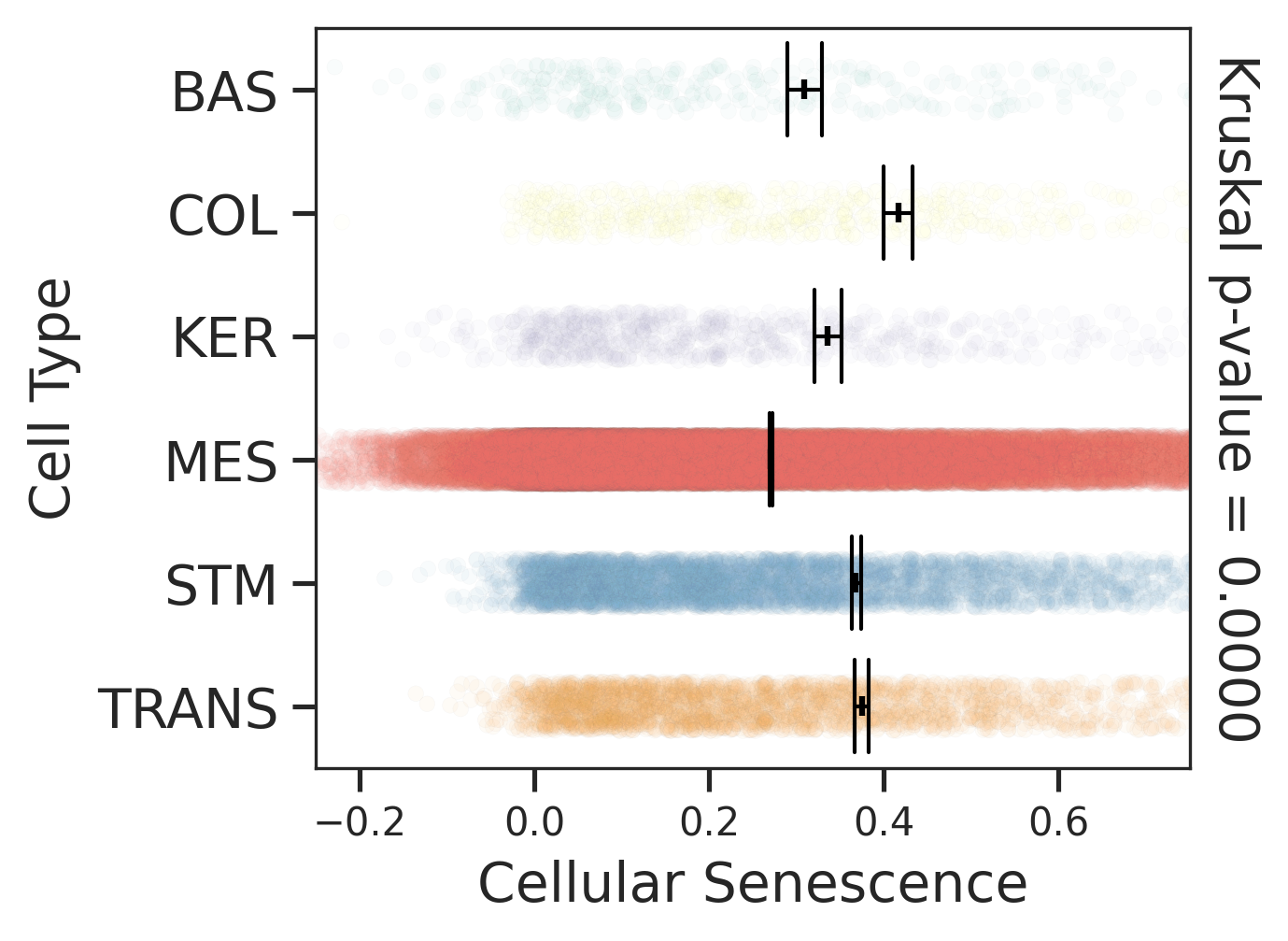 | 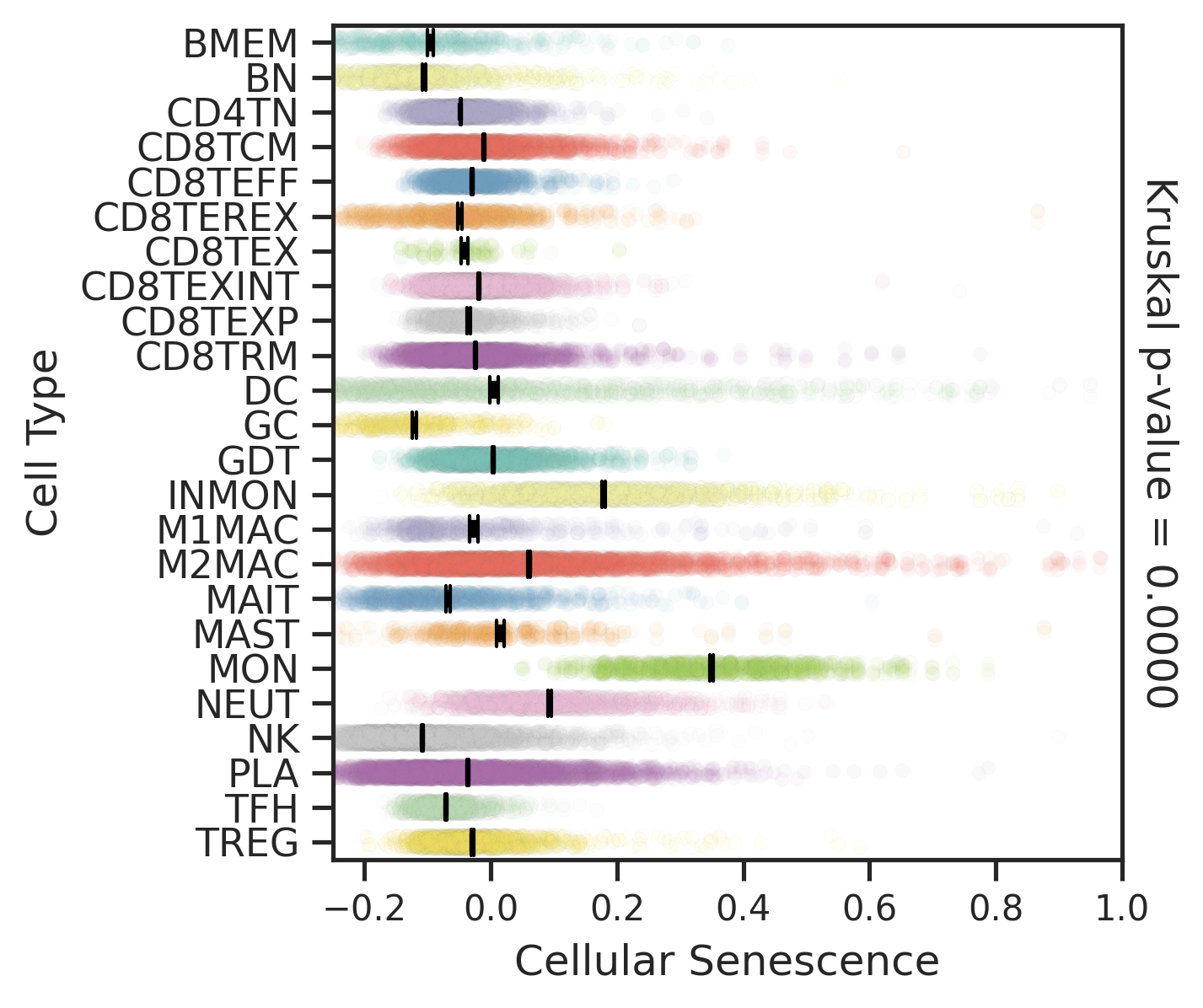 | 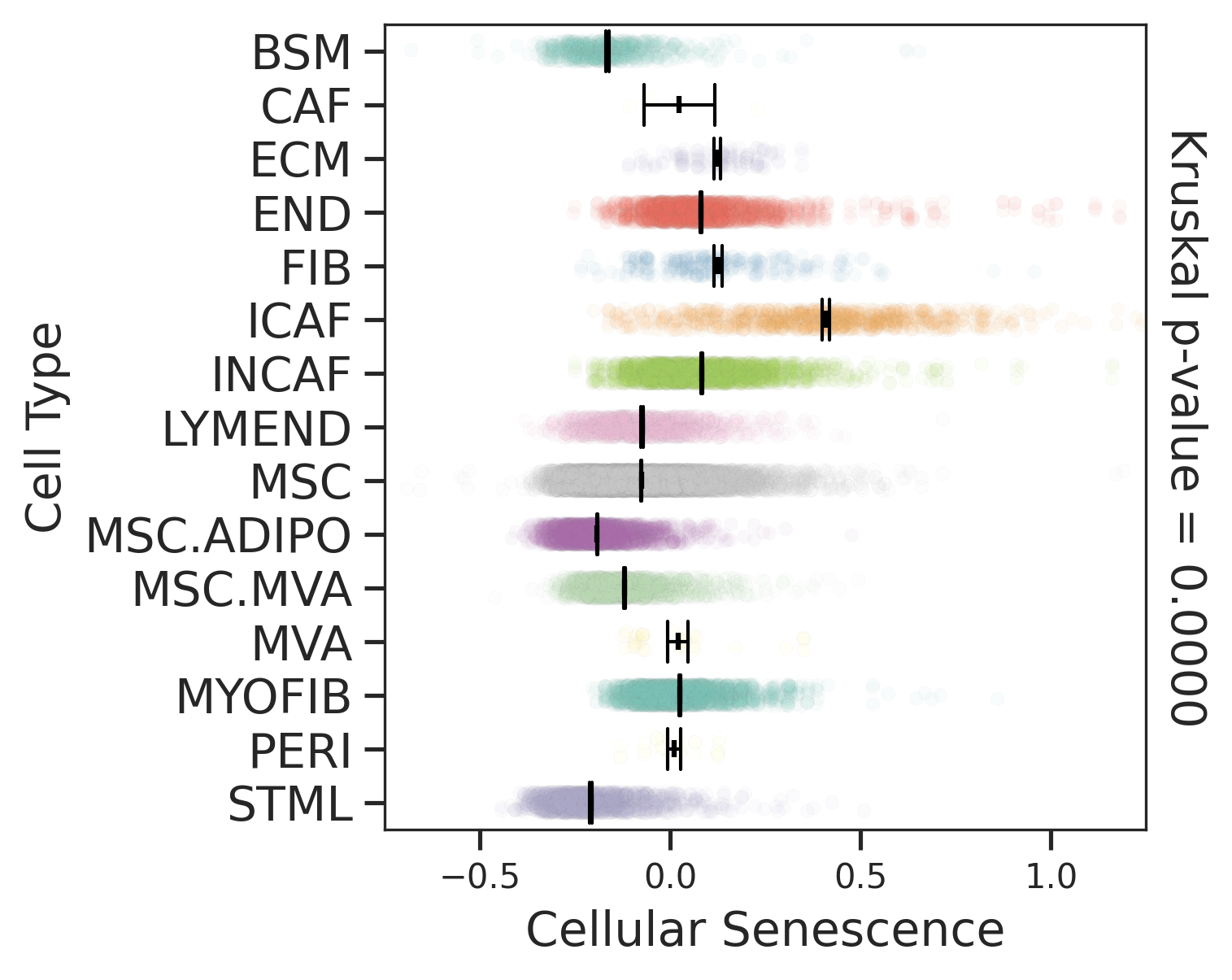 |
| ∗Comparisons for degree of cellular senescence among epithelial, immune and stromal cell populations of Cervix tissue with different disease states. |
| Healthy | Precancer | CC |
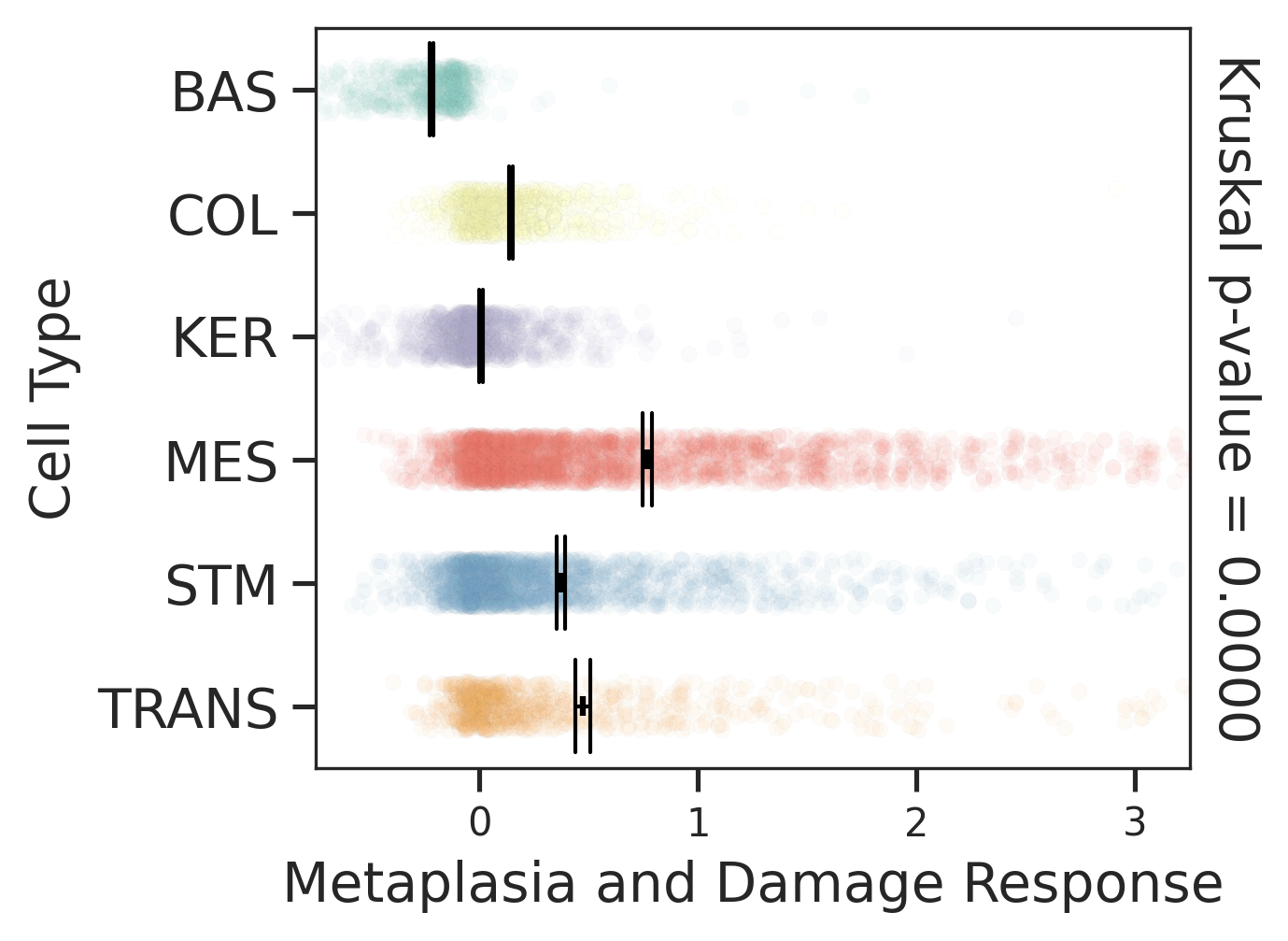 | 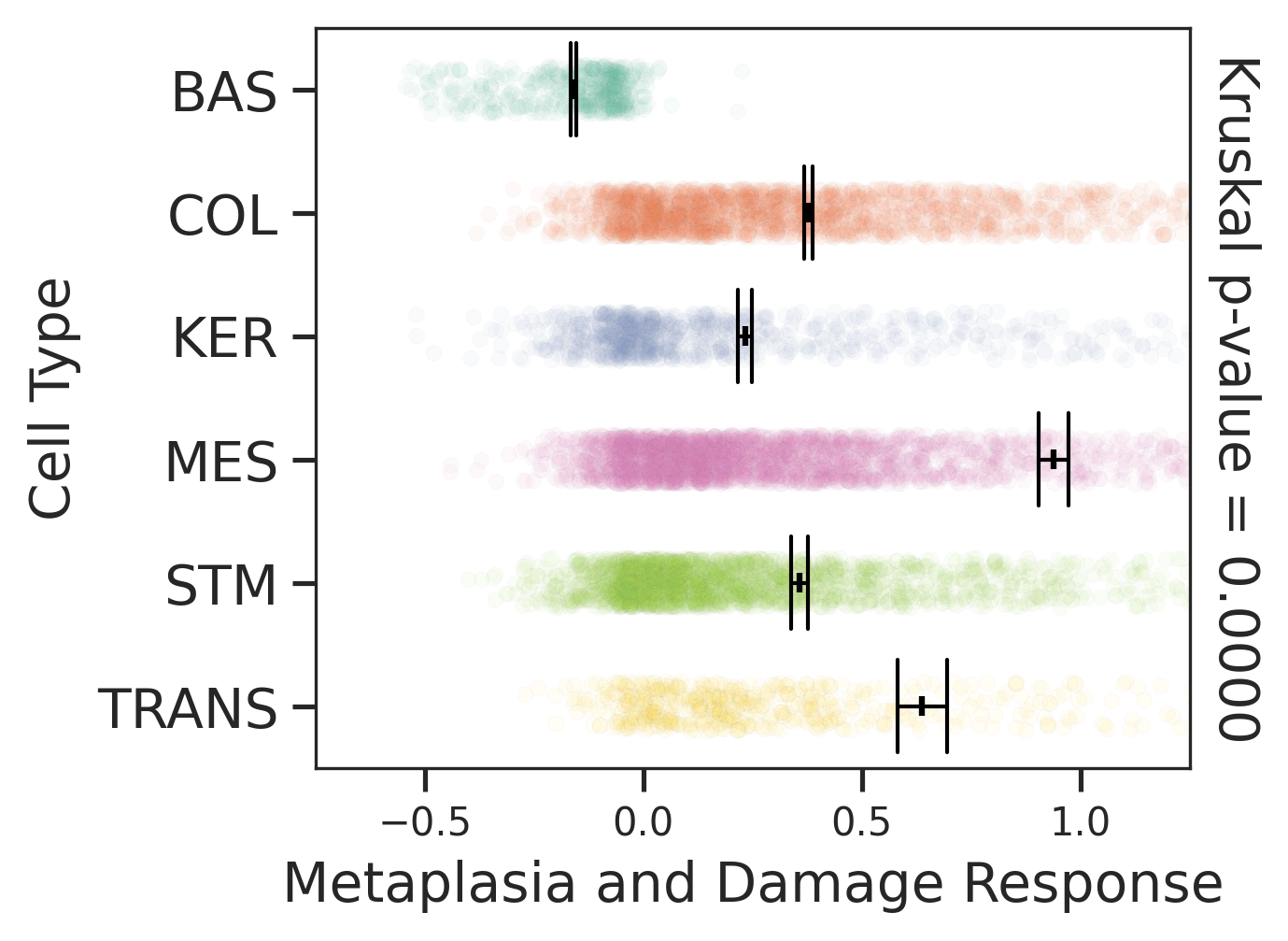 | 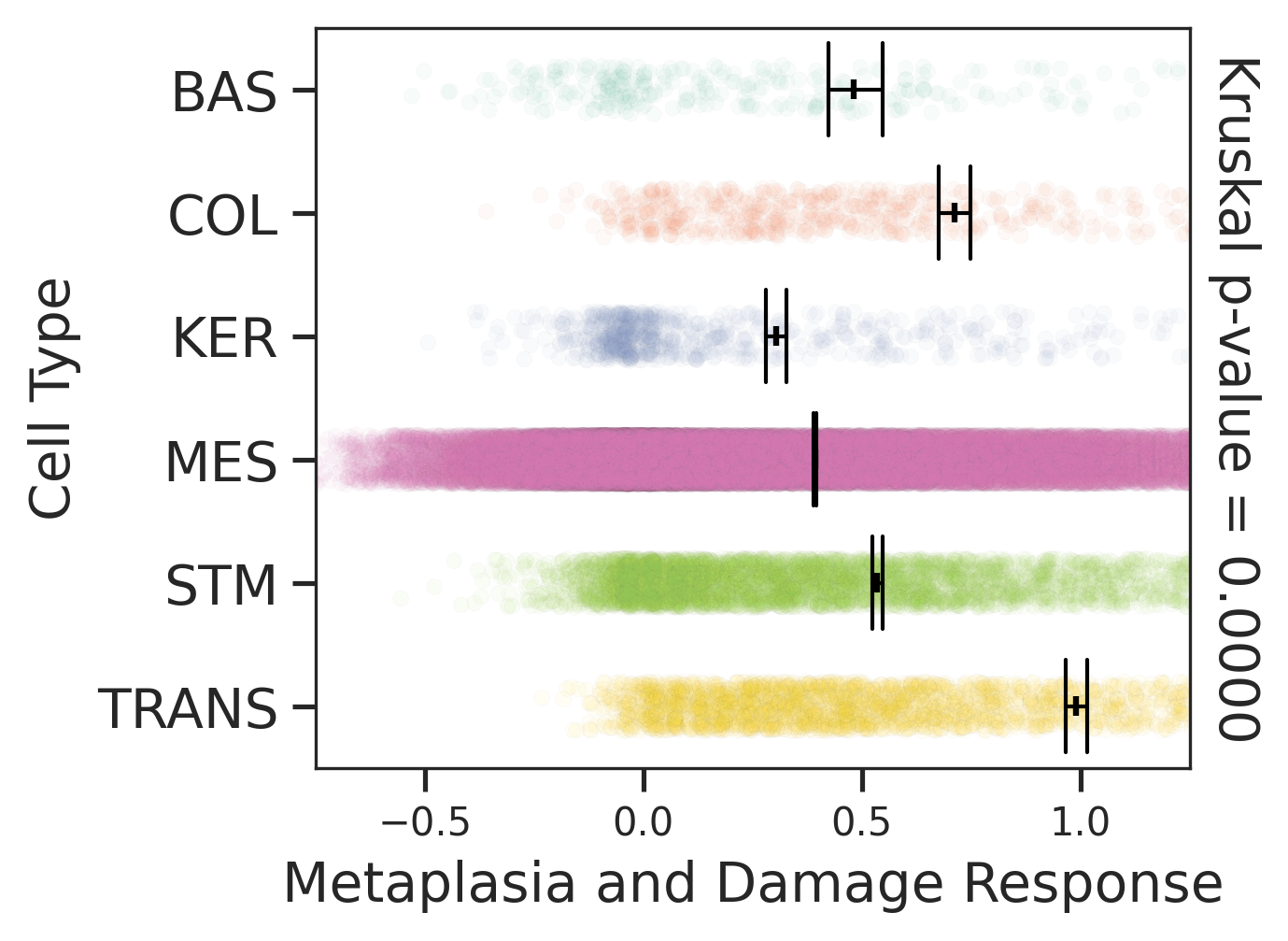 |
| ∗Comparisons of Metaplasia-associated damage scores among epithelial cell subpopulations. |
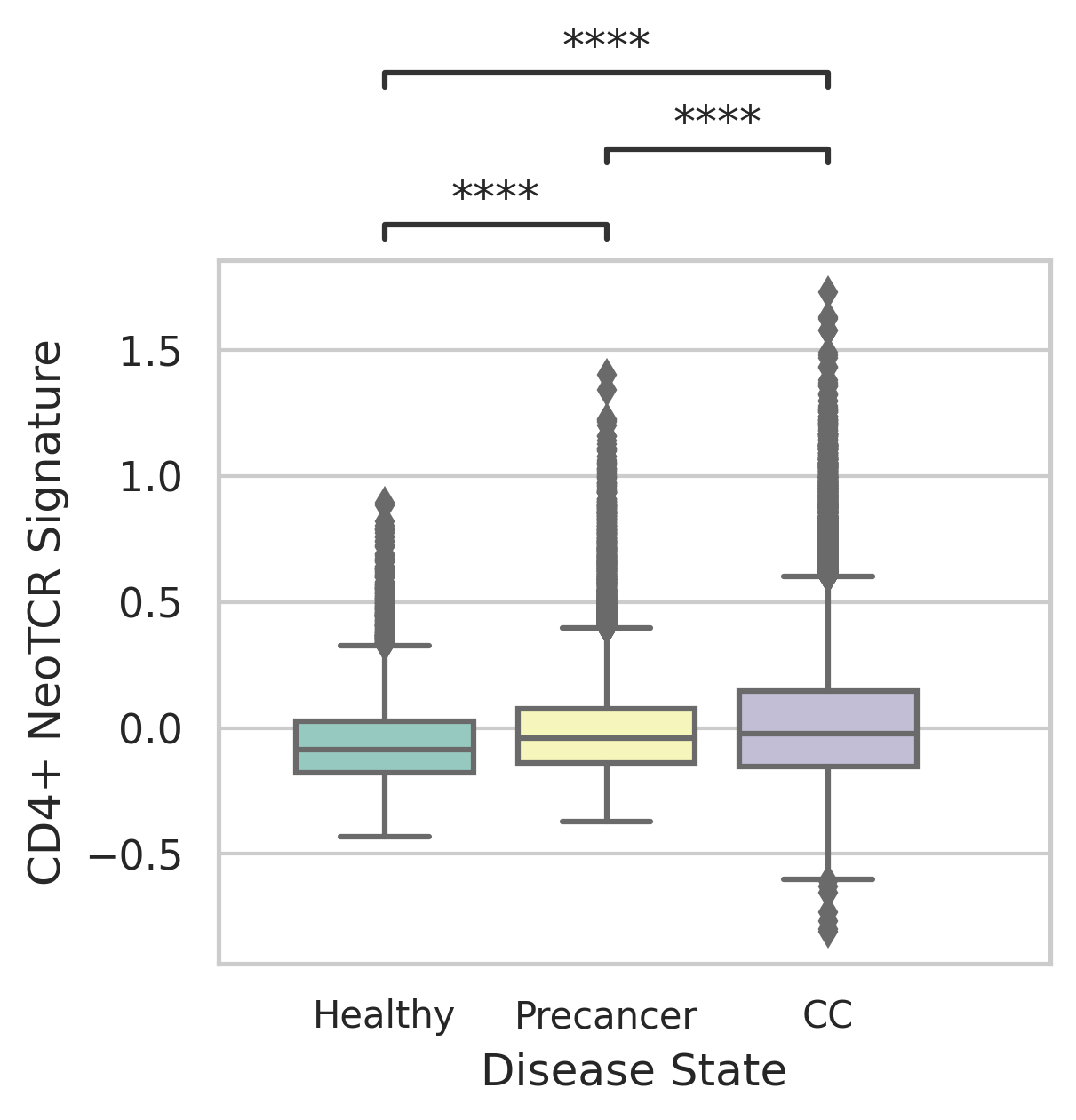 | 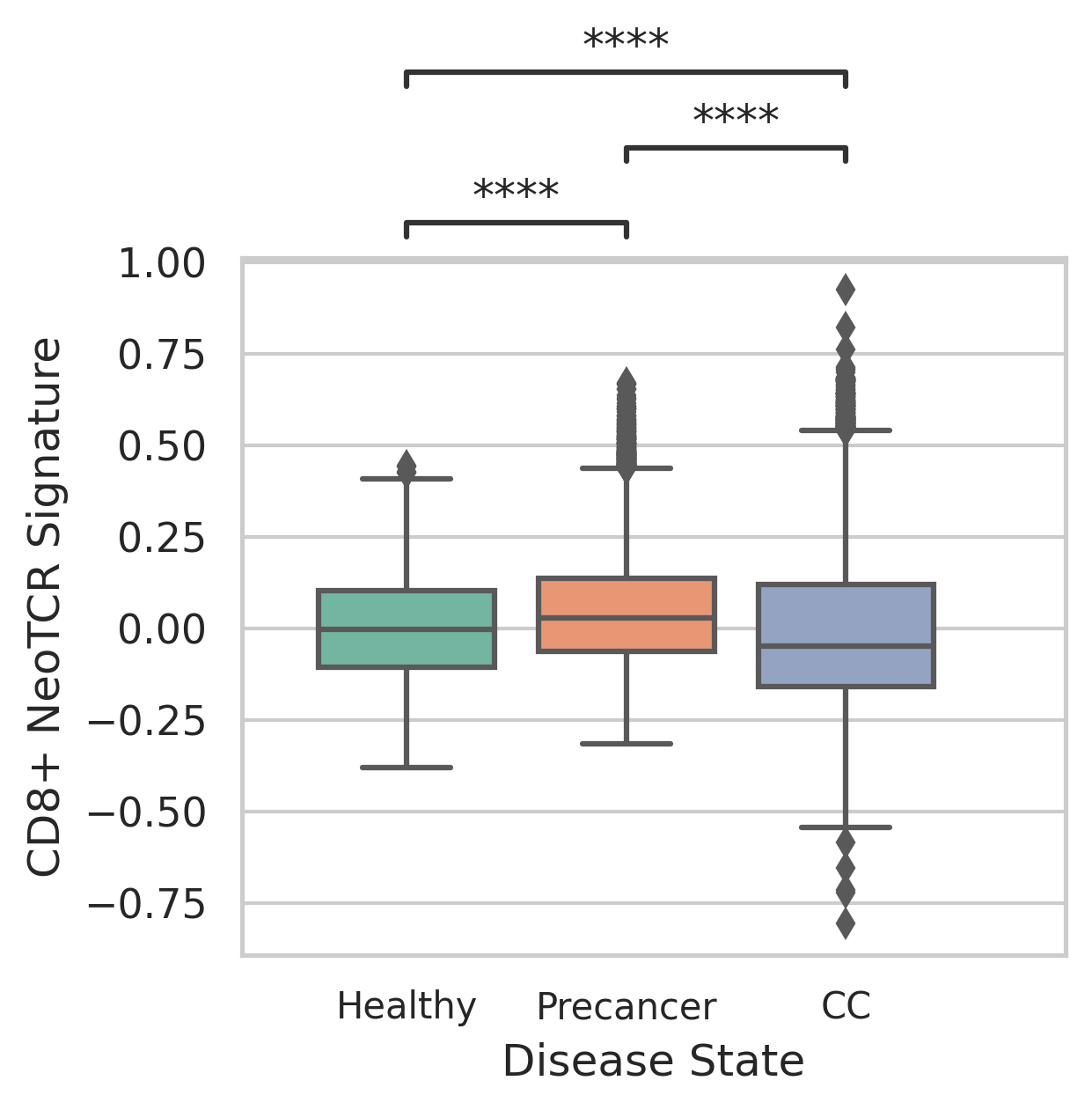 |
| ∗Comparisons of CD4+ and CD8+ NeoTCR signature scores among different disease states. |
